What is CyberArk?

CyberArk is a leading cybersecurity company known for its privileged access management (PAM) solutions. PAM is essential for securing sensitive data, infrastructure, and systems by protecting and managing privileged accounts and credentials.
CyberArk’s PAM solutions are designed to help organizations protect their critical assets, prevent security breaches, and achieve compliance with security regulations. These use cases address the unique challenges associated with managing privileged access in modern IT environments.
Top 10 use cases of CyberArk:
Here are the top 10 use cases of CyberArk:
- Privileged Account Security: CyberArk helps organizations secure and manage privileged accounts, such as administrator and service accounts, which are often targeted by attackers seeking unauthorized access.
- Password Vaulting: Store privileged account passwords and credentials securely in a centralized vault, ensuring they are protected from unauthorized access and exposure.
- Session Recording and Monitoring: Record and monitor privileged sessions to provide visibility into activities performed by administrators and detect suspicious behavior or unauthorized access.
- Privilege Elevation and Delegation: Implement just-in-time privilege elevation to allow users to temporarily access privileged accounts with appropriate permissions for specific tasks.
- Application-to-Application Password Management: Automatically manage and rotate passwords used by applications to communicate securely with other systems and services.
- Endpoint Least Privilege: Enforce the principle of least privilege on endpoints by controlling which applications and processes can access privileged credentials and accounts.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthen security by requiring multi-factor authentication for accessing privileged accounts and sensitive systems.
- Privilege Threat Analytics: Analyze user behavior and privileged account usage to detect anomalous activities and potential security threats.
- Compliance and Auditing: Facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements by providing audit trails and reports of privileged account access and activities.
- DevOps and Automation: Securely manage and rotate secrets, API keys, and other credentials used in automated processes and DevOps workflows, ensuring that sensitive data remains protected.
- Cloud Security: Extend PAM to cloud environments to secure and manage privileged accounts and access to cloud-based resources.
- Container Security: Integrate with container orchestration platforms to secure access to containers and microservices, ensuring that secrets and credentials are managed securely.
What are the feature of CyberArk?
CyberArk is a comprehensive Privileged Access Management (PAM) solution designed to protect, manage, and monitor privileged accounts and access to critical systems and data. Here are the key features of CyberArk, along with an overview of how it works and its architecture:
Key Features of CyberArk:
- Privileged Account Discovery: Automatically discover and inventory privileged accounts across your organization’s IT environment, including on-premises and cloud resources.
- Password Vaulting: Securely store and manage privileged account passwords and credentials in a centralized vault, ensuring that they are protected from unauthorized access and exposure.
- Privilege Elevation and Delegation: Implement just-in-time privilege elevation, allowing users to access privileged accounts temporarily for specific tasks without sharing permanent credentials.
- Session Recording and Monitoring: Record and monitor privileged sessions in real-time, providing visibility into activities performed by administrators and detecting suspicious behavior.
- Password Rotation: Automatically change passwords for privileged accounts at regular intervals to reduce the risk of credential theft or misuse.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthen security by requiring multi-factor authentication for accessing privileged accounts and systems.
- Application-to-Application Password Management: Securely manage passwords used by applications to communicate with other systems, ensuring they are rotated and protected.
- Privilege Threat Analytics: Analyze user behavior and privileged account usage to detect anomalous activities and potential security threats.
- Compliance and Auditing: Facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements by providing detailed audit trails and reports of privileged account access and activities.
- Endpoint Least Privilege: Control and restrict which applications and processes can access privileged credentials and accounts on endpoints, adhering to the principle of least privilege.
- DevOps and Automation: Securely manage and rotate secrets, API keys, and other credentials used in automated processes and DevOps workflows.
How CyberArk works and Architecture?
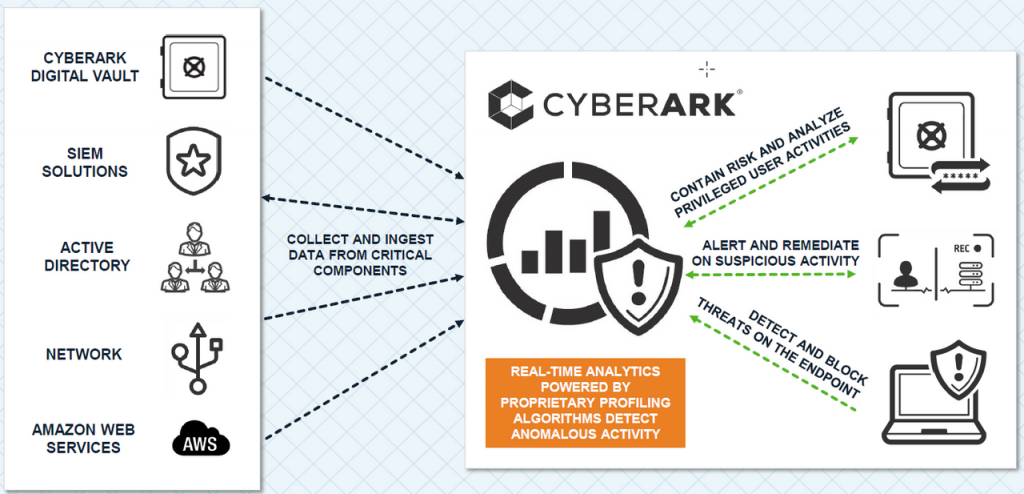
CyberArk operates as a multi-component solution to protect privileged access within an organization:
- Credential Vault: CyberArk’s central vault securely stores and manages privileged account credentials. It uses encryption and access controls to protect sensitive data.
- Access Control: Users and systems access privileged accounts through CyberArk, which enforces authentication, authorization, and auditing policies.
- Session Monitoring: For sessions initiated by users or applications, CyberArk records and monitors activities in real-time, providing visibility and alerts for suspicious actions.
- Privilege Elevation: When users need privileged access, CyberArk can grant temporary elevation, allowing them to perform tasks without exposing or sharing permanent credentials.
- Credential Rotation: CyberArk automates the process of changing privileged account passwords at specified intervals, reducing the risk of credential compromise.
- Integration: CyberArk integrates with various systems, applications, and endpoints to ensure that privileged access is managed across the entire IT environment.
CyberArk’s architecture is designed for scalability, security, and high availability. It typically consists of the following components:
- CyberArk Vault: The core component, the vault, securely stores and manages privileged account credentials and access policies.
- Privileged Session Manager: This module records and monitors privileged sessions in real-time, providing audit trails and alerting capabilities.
- Credential Provider: Installed on endpoints, this component retrieves credentials from the vault and ensures that they are used securely by applications and users.
- Privileged Access Security (PAS) Suite: CyberArk’s comprehensive suite includes various modules for password management, privilege management, session management, and threat analytics.
- Integration Connectors: CyberArk provides connectors and APIs for integrating with a wide range of systems, applications, and platforms.
- Central Policy and Reporting: CyberArk’s central console allows administrators to configure policies, monitor activities, and generate compliance reports.
CyberArk’s architecture is highly adaptable and can be deployed to meet the specific needs of organizations, whether they operate on-premises, in the cloud, or in hybrid environments. It plays a critical role in protecting organizations from security threats related to privileged access and credentials.
How to Install CyberArk?
To install CyberArk, you will need to download the installation package from the CyberArk website. Once you have downloaded the installation package, you can install it on your server using the following steps:
- Extract the installation package
Extract the CyberArk installation package to a directory on your server.
- Run the installation script
Run the CyberArk installation script to install CyberArk on your server. The installation script will prompt you for information about your CyberArk installation, such as the installation directory, the database connection information, and the administrator account information.
- Configure CyberArk
Once CyberArk is installed, you will need to configure it. You can configure CyberArk using the CyberArk configuration console. The configuration console is a web-based application that allows you to configure CyberArk and manage your CyberArk environment.
Some of the steps involved in configuring CyberArk:
- Create a CyberArk vault
A CyberArk vault is a secure storage repository for privileged credentials. To create a CyberArk vault, you will need to specify the vault name, the vault type, and the vault location.
- Create CyberArk users and groups
CyberArk users and groups are used to manage access to privileged credentials. To create a CyberArk user or group, you will need to specify the user name or group name, and the user or group type.
- Create CyberArk safes
CyberArk safes are used to organize privileged credentials. To create a CyberArk safe, you will need to specify the safe name, the safe description, and the safe permissions.
- Import privileged credentials into CyberArk
You can import privileged credentials into CyberArk from a variety of sources, such as text files, spreadsheets, and other password management systems.
- Configure CyberArk policies
CyberArk policies are used to control access to privileged credentials and to automate the management of privileged credentials. To configure a CyberArk policy, you will need to specify the policy name, the policy type, and the policy settings.
Once you have configured CyberArk, you can start using it to manage your privileged credentials. CyberArk provides a number of features that can help you to improve your security posture, such as:
- Secure storage: CyberArk provides a secure storage repository for privileged credentials.
- Access control: CyberArk allows you to control access to privileged credentials through users, groups, and policies.
- Auditing and reporting: CyberArk provides auditing and reporting capabilities that can help you to track user activity and identify potential security risks.
Basic Tutorials of CyberArk: Getting Started

The following steps are the Basic Tutorials of CyberArk:
Tutorial 1: Logging in to the Password Vault Web Access (PVWA)
- Open a web browser and navigate to the URL of the PVWA server.
- Enter your username and password.
- Click Login.
Tutorial 2: Viewing and managing passwords
- In the PVWA console, click Passwords.
- To view a list of all passwords, click All Passwords.
- To view a specific password, click the name of the password.
- To manage a password, such as rotating it or changing its description, click the Manage button.
Tutorial 3: Creating a new password
- In the PVWA console, click Create New.
- Select the type of password you want to create, such as a Windows password or a Linux password.
- Enter the required information, such as the name of the password and the system where the password is used.
- Click Create.
Tutorial 4: Using the Privileged Session Manager (PSM)
- In the PVWA console, click PSM.
- Click the Connect button next to the system you want to connect to.
- Enter your credentials to authenticate to the PSM.
- Select the type of session you want to start, such as an RDP session or an SSH session.
- Click Connect.
Tutorial 5: Monitoring privileged sessions
- In the PVWA console, click PSM.
- Click the Sessions tab.
- To view a list of all active sessions, click Active Sessions.
- To view a specific session, click the name of the session.
- To monitor a session in real time, click the Watch Live button.
These are just a few basic tutorials for CyberArk. For more detailed information, please refer to the CyberArk documentation.
Some additional tips for using CyberArk:
- Use strong passwords for your CyberArk accounts.
- Enable multi-factor authentication for your CyberArk accounts.
- Use CyberArk to manage all of your privileged accounts, including passwords, SSH keys, and certificates.
- Use CyberArk PSM to record and monitor all privileged sessions.
- Use CyberArk policies to control who can access privileged accounts and what actions they can perform.
- Implement a regular password rotation schedule for all privileged accounts.
By following these tips, you can help to protect your organization from privileged account attacks.
- Building a DevOps Culture: Tips and Strategies - April 4, 2024
- Why Understanding DevOps Could Be Your Key To Success In The Music Industry - April 4, 2024
- Top Picks: The Best Laptops for Graphic Designers in 2024 - March 31, 2024

