What is iPhone?

The iPhone is a line of smartphones sketched and marketed by Apple Inc. It was first introduced by Steve Jobs, Apple’s co-founder, in 2007, revolutionizing the smartphone industry with its innovative design, user interface, and capabilities. iPhones run Apple’s iOS operating system and have become one of the most popular and iconic smartphones globally.
Key Features of iPhone:
- iOS Operating System:
- iPhones run on Apple’s iOS, a mobile operating system known for its simplicity, security, and integration with other Apple devices and services.
- App Store:
- The App Store provides a vast ecosystem of applications developed for iPhones, offering a wide range of functionalities, including productivity, entertainment, communication, and more.
- Design and Build Quality:
- iPhones are known for their sleek and premium design, often featuring high-quality materials like glass and aluminum. The build quality and attention to detail contribute to their aesthetic appeal.
- Retina Display:
- Many iPhones feature Retina Displays, offering high-resolution and vibrant screens that enhance the visual experience for users.
- Performance:
- iPhones are equipped with powerful processors and hardware, providing smooth performance for various tasks, including gaming, multitasking, and running demanding applications.
- Security Features:
- iPhones are known for their robust security features, including Face ID (facial recognition) or Touch ID (fingerprint recognition), as well as data encryption and a secure enclave for protecting sensitive information.
- Camera Technology:
- iPhones are renowned for their high-quality camera technology. They often include advanced features like optical image stabilization, Night mode, and computational photography for capturing impressive photos and videos.
- Integration with Apple Ecosystem:
- iPhones seamlessly integrate with other Apple devices and services, such as Macs, iPads, Apple Watch, iCloud, and Apple Music, providing a cohesive user experience across the ecosystem.
- Regular Software Updates:
- Apple releases regular iOS updates, ensuring that iPhones receive new features, security enhancements, and performance improvements over time.
- Augmented Reality (AR):
- iPhones support augmented reality applications, leveraging ARKit to provide immersive and interactive experiences.
What is top use cases of iPhone?
Top Use Cases of iPhone:
- Communication:
- iPhones are widely used for communication purposes, including voice calls, messaging, and video calls. Apps like FaceTime and iMessage are popular among iPhone users.
- Mobile Internet Browsing:
- iPhones offer a smooth and responsive web browsing experience, with support for Safari and a wide range of third-party browsers.
- Multimedia and Entertainment:
- iPhones serve as portable multimedia devices, allowing users to listen to music, watch videos, and play games. The App Store offers a plethora of entertainment apps.
- Productivity:
- iPhones are utilized for productivity tasks, including email, calendar management, document editing, and note-taking. Apps like Pages, Numbers, and Keynote facilitate productivity on the go.
- Photography and Videography:
- The advanced camera capabilities of iPhones make them popular for photography and videography. Users can capture high-quality images, record videos, and edit media directly on their devices.
- Social Media and Networking:
- Social media apps, such as Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn, are widely used on iPhones for social networking and staying connected with friends and colleagues.
- Health and Fitness:
- iPhones include health and fitness features, and the App Store offers a variety of apps for tracking physical activity, monitoring health metrics, and providing workout routines.
- Navigation and Maps:
- iPhones serve as reliable navigation devices, offering GPS capabilities and applications like Apple Maps or third-party navigation apps for driving, walking, or public transportation.
- E-Commerce and Shopping:
- Users frequently use iPhones for online shopping, with apps like Amazon, eBay, and various e-commerce platforms providing a convenient way to browse and purchase products.
- Education and Learning:
- iPhones are used for educational purposes, with apps supporting e-learning, language learning, and educational games. The iPad, another Apple device, is particularly popular in the education sector.
- Mobile Banking and Finance:
- iPhones support mobile banking apps, allowing users to manage their finances, make transactions, and monitor accounts securely.
- Augmented Reality Experiences:
- iPhones support augmented reality applications, ranging from gaming and educational experiences to interactive shopping and navigation.
The iPhone’s versatility, powerful hardware, and extensive app ecosystem contribute to its widespread adoption across various use cases, making it a integral part of many users’ daily lives.
What are feature of iPhone?

iPhones come with a range of features that contribute to their popularity and user satisfaction. Following are some key features of iPhones:
- iOS Operating System:
- iPhones run on Apple’s iOS, known for its intuitive user interface, stability, and security.
- App Store:
- The App Store provides access to a vast ecosystem of applications, offering everything from productivity tools and games to health and education apps.
- Design and Build Quality:
- iPhones are known for their sleek and premium design, often featuring high-quality materials such as glass and aluminum.
