Data is used everywhere, but do you know all the commonly used data terms?
.
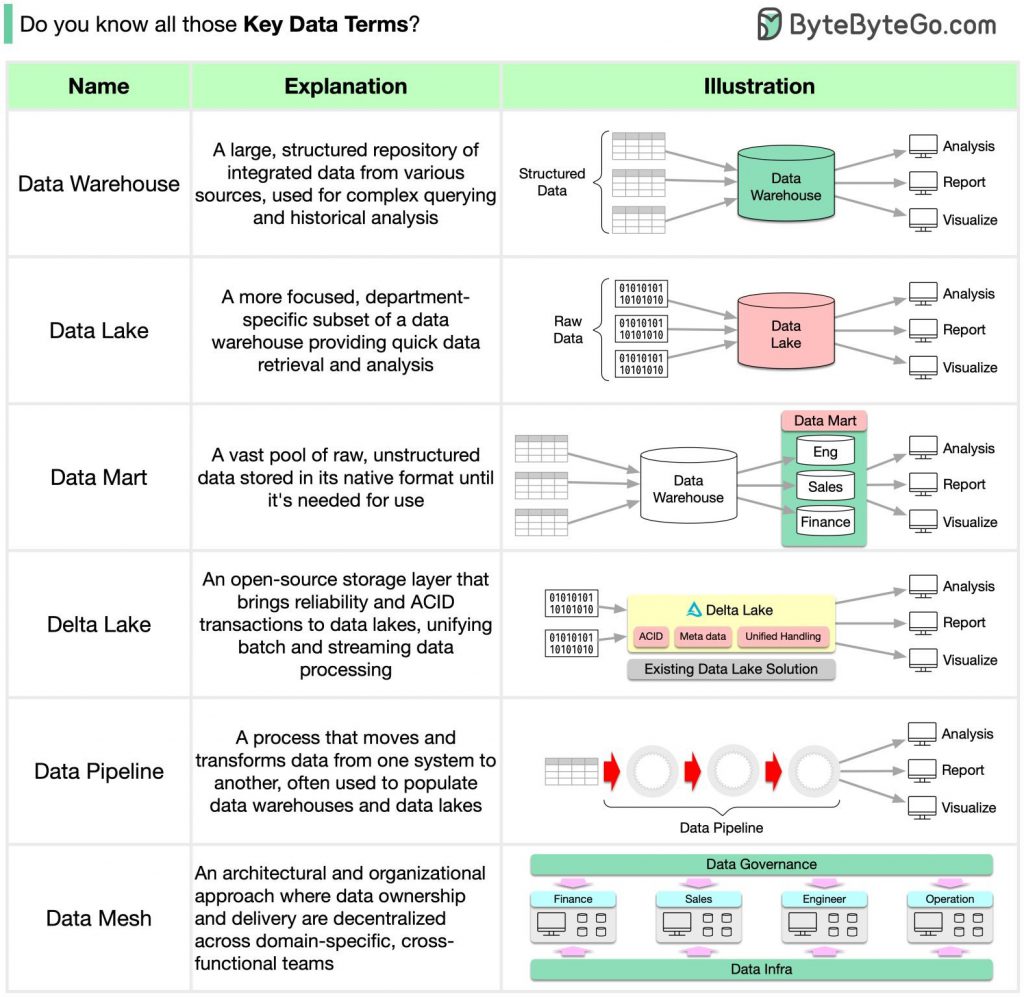
🔹Data Warehouse: A large, structured repository of integrated data from various sources, used for complex querying and historical analysis.
🔹Data Mart: A more focused, department-specific subset of a data warehouse providing quick data retrieval and analysis.
🔹Data Lake: A vast pool of raw, unstructured data stored in its native format until it’s needed for use.
🔹Delta Lake: An open-source storage layer that brings reliability and ACID transactions to data lakes, unifying batch, and streaming data processing.
🔹Data Pipeline: A process that moves and transforms data from one system to another, often used to populate data warehouses and data lakes.
🔹Data Mesh: An architectural and organizational approach where data ownership and delivery are decentralized across domain-specific, cross-functional teams.
Over to you: do you know the difference between a data engineer and a data scientist?
Here’s an overview of each term:
- Data Warehouse: A data warehouse is a central repository of integrated and structured data from various sources within an organization. It is designed to support business intelligence (BI) and analytics activities by providing a unified and consistent view of data. Data warehouses typically follow a schema-on-write approach, where data is transformed and loaded into predefined schemas optimized for reporting and analysis.
- Data Mart: A data mart is a subset of a data warehouse focused on a specific business function or department. It contains a subset of data relevant to a particular group of users, making it more targeted and specialized. Data marts are often designed to provide faster and more specific insights compared to the broader data warehouse. They can be structured similarly to a data warehouse or may use different schemas and models.
- Data Lake: A data lake is a large, centralized repository that stores structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in its raw and unprocessed form. It allows organizations to store vast amounts of data from different sources without predefined schemas. Data lakes enable data exploration, advanced analytics, and machine learning by providing flexibility in data processing and analysis. The data lake architecture typically follows a schema-on-read approach, where data is transformed and structured at the time of analysis.
- Delta Lake: Delta Lake is an open-source storage layer built on top of a data lake, often used in conjunction with Apache Spark. It provides ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions, data versioning, and data reliability features to improve the quality and reliability of data in a data lake. Delta Lake combines the scalability and flexibility of a data lake with the reliability and transactional capabilities of a data warehouse.
- Data Pipeline: A data pipeline is a system or framework that facilitates the automated extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from various sources into a target storage or processing system. It enables the smooth flow of data from source systems to data warehouses, data lakes, or other destinations. Data pipelines handle tasks such as data ingestion, data transformation, data quality checks, and data delivery.
- Data Mesh: Data Mesh is a decentralized approach to data architecture and management. It emphasizes domain-oriented, self-serve data products, where cross-functional teams take ownership of their data domains. Data Mesh aims to empower teams with data autonomy, allowing them to define their data models, data pipelines, and data products. It promotes the idea of treating data as a product and advocates for data democratization and data collaboration across an organization.
- What is Mobile Virtual Network Operator? - April 18, 2024
- What is Solr? - April 17, 2024
- Difference between UBUNTU and UBUNTU PRO - April 17, 2024

