What is Check Point ?

Check Point is a leading provider of cybersecurity solutions, offering a wide range of products and services to protect organizations from various cyber threats. Check Point’s solutions cover network security, cloud security, mobile security, threat prevention, and management.
Top 10 use cases of Check Point?
Here are the top 10 use cases of Check Point:
- Firewall Protection:
- Check Point provides robust firewall solutions to secure network perimeters, controlling incoming and outgoing traffic and preventing unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS):
- Check Point’s IPS capabilities detect and block known and unknown threats by inspecting network traffic for malicious activity, helping organizations proactively defend against cyber threats.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network):
- Check Point offers VPN solutions to establish secure and encrypted connections for remote users, allowing secure access to corporate networks over the internet.
- Threat Prevention:
- Check Point’s Threat Prevention solutions use advanced threat intelligence and real-time analysis to detect and block various cyber threats, including malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks.
- Cloud Security:
- Check Point provides cloud security solutions to protect assets and data hosted in cloud environments. This includes security for public clouds, private clouds, and hybrid cloud architectures.
- Mobile Security:
- Check Point offers mobile security solutions to protect mobile devices and the data they access. This includes securing mobile applications, preventing mobile threats, and ensuring secure mobile communication.
- Endpoint Security:
- Check Point’s endpoint security solutions protect individual devices, such as desktops, laptops, and servers, from malware, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
- Security Management:
- Check Point provides a centralized security management platform that allows organizations to configure, monitor, and manage their security policies across the entire network infrastructure.
- Identity Awareness:
- Check Point’s Identity Awareness feature enables organizations to implement granular access control based on user identities, ensuring that only authorized users can access specific resources.
- Zero-Day Threat Protection:
- Check Point’s solutions include technologies to defend against zero-day threats by using advanced threat emulation and sandboxing techniques to analyze and block unknown or evasive threats.
These use cases demonstrate the versatility and comprehensive nature of Check Point’s cybersecurity offerings. Organizations can leverage Check Point solutions to build a layered defense strategy, securing their networks, cloud environments, endpoints, and mobile devices from a wide range of cyber threats.
What are the feature of Check Point?
Check Point Software offers a broad spectrum of security features across its diverse product portfolio, addressing various needs for individuals and organizations. Here’s a breakdown of key areas and features:
Network Security:
- Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs): Provide deep packet inspection, intrusion prevention, application control, and threat prevention against known and zero-day attacks.
- SandBlast Network: Utilizes advanced sandboxing technology to detect and detonate sophisticated threats in real-time.
- Quantum Security Gateways: Delivers high-performance security with threat prevention, IPS, and advanced networking capabilities.
- Infinity Next-Gen Security: Unifies network, cloud, and mobile security under a single management platform.
Endpoint Security:
- Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP): Protects endpoints from malware, ransomware, and other threats with real-time protection, behavioral analysis, and endpoint detection and response (EDR).
- SandBlast Agent: Provides advanced threat prevention with sandboxing, exploit mitigation, and behavioral analysis.
- Anti-Bot: Protects against botnet infections and data exfiltration.
- Mobile Threat Prevention: Secures mobile devices with data encryption, application control, and secure access controls.
Cloud Security:
- CloudGuard Cloud Native Protection Platform (CNP): Protects cloud workloads and applications from attacks with container security, serverless security, and API security.
- CloudGuard Network Security: Extends on-premises security to cloud environments with advanced threat prevention and network security controls.
- CloudGuard Workload Protection: Provides deep visibility and security for cloud workloads across various platforms.
Data Security:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevents sensitive data from being leaked or stolen with data encryption, content inspection, and activity monitoring.
- Quantum Security Gateways: Offers data encryption capabilities for secure communication and data storage.
- SandBlast Network: Detects and blocks data exfiltration attempts during threat analysis.
Additional Features:
- Web Security: Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) protect web applications and APIs from attacks with URL filtering, anomaly detection, and bot mitigation.
- Zero Trust Security: Implements a zero-trust approach by verifying all users and devices before granting access to resources.
- Threat Intelligence: Provides real-time threat intelligence feeds to stay informed about emerging threats and adapt your security posture proactively.
- Compliance Management: Simplifies compliance with regulations and industry standards with automated reporting and centralized evidence collection.
- Managed Security Services (MSS): Offers 24/7 security monitoring and management by Check Point’s expert team.
How Check Point works and Architecture?
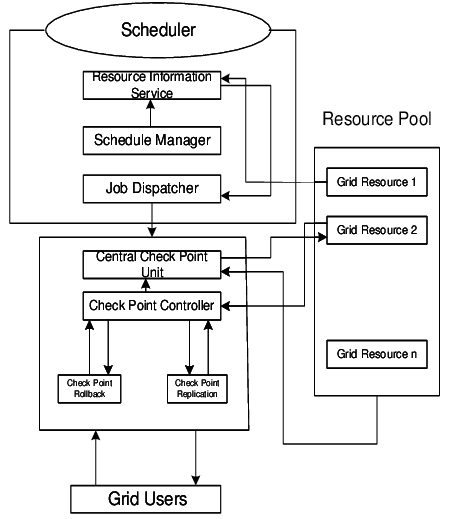
Check Point’s security solutions boast a comprehensive yet flexible architecture designed for scalability, efficiency, and adaptability. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and how they work together:
Three-Tier Architecture:
- Security Gateway (SG): Deployed at the network perimeter, it acts as the first line of defense, inspecting and filtering traffic based on security policies. It offers features like firewalling, intrusion prevention, application control, and threat prevention.