- Retina Display:
- Many iPhones come with Retina Displays, offering high-resolution screens with vivid colors and sharp details.
- Security Features:
- iPhones incorporate advanced security features, including Face ID (facial recognition) or Touch ID (fingerprint recognition), as well as data encryption and a secure enclave.
- Powerful Performance:
- iPhones are equipped with powerful processors, ensuring smooth performance for various tasks, including multitasking and running demanding applications.
- Camera Technology:
- iPhones are known for their advanced camera technology, supporting features such as Night mode, Portrait mode, and computational photography.
- Integration with Apple Ecosystem:
- iPhones seamlessly integrate with other Apple devices and services, such as Macs, iPads, Apple Watch, iCloud, and Apple Music.
- Regular Software Updates:
- Apple provides regular iOS updates, delivering new features, security enhancements, and performance improvements.
- Augmented Reality (AR):
- iPhones support augmented reality experiences through ARKit, allowing developers to create immersive and interactive applications.
- Health and Fitness Tracking:
- iPhones include health and fitness features, with the Health app tracking metrics such as steps, heart rate, and sleep.
- Animoji and Memoji:
- iPhones with Face ID support Animoji and Memoji, allowing users to create animated characters based on their facial expressions.
- Siri:
- Siri, Apple’s virtual assistant, is integrated into iPhones, providing voice-activated assistance for various tasks.
- AirDrop and AirPlay:
- AirDrop enables easy file sharing between Apple devices, while AirPlay allows wireless streaming of audio and video content.
- iCloud:
- iCloud provides cloud storage and synchronization of data, ensuring that users can access their content seamlessly across devices.
What is the workflow of iPhone?
Workflow of iPhone:
- Setup:
- When a user purchases a new iPhone or resets an existing one, the initial setup involves selecting the language, connecting to Wi-Fi, and signing in with an Apple ID.
- Home Screen:
- The iPhone’s home screen is the central hub for accessing apps and features. Users can organize apps into folders, customize the layout, and set wallpapers.
- App Interaction:
- Users can launch apps by tapping on their icons. Apps are designed to provide a user-friendly interface for various functionalities, such as messaging, browsing, and productivity.
- Control Center:
- Accessible by swiping down from the top-right corner, the Control Center provides quick access to essential settings, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, brightness, and music controls.
- Notification Center:
- Swiping down from the top of the screen reveals the Notification Center, displaying notifications from apps, messages, and other alerts.
- Multitasking:
- Users can switch between open apps and access the app switcher by swiping up from the bottom of the screen. This enables efficient multitasking and app management.
- Settings App:
- The Settings app allows users to customize various aspects of their iPhone, including network settings, display preferences, security options, and more.
- App Store:
- The App Store is the go-to place for discovering and installing new apps. Users can search for apps, read reviews, and download them directly to their device.
- Camera App:
- The Camera app provides access to the iPhone’s camera and various shooting modes, allowing users to capture photos, videos, and panoramic shots.
- FaceTime and Messages:
- FaceTime and Messages apps enable users to make video calls and send text messages, photos, and videos to contacts.
- Health App:
- The Health app tracks and displays health-related data, including activity, sleep, and wellness metrics.
- Music and Podcasts:
- The Music app allows users to listen to their favorite songs, playlists, and podcasts. Apple Music provides a subscription service for accessing a vast music library.
- Photos App:
- The Photos app organizes and displays photos and videos stored on the device, offering features for editing and organizing media content.
- iCloud Integration:
- iCloud ensures synchronization of data across devices. Photos, contacts, notes, and other content can be accessed seamlessly on other Apple devices.
- Siri:
- Users can activate Siri by voice command or by holding down the side button. Siri can provide information, set reminders, send messages, and perform various tasks.
- Security Features:
- Face ID or Touch ID provides secure authentication, allowing users to unlock their device, make purchases, and access sensitive information.
The workflow of an iPhone involves navigating through the user interface, interacting with apps, and utilizing features designed to enhance productivity, entertainment, and communication. The cohesive integration of hardware and software contributes to the overall user experience on the iPhone.
How iPhone Works & Architecture?
