🔍 Difference Between Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients in Confluent Kafka
Confluent Kafka provides various tools for event streaming and real-time data processing. The key components include Topics, ksqlDB, Connectors, and Clients, each serving a distinct role.
1️⃣ Topics (Core Kafka Component)
📌 What Are Kafka Topics?
- Kafka Topics are logical channels where messages (events) are published by producers and consumed by consumers.
- They act as distributed logs storing ordered events.
- Producers write data to a topic, and consumers read from it.
✅ Use Case of Topics
- Used for event-driven applications.
- Acts as a buffer between producers and consumers.
- Example: A payment service publishes transactions to a "payments" topic, and a fraud detection service consumes those events.
🚀 Key Features
- Supports multiple partitions for parallelism.
- Retains messages based on retention policies (time-based or size-based).
- Enables real-time streaming and event sourcing.
2️⃣ ksqlDB (Real-time SQL Processing on Kafka)
📌 What Is ksqlDB?
- ksqlDB is a SQL engine for Kafka that allows users to query and process real-time streaming data without writing Java/Python code.
- It enables stateful stream processing on Kafka topics using SQL-like queries.
✅ Use Case of ksqlDB
- Real-time data transformation, aggregation, filtering, and joins across Kafka topics.
- Example: If a topic contains raw clickstream data, you can use ksqlDB to filter only clicks from India and write the output to another topic.
🚀 Key Features
- SQL-based stream processing (easier than Java/Python Kafka Streams API).
- Real-time analytics on Kafka events.
- Stateful computations (aggregations, windows, joins).
- Materialized views for fast querying.
🔹 Example Query in ksqlDB
CREATE STREAM filtered_users AS
SELECT user_id, page_url FROM user_clicks
WHERE country = 'India';
3️⃣ Kafka Connectors (Data Integration Layer)
📌 What Are Kafka Connectors?
- Kafka Connect provides pre-built connectors to integrate Kafka with external systems (databases, cloud storage, etc.).
- Types:
- Source Connector → Brings data into Kafka from databases, APIs, etc.
- Sink Connector → Sends data from Kafka to databases, Elasticsearch, S3, etc..
✅ Use Case of Kafka Connect
- Moves data from an external database to Kafka (CDC) or from Kafka to a data warehouse.
- Example:
- A JDBC Source Connector reads customer data from MySQL and sends it to a Kafka topic.
- A S3 Sink Connector stores Kafka topic data in Amazon S3.
🚀 Key Features
- Pre-built connectors for MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, AWS S3, Elasticsearch, etc.
- Scalable & distributed data movement.
- Fault-tolerant & auto-retry mechanisms.
🔹 Example Connector Configuration (JDBC Source)
{
"name": "jdbc-source",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.confluent.connect.jdbc.JdbcSourceConnector",
"connection.url": "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb",
"topic.prefix": "mysql-data-"
}
}
4️⃣ Kafka Clients (Producers & Consumers)
📌 What Are Kafka Clients?
- Kafka Clients are the applications that produce or consume messages from Kafka topics.
- Clients use Kafka APIs to interact with topics.
✅ Use Case of Kafka Clients
- Producers send data to Kafka topics.
- Consumers read data from Kafka topics.
- Example: A Python application writes stock prices to Kafka, and a Java application reads and processes them.
🚀 Key Features
- Available in multiple languages: Java, Python, Go, C++, .NET.
- Supports batch & real-time data processing.
- Uses consumer groups for parallel processing.
🔹 Example Python Producer (Kafka Client)
from kafka import KafkaProducer
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers='localhost:9092')
producer.send('stock-prices', key=b'TSLA', value=b'900')
🔹 Example Java Consumer (Kafka Client)
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("stock-prices"));
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
System.out.println(record.value());
}
}
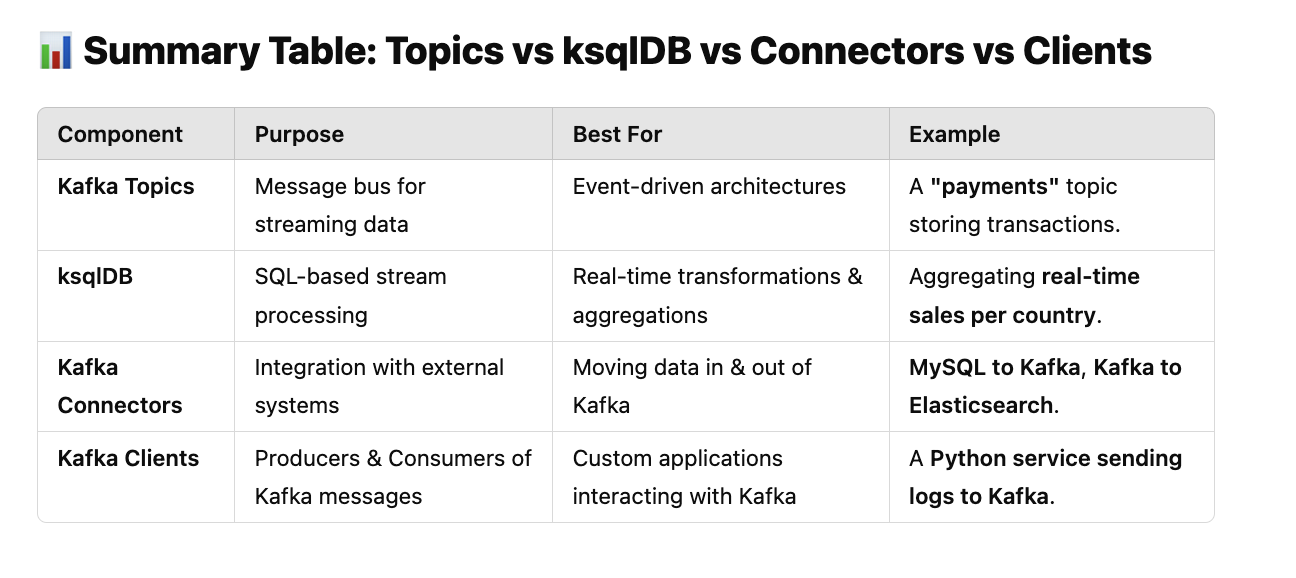
📊 Summary Table: Topics vs ksqlDB vs Connectors vs Clients
| Component | Purpose | Best For | Example |
|--------------|------------|--------------|-------------|
| Kafka Topics | Message bus for streaming data | Event-driven architectures | A "payments" topic storing transactions. |
| ksqlDB | SQL-based stream processing | Real-time transformations & aggregations | Aggregating real-time sales per country. |
| Kafka Connectors | Integration with external systems | Moving data in & out of Kafka | MySQL to Kafka, Kafka to Elasticsearch. |
| Kafka Clients | Producers & Consumers of Kafka messages | Custom applications interacting with Kafka | A Python service sending logs to Kafka. |
🚀 When to Use What?
✅ Use Kafka Topics:
- If you need a scalable message queue for real-time streaming.
✅ Use ksqlDB:
- If you want to process, transform, and filter Kafka streams using SQL.
✅ Use Kafka Connectors:
- If you need to move data between Kafka and databases/cloud storage.
✅ Use Kafka Clients:
- If you need custom producers and consumers in Java, Python, etc.