- Security Management Server (SMS): Serves as the central management console, defining and distributing security policies to gateways, monitoring security events, and generating reports.
- SmartDashboard: Provides a user-friendly interface for managing security policies, monitoring security events, and generating reports. Additionally, Check Point offers various other components depending on your specific needs, such as:
- SandBlast Network: Analyzes suspicious files in a sandbox environment to detect and detonate advanced threats.
- Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP): Protects endpoints from malware, ransomware, and other threats with real-time protection and endpoint detection and response (EDR).
- CloudGuard: Secures cloud workloads and environments with threat prevention, workload protection, and network security controls.
Core Architectural Principles:
- Centralized Policy Management: Security policies are defined once on the SMS and then distributed to all gateways, ensuring consistent security across the network.
- Scalability: The architecture can be scaled horizontally by adding more gateways and vertically by upgrading hardware or using virtual appliances.
- Flexibility: The modular design allows you to mix and match different components to meet your specific security needs.
- Openness: Integrates with various security tools and platforms for broader security visibility and management.
Benefits of Check Point’s Architecture:
- Simplified Management: Manage security from a single console, reducing complexity and administrative overhead.
- Enhanced Security: Comprehensive security features and centralized policy management provide robust protection.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Adapts to your evolving security needs and network size.
- Open Integration: Integrates with existing security investments for efficient management.
How to Install Check Point it?
Installing Check Point solutions involves several steps, and the specific process depends on your chosen product, deployment method, and environment. Here’s a general overview to guide you:
1. Choose your Check Point product and deployment method:
- Identify the specific Check Point product that suits your needs. Consider options like Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFWs), Endpoint Protection Platform (EPP), CloudGuard, and more.
- Decide on your deployment method: Cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid.
- Cloud-based: Managed entirely by Check Point in their cloud environment. No installation on your end required.
- On-premises: Requires installing software on your physical or virtual machines.
- Hybrid: Combines cloud-based and on-premises components for a mix of flexibility and control.
2. Gather necessary information:
- Subscription details: Your Check Point subscription plan and activation key.
- System requirements: Ensure your devices or cloud environment meet the system requirements for the chosen product. Find these on the Check Point website or in the product documentation.
- Network configuration details: Understand your network topology, IP addressing scheme, and any relevant firewall configurations (especially for on-premises deployments).
3. Follow the installation guide:
- Check Point provides detailed installation guides on their website for each product and deployment method. Navigate to the support section and search for your chosen product and deployment type.
- These guides typically cover:
- Cloud deployment: Activating your subscription and configuring your cloud environment through the Check Point Cloud Management Portal.
- On-premises deployment: Downloading and installing software on your devices, configuring the Security Management Server (SMS) (if applicable), and integrating with your network.
- Hybrid deployment: Following steps for both cloud and on-premises components based on your specific configuration.
4. Additional considerations:
- Licensing: Ensure you have the necessary licenses for your chosen product and devices.
- Configuration customization: Tailor security policies and settings based on your specific needs and environment.
- Post-installation tasks: Update software, apply security policies, and monitor system health.
Important notes:
- Due to variations in products, deployment methods, and configurations, I cannot provide specific installation instructions without knowing your chosen details.
- Consider seeking professional assistance for complex on-premises or hybrid deployments, especially if you lack technical expertise.
Basic Tutorials of Check Point: Getting Started

Setting up and configuring Check Point involves several steps, and the exact procedures can vary based on the specific Check Point product or solution you are using. Below is a general guideline for setting up a basic firewall policy using Check Point.
Prerequisites:
- Check Point Installation:
- Ensure that Check Point is correctly installed on your chosen platform (appliance, hardware, or virtual machine).
2. Access to the Check Point Management Server:
- Have access to the Check Point Management Server where you can configure policies.
Tutorial: Basic Firewall Policy Configuration
Step 1: Accessing the Check Point SmartConsole
- Open the Check Point SmartConsole on the machine where you have it installed.
Step 2: Connecting to the Management Server
- In the SmartConsole, connect to your Check Point Management Server by providing the necessary credentials.
Step 3: Creating a New Security Policy
- Navigate to the “Security Policies” tab in the SmartConsole.
- Click on “Policy” and then “Policy Installation.”
- Select “Install” to create a new policy.
Step 4: Configuring Firewall Rules
- In the “Access Control” tab, click on the “+” icon to create a new rule.
- Define the source, destination, and services for the rule, specifying the traffic you want to permit or deny.
- Set the action for the rule (e.g., “Accept” or “Drop”).
- Configure additional rule properties, such as logging options.
- Click “OK” to save the rule.
Step 5: Installing the Policy
- Go back to the “Policy Installation” window.
- Select the target Check Point Security Gateway where you want to install the policy.
- Click “Install” to deploy the configured security policy.
Step 6: Monitoring and Logging
- Navigate to the “Logs & Monitor” tab to view real-time logs and monitor traffic.
- Review logs for any denied or accepted traffic based on your configured policy.
Note:
- This tutorial provides a basic overview, and the actual configuration might involve more detailed settings based on your organization’s requirements.
- It is recommended to follow best practices and consider the specific features of your Check Point solution for a comprehensive security posture.
- PPG Industries: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 3, 2024
- Fiserv: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 3, 2024
- Estee Lauder: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 3, 2024