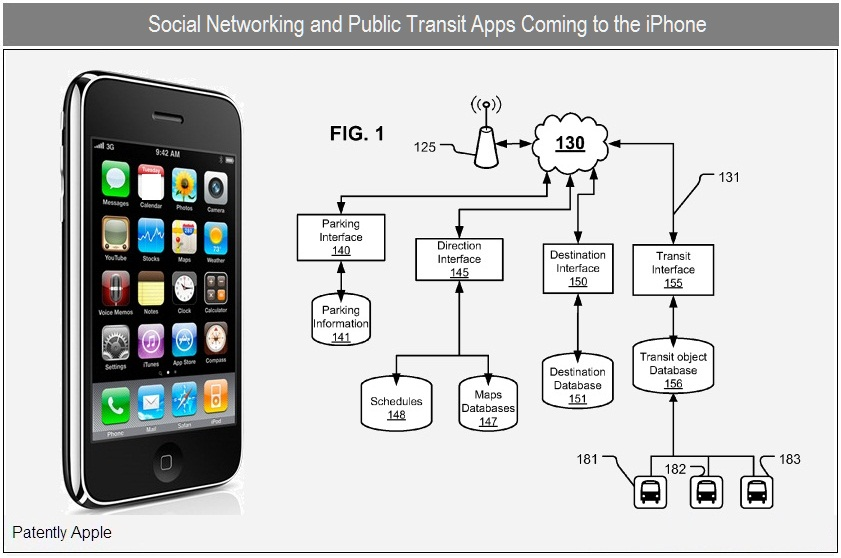
The iPhone is a complex device, but its core functionality can be broken down into several key layers:
1. Hardware:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Handles the main computational tasks.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Renders graphics and animations.
- Memory (RAM): Stores temporary data for running applications.
- Storage (ROM): Stores permanent data like apps, music, and photos.
- Sensors: Accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer, proximity sensor, ambient light sensor, etc.
- Cameras: Front and rear cameras for capturing photos and videos.
- Display: Multi-touch display for user interaction.
- Touch ID/Face ID: Biometric authentication for unlocking the device.
- Cellular Radio: Connects to cellular networks for voice calls and data.
- Wi-Fi: Connects to wireless networks for internet access.
- Bluetooth: Connects to wireless devices like headphones and speakers.
- Battery: Provides power to the device.
2. Operating System (iOS):
- The iOS operating system controls all the hardware and provides the core functionality of the device.
- It includes features like the home screen, app management, multitasking, notifications, and access to iCloud services.
- iOS is also responsible for app security and sandboxing, which prevents apps from accessing each other’s data or harming the system.
3. Applications:
- Apps are the software programs that run on the iPhone and provide specific functionality.
- They can be downloaded from the App Store and installed on the device.
- Apps access hardware and system resources through iOS APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
4. Data Services:
- The iPhone connects to cellular networks and Wi-Fi to access data services like internet access, email, and messaging.
- It also uses these services for features like App Store downloads, iCloud synchronization, and online games.
5. iCloud:
- iCloud is Apple’s cloud storage service that allows users to store data like photos, documents, and contacts online.
- It also provides features like Find My iPhone and iCloud backup for restoring data to a new device.
6. User Interface:
- The iPhone’s user interface is based on the concept of touch gestures.
- Users interact with the device by tapping, swiping, pinching, and spreading on the display.
- The iOS interface is designed to be intuitive and easy to use, even for first-time users.
Overall Architecture:
The iPhone’s architecture can be summarized as a layered system:
- Hardware: Provides the physical resources and capabilities.
- Operating System (iOS): Controls the hardware and provides core functionality.
- Applications: Offer specific features and functionalities to users.
- Data Services: Connect the device to the internet and other networks.
- iCloud: Provides cloud storage and synchronization services.
- User Interface: Permits users to interact with the device.
Understanding this architecture can help users appreciate the complexity of the iPhone and the seamless interaction between its various components.
How to Install and Configure iPhone?
Installing and Configuring an iPhone:
Following is a step-by-step guide on how to install and configure an iPhone:
1. Hardware Setup:
- Unbox the iPhone: Remove the phone, charging cable, and power adapter from the box.
- Insert the SIM card (optional): If your iPhone requires a SIM card for cellular service, insert it into the SIM tray using the provided tool.
- Charge the iPhone: Connect the charging cable to the phone and power adapter, and plug it into a power outlet. Leave it to charge for a while.
2. Software Setup:
- Turn on the iPhone: Press and hold the side button until you see the Apple logo.
- Choose language and region: Choose your preferred region and language.
- Quick Start (optional): If you have another iPhone nearby, use Quick Start to automatically transfer your settings and data to the new device.
- Connect to Wi-Fi: Select a Wi-Fi network and enter the password.
- Activate your iPhone: Follow the on-screen instructions to activate your iPhone with your cellular provider.
- Set up Face ID or Touch ID: Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your preferred biometric authentication method.
- Create a passcode: Set a passcode for additional security.
- Restore or transfer data: If you backed up your previous iPhone, you can restore your data from iCloud or iTunes. You can also choose to set up the iPhone as new.
- Customize settings: Explore and personalize various settings like wallpaper, ringtones, notifications, and accessibility features.
3. App Downloads and Installation:
- Open the App Store: This is the official app store for iPhones, where you can download and install various applications.
- Browse or search for apps: Explore different categories or search for specific apps you need.
- Download and install apps: Tap on the app you want and choose “Get” or the price tag. You might need to enter your Apple ID password or authenticate with Face ID or Touch ID.
- Update apps: The App Store will automatically notify you of available updates for your installed apps. You can upgrade them individually or all at once.
4. Additional Configurations:
- Sign in to iCloud: Use your Apple ID to sign in to iCloud and access your data across all your Apple devices.
- Set up Apple Pay: This allows you to make contactless payments using your iPhone.
- Customize notification settings: Choose which apps can send you notifications and how they are displayed.
- Explore Apple services: Get familiar with services like Apple Music, Apple TV+, iMessage, FaceTime, and others.
5. Resources:
- Apple iPhone User Guide
- Apple Support website
- Apple Support app: Download the app for quick access to support articles and contact options.
Points to Remember:
- Keep your iPhone updated to the latest iOS version for security and stability.
- Back up your iPhone regularly to iCloud or iTunes in case of data loss.
- Explore the various features and settings available to personalize your iPhone experience.
- Contact Apple Support if you encounter any difficulties during setup or use.
By following these steps and exploring the provided resources, you can easily install, configure, and personalize your new iPhone to suit your needs and preferences.
Fundamental Tutorials of iPhone: Getting started Step by Step

Following is a step-by-step basic tutorials for getting started with your iPhone:
1. Getting Started:
- Turn on your iPhone: Tap and hold the side button until you see the Apple logo.
- Follow the on-screen instructions: You will be guided through the setup process, including choosing a language, connecting to Wi-Fi, and creating a passcode.
- Set up Face ID or Touch ID: This allows you to unlock your iPhone using your face or fingerprint.
2. Basic Gestures:
- Tap: Use your finger to tap on the screen to select items, open apps, and type.
- Swipe: Slide your finger across the screen to scroll through lists, navigate between home screens, and go back.
- Pinch: Place two fingers on the screen and pinch them together or apart to zoom in and out.
- Double-tap: Quickly tap on the screen twice to zoom in or out on a map or image.
- 3D Touch (if applicable): Press firmly on the screen to access additional options for apps and shortcuts.
3. Home Screen:
- The Home screen is where you find all of your apps.
- You can arrange your apps in folders to keep them organized.
- To open an app, press on its icon.
- To close an app, swipe up on the app preview.
4. App Store:
- The App Store is where you download apps for your iPhone.
- You can browse for apps by category, search for specific apps, or read reviews.
- To download an app, tap on its Get button and enter your Apple ID password.
- Once the app is downloaded, you can find it on your Home screen.
5. Making Calls:
- Open the Phone app.
- Enter the phone number you want to call, or tap on a contact from your list.
- Tap on the Call button.
- To end the call, tap on the End button.
6. Sending Messages:
- Open the Messages app.
- Tap on the Compose button.
- Enter the phone number or contact of the person you want to message.
- Type your message in the text field.
- Tap on the Send button.
7. Taking Photos and Videos:
- Open the Camera app.
- Point the camera at what you want to take a picture or video of.
- Press the shutter button to take a picture.
- Tap and hold the shutter button to record a video.
- To view your photos and videos, open the Photos app.
8. Browsing the Web:
- Open the Safari app.
- Enter the website URL you want to visit.
- You can also tap on a link to open a website.
- To go back a page, tap on the Back button.
- To refresh the page, pull down on the screen.
9. Using Siri:
- Press and hold the side button or home button to activate Siri.
- Ask Siri a question or give it a command.
- Siri will respond to you using voice or text.
10. Important Points:
- You can personalize your iPhone by changing the wallpaper, ringtones, and other settings.
- You can find more information and tutorials on the Apple website and in the iPhone User Guide.
- If you have any queries, you can contact Apple Support.
These are just some of the basic things you can do with your iPhone. There are many other features and capabilities to explore. With a little practice, you’ll be a pro at using your iPhone in no time.
- Mutual of Omaha: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- AES: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- Amphenol: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024

