What is Infosec?

Infosec, short for information security, refers to the practices and technologies used to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. It includes a wide range of activities, tools, and processes aimed at maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad) of data and systems.
Confidentiality ensures only authorized individuals can access information. Integrity guarantees data accuracy and completeness, preventing unauthorized alterations. Availability assures information and systems are accessible to authorized users whenever needed.
Infosec applies to all types of information, both digital and physical, ranging from personal data, such as financial records and medical information, to corporate secrets and intellectual property.
Top 10 use cases of Infosec?
Top 10 Use Cases of Infosec:
- Protecting against cyberattacks: This includes defending against various threats like malware, phishing, ransomware, social engineering, and hacking attempts.
- Data security and privacy compliance: Ensuring sensitive data is stored, accessed, and used in accordance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Network security: Securing internal and external networks to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Cloud security: Protecting data and systems hosted in cloud environments.
- Endpoint security: Securing laptops, mobile devices, and other endpoints from malware and unauthorized access.
- Application security: Ensuring the security of web and mobile applications to prevent vulnerabilities and data leaks.
- Incident response: Responding to security incidents like data breaches or malware infections effectively and minimizing damage.
- Disaster recovery: Ensuring the availability of systems and data in case of natural disasters or other disruptions.
- Security awareness training: Educating employees and stakeholders about cybersecurity best practices to avoid falling victim to common threats.
- Physical security: Implementing physical controls like locks, cameras, and access control systems to protect physical assets and sensitive information.
These are just a few examples, and the specific use cases of Infosec will vary depending on the organization’s needs and industry. However, the core principles of protecting information and maintaining the CIA triad remain the same.
What are the feature of Infosec?
The term “features” can be interpreted in different ways when talking about Infosec. Here are two interpretations, each with some potential answers:
1. Features as capabilities:
- Confidentiality: This ensures only authorized users can access and view information. This can be achieved through methods like access control, encryption, and data anonymization.
- Integrity: This guarantees the accuracy and completeness of data, preventing unauthorized changes or modification. Techniques like data validation, checksums, and digital signatures can be used.
- Availability: This ensures authorized users have timely access to information and systems when needed. Redundancy, disaster recovery plans, and performance optimization are crucial here.
- Threat detection and prevention: This involves proactive measures to identify and stop potential security threats before they cause damage. Examples include intrusion detection systems, malware scanning, and vulnerability management.
- Incident response: This includes effectively handling security incidents like data breaches or system outages to minimize damage and restore normal operations. Incident response plans, forensics tools, and communication protocols are important components.
- Compliance: This ensures adherence to relevant data privacy and security regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. Data governance, policy management, and audit trails are key features for compliance.
- Awareness and training: Equipping employees and stakeholders with knowledge and best practices to recognize and avoid security risks through training programs, phishing simulations, and awareness campaigns.
- Continuous improvement: Infosec is an ongoing process, and features like threat intelligence, risk assessments, and regular security audits are crucial for adapting to evolving threats and improving defenses.
2. Features as specific tools or technologies:
- Firewalls: These control incoming and outgoing network traffic, filtering out unauthorized access attempts.
- Antivirus and anti-malware software: These programs detect and remove malicious software from devices.
- Encryption tools: These scramble data to protect it from unauthorized access while it’s stored or transmitted.
- Identity and access management (IAM) solutions: These manage user access to systems and data based on permissions and roles.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems: These aggregate and analyze logs from various security tools to provide a holistic view of security events.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions: These actively monitor endpoints for suspicious activity and can take automated actions to contain threats.
- Vulnerability scanners: These tools identify security weaknesses in software and systems that could be exploited by attackers.
- Phishing simulations: These simulated attacks help train employees to recognize and avoid phishing attempts.
It’s important to remember that Infosec is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The specific features and tools needed will depend on the organization’s size, industry, risk profile, and specific needs.
How Infosec works and Architecture?
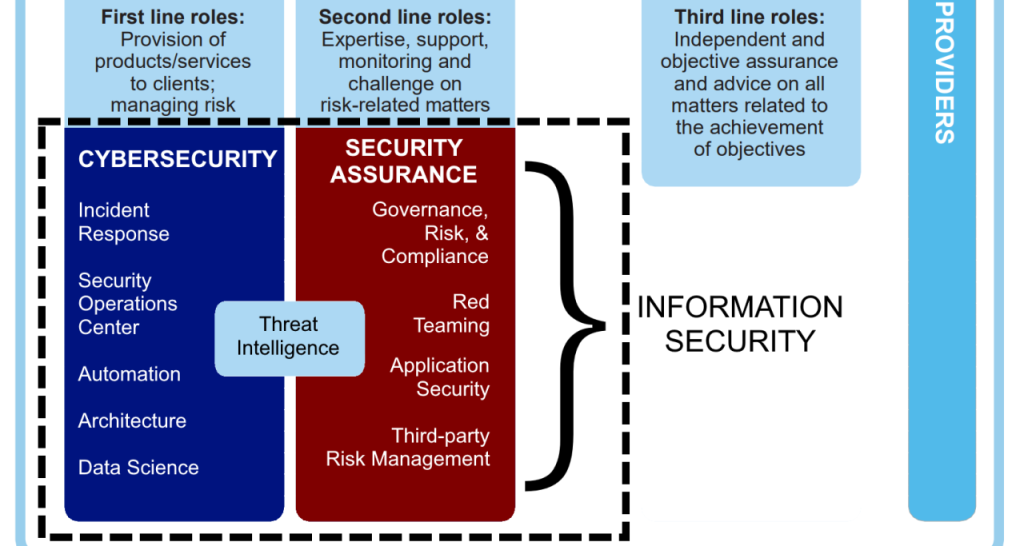
Infosec works through a layered approach, much like building a castle with multiple walls and defenses. Each layer provides protection and acts as a backup if another layer is breached. Here are some key layers:
1. Physical Layer:
- Secures physical infrastructure like servers, data centers, and equipment.
