
Kotlin is a fast-growing cross-platform and statically typed programming language. The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is used to implement programming for application development. As an alternative to Java language, Kotlin is becoming more popular in Android application development. JetBrains and Google created and maintain it as an open-source programming language. Kotlin is an object-oriented programming language that has data types, operators, I/O comments, control statements, functions, classes, object expressions, and constructors, among other features. Because of its compatibility, low runtime, and efficient coding characteristics, many companies are switching to Kotlin as a recommended language for development.
What is Kotlin?
Let’s take a closer look at Kotlin, which is one of the trendiest subjects in social media right now and the new future for software professionals. Kotlin is a Java Virtual Machine-based statically typed cross-programming language. The Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is a popular tool for creating Java code. Returning to the subject of history and progress. Jet-brains was in charge of the design and development. Kotlin is a computer language named after a small island near St. Petersburg called “kotlin.” The Java computer language was named after the Indonesian island of Java. In the current industry, it might be referred to as Java’s successor.

Why Kotlin Make Working so Easy?
It is now officially recognised by Google as the programming language for Android development. Please explain how Kotlin can make our work so much easier and more enjoyable. The Kotlin programming language is short and provides the programmer with extra conveniences thanks to its built-in applications. Long Java programmes may be developed in a short time using Kotlin. That is, it consumes less code while producing the same outputs. Writing a shortcode requires less time, which is directly related to financial factors, i.e.,
What is the Use of Kotlin?
Understanding the usage of Kotlin, the successor to Java, will be easier if you compare Java with Kotlin. This may be utilised on both the client and the source side. It works with all operating systems, including iOS, MacOS, and embedded systems. Server-side apps, java scripts, and data science all make use of it.
In Kotlin, less code is produced, and there are fewer bugs. It also allows test-driven development, which minimises the amount of bugs. Even if you make an error when coding the code, you can easily rectify it. Because of its brevity and fewer issues, it is simple to maintain and may be handled by a new team.
Why Should We Use Kotlin?
In most applications in the 1990s, Java was the mainstream programming language; but, by 2019, Java has become outdated, time-consuming, and lacking some built-in language capabilities. In that scenario, Kotlin is built to address all of these issues. Java is a long, time-consuming, and error-prone programming language. It’s quick, straightforward, and most importantly, it’s compatible with Java code and vice versa, which means you can create code in both Kotlin and Java, and they’ll both operate together.
What are the Scope?
Companies are steadily transferring their programming languages from Java to Kotlin, therefore we can see that Kotlin has a lot of potential in the future. In the eight months after Google announced Kotlin as an official programming language for Android development, its usage has increased from 7% to 14%. Google is heavily funding in the development of Kotlin, implying that Kotlin will be used in Google projects.
What are the Career Growth?
There will undoubtedly be job advancement if there is future potential. Many firms, such as Pinterest, Basecamp, Netflix, Uber, and others, are already utilising it; this will undoubtedly benefit your career; all you need is a strong desire to learn the language.
What are the Functional programming in Kotlin?
Allowing top-level functions is only the start of Kotlin’s functional programming journey. Higher-order functions, anonymous functions, lambdas, inline functions, closures, tail recursion, and generics are also supported by the language. Kotlin, in other words, offers all of the benefits and characteristics of a functional language. Consider the following examples of functional Kotlin idioms.
Filtering a list in Kotlin:-
val positives = list.filter { x -> x > 0 }When the lambda function only has one parameter, use it for an even shorter expression:
val positives = list.filter { it > 0 }Traversing a map/list of pairs in Kotlin:-
for ((k, v) in map) { println(“$k -> $v”) }
The letters k and v can be given any name.
How do we Use Kotlin?
for (i in 1..100) { ... } // closed range: includes 100
for (i in 1 until 100) { ... } // half-open range: does not include 100
for (x in 2..10 step 2) { ... }
for (x in 10 downTo 1) { ... }
if (x in 1..10) { ... }The for keyword, as well as the usage of ranges, are demonstrated in the examples above.
Despite the fact that Kotlin is a full-fledged functional programming language, it retains the majority of Java’s object-oriented nature as an alternative programming style, which comes in useful when converting existing Java code. Kotlin provides constructors for classes, as well as nested, inner, and anonymous inner classes, and interfaces similar to Java 8. There is no new keyword in Kotlin. Call the function Object() { [native code] } like any other method to generate a class instance. That may be seen in the screenshot above.
All Kotlin classes have a default superclass Any, which is not the same as the Java base class java.lang.Object. Kotlin allows single inheritance from a named superclass, and all Kotlin classes have a default superclass Any, which is not the same as the Java base class java.lang.Object. There are exactly three member methods in any: equals(), hashCode(), and function toString().
To allow other classes to inherit from Kotlin classes, they must be tagged with the open keyword; Java classes, on the other hand, are inheritable unless marked with the final keyword. The method must be designated open, and the subclass method must be marked override, in order to override a superclass method. This fits in with Kotlin’s concept of making things clear instead than depending on defaults. I can see how Kotlin’s method of explicitly designating base class elements as open for inheritance and derived class members as overrides prevents numerous types of frequent Java mistakes in this scenario.
What Are The best features and Advantages of Kotlin?
Readability:-
Kotlin has more understandable and accurate code than Java, making the application easier to grasp. A Java developer may rapidly comprehend how to create Kotlin after a short learning curve.
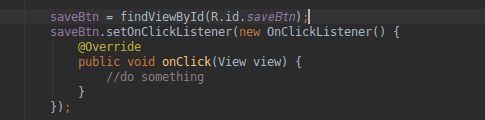
After studying Kotlin, I saw that it required far less code than Java, as demonstrated in the diagram below.
Java:-
Kotlin:-
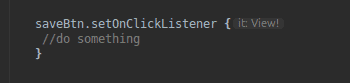
As can be seen, Kotlin has less boilerplate than Java. The term “boilerplate” now refers to code that must be repeated many times but does not contribute to the application’s functionality. Kotlin is built in such a way that it doesn’t require boilerplate code.
In comparison to Java, Kotlin requires less lines of code.
We must use findViewById to establish references for views in Java. That is handled automatically in Kotlin, resulting in a significant reduction in the number of lines of code. This makes learning Kotlin easier for a newbie.
Null-Safe:-
Null pointer exceptