
What is Cloudera?
Cloudera is a leading provider of big data management and analytics solutions. It was founded in 2008 and has since then become a popular choice for businesses looking to manage and analyze large volumes of data.
Top 10 Use Cases of Cloudera
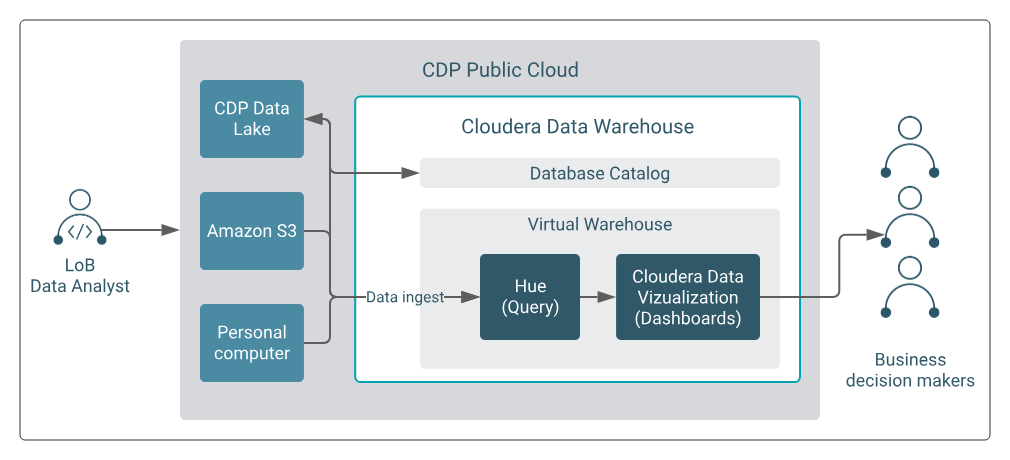
- Predictive Analytics
- Fraud Detection
- Customer Segmentation
- Supply Chain Optimization
- Log Analysis
- Sentiment Analysis
- Risk Management
- Sales Forecasting
- Network Optimization
- Personalized Marketing
Features of Cloudera
Cloudera offers a wide range of features that make it a popular choice for businesses. Some of these features include:
- Scalability: Cloudera can handle large volumes of data and can scale to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes.
- Security: Cloudera offers robust security features, including encryption, authentication, and authorization.
- Analytics: Cloudera includes a variety of analytics tools to help businesses gain insights from their data.
- Integration: Cloudera can integrate with other tools and technologies, making it a versatile solution for businesses.
- Support: Cloudera offers extensive support and resources to help businesses get the most out of their data.
How Cloudera Works and Architecture?
Cloudera’s architecture is based on Apache Hadoop’s distributed computing model. The key components are:
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): It stores and manages the data across the cluster, providing fault tolerance and scalability.
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): YARN manages cluster resources and schedules jobs for processing.
Cloudera Manager: It provides a centralized management console to monitor and manage the entire cluster.
Cloudera Navigator: It offers data governance and management features, including data discovery, lineage, and metadata management.
Hive and Impala: These SQL query engines allow users to interact with data using familiar SQL commands.
Spark and Kudu: Spark is used for in-memory data processing, while Kudu provides fast analytics on streaming and historical data.
How to Install Cloudera

Installing Cloudera is a straightforward process. First, you’ll need to download the Cloudera Manager and Cloudera Distribution of Hadoop. Once you have these files, you can run the installation wizard, which will guide you through the process of setting up Cloudera on your system.
Basic Tutorials of Cloudera: Getting Started

Sure! Here’s a step-by-step guide with basic tutorials for Cloudera:
Cloudera Installation
Before you start using Cloudera, you need to install it on your system. Follow these steps to install Cloudera:
- Check System Requirements: Review the system requirements and ensure that your hardware and software meet them.
- Download Cloudera Distribution: Visit the official Cloudera website and download the latest stable distribution.
- Prepare the Environment: Install required dependencies and configure network settings as per the installation guide.
- Install Cloudera Manager: Install Cloudera Manager, the web-based management console for Cloudera clusters.
- Configure Cloudera Manager: Set up Cloudera Manager to manage your cluster.
- Add Hosts: Add the nodes (servers) that will be part of the Cloudera cluster.
- Install Cloudera Agents: Install Cloudera Agents on each node to enable communication with Cloudera Manager.
- Create Cluster: Use Cloudera Manager to create and configure the cluster, including services like HDFS, YARN, Hive, Impala, etc.
- Start Services: Start the necessary services and components of the Cloudera cluster.
Cloudera Manager and Web UI
Cloudera Manager is the central management console for Cloudera clusters. Learn how to navigate the Cloudera Manager web UI and perform essential tasks such as monitoring, configuring services, and managing hosts.
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
Understand HDFS, the distributed file system provided by Cloudera. Learn how to interact with HDFS using the command-line interface and the Cloudera Manager web UI.
Resource Management with YARN
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator) is responsible for resource management in a Hadoop cluster. Explore how YARN allocates resources and runs applications across the cluster.
Hive and Impala for SQL Querying
Hive and Impala are SQL query engines provided by Cloudera for running interactive SQL queries on Hadoop data. Learn how to use Hive and Impala to query and analyze data.
Data Ingestion and ETL with Cloudera
Explore various methods of data ingestion into the Cloudera cluster, including loading data from local files, HDFS, and external data sources. Learn about ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes and data integration.
Data Processing with Apache Spark
Apache Spark is a powerful data processing engine used with Cloudera. Learn how to use Spark for data processing, analytics, and machine learning tasks.
Security and Governance in Cloudera
Cloudera provides robust security features and tools for data governance and compliance. Learn how to set up authentication, authorization, and encryption to secure your Cloudera cluster.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Explore how to monitor the health and performance of your Cloudera cluster using Cloudera Manager. Learn common troubleshooting techniques for resolving issues.
Data Science Workbench
Learn about Cloudera’s Data Science Workbench, which provides data scientists with a collaborative platform for developing and deploying machine learning models.
These tutorials will provide you with a solid foundation to begin working with Cloudera and leveraging its capabilities for big data processing and analytics. As you gain more experience, you can delve into more advanced features and use cases provided by Cloudera’s platform. Happy learning!
- Why Can’t I Make Create A New Folder on External Drive on Mac – Solved - April 28, 2024
- Tips on How to Become a DevOps Engineer - April 28, 2024
- Computer Programming Education Requirements – What You Need to Know - April 28, 2024