- Includes secure facilities, controlled access, and environmental controls like firewalls and temperature monitoring.
2. Network Layer:
- Protects internal and external networks from unauthorized access.
- Uses firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), network segmentation, and access control lists (ACLs).
3. Endpoint Layer:
- Secures laptops, desktops, mobile devices, and other endpoints.
- Utilizes antivirus/anti-malware software, endpoint detection and response (EDR), application whitelisting, and data loss prevention (DLP).
4. Data Layer:
- Protects data at rest and in transit.
- Employs encryption technologies, data masking, and secure deletion practices.
5. Application Layer:
- Secures web and mobile applications against vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Involves secure coding practices, penetration testing, and vulnerability management.
6. Human Layer:
- Educates and empowers employees to recognize and avoid cyber threats.
- Uses security awareness training, phishing simulations, and incident reporting procedures.
Infosec Architecture: Building the Walls
Beyond the layered approach, Infosec architecture refers to the overall design and implementation of security controls and technologies within an organization. Here are some key components:
1. Risk Assessment: Identifying and prioritizing potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
2. Security Policy and Standards: Defining acceptable usage, access control, and incident response procedures.
3. Technology Stack: Implementing the necessary tools and software for each layer of defense.
4. Incident Response Plan: Outlining steps to handle security breaches and minimize damage.
5. Monitoring and Logging: Continuously tracking security events and system activity for suspicious behavior.
6. Testing and Auditing: Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of security controls and identifying areas for improvement.
Note:
- Infosec is an ongoing process, not a one-time fix.
- Layering defenses and building a comprehensive architecture is crucial.
- Adapting to new threats and updating protocols is essential for long-term protection.
How to Install Infosec it?
I’ll do my best to provide a comprehensive response, but I’ll need more information to give specific installation instructions.
Here are some key questions to consider:
- What specific Infosec tool or technology are you referring to? There are countless software, platforms, and services within the Infosec domain, each with its own installation process.
- Where are you planning to install it? The installation process can vary depending on whether you’re installing on a personal device, a corporate network, or a cloud environment.
- What are your goals and objectives with the Infosec tool? Understanding the purpose will help determine the appropriate installation approach and configuration.
Here are some general guidelines that might apply, but please provide more context for specific instructions:
1. Clarify the Tool or Technology:
- Identify the exact name and vendor of the Infosec tool you want to install.
- Research its official website or documentation to find detailed installation instructions.
2. Determine the Deployment Environment:
- Personal Device:
- Check for compatibility with your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Download the installation file from the official website or vendor.
- Follow the on-screen prompts for a typical software installation process.
- Corporate Network:
- Coordinate with IT administrators for approval and guidance.
- Follow specific procedures for network deployment and configuration.
- Consider factors like user permissions, access controls, and integration with other security systems.
- Cloud Environment:
- Sign up for an account with the cloud provider offering the Infosec tool.
- Navigate their web interface or API to initiate the installation and configuration process.
3. Follow Vendor Documentation:
- Always refer to the official documentation or support resources for the specific tool.
- They often provide detailed installation guides, troubleshooting tips, and best practices.
4. Seek Additional Assistance:
- If you encounter challenges or need further guidance, contact the vendor’s technical support team for assistance.
- For enterprise-level tools, your IT department can provide support and expertise.
5. Consider Security Best Practices:
- Adhere to security measures during installation to avoid vulnerabilities.
- This might include verifying file integrity, using strong passwords, and configuring appropriate access controls.
Tips:
- Each Infosec tool has its unique installation process.
- Providing more details about the specific tool and deployment environment will enable me to offer more accurate instructions.
Basic Tutorials of Infosec: Getting Started

Welcome to the exciting world of information security! This field is crucial in protecting our data and systems in an increasingly digital age. Whether you’re curious about cybersecurity or want to pursue a career in the field, these basic tutorials will equip you with essential knowledge and skills.
1. Understand the Core Concepts:
- CIA Triad: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability are the fundamental principles of infosec. They ensure data privacy, accuracy, and accessibility.
- Threats and Vulnerabilities: Threats are malicious actors or events that exploit vulnerabilities, weaknesses in systems or processes. Understanding both is crucial for effective defense.
- Risk Management: Identify, assess, and prioritize risks to your systems and data. Implement appropriate controls to mitigate them.
2. Secure Your Online Presence:
- Strong Passwords: Use unique, complex passwords for every account and enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Beware of Phishing: Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments, and verify sender legitimacy before interacting.
- Software Updates: Regularly update your operating system, applications, and firmware to patch vulnerabilities.
3. Network Security Fundamentals:
- Firewalls: These act as gatekeepers, controlling traffic flow into and out of your network. Configure them to allow only authorized access.
- Antivirus and Anti-malware: Install and update these programs to protect your devices from malicious software.
- Wireless Security: Use strong encryption (WPA2 or higher) for your Wi-Fi network and avoid using public Wi-Fi for sensitive activities.
4. Explore Ethical Hacking:
- Kali Linux: This open-source operating system includes various tools for penetration testing and security assessments. Learn its basics to understand how attackers operate.
- Vulnerability Scanners: These tools automatically identify weaknesses in your systems. Use them to find and fix vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
- Coding Languages: Python and Bash are popular choices for security automation and scripting. Learning basic coding can enhance your infosec skills.
Remember, information security is a continuous learning process. Stay updated on the latest threats and trends, and keep practicing your skills to stay ahead of the curve.
- Mutual of Omaha: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- AES: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- Amphenol: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024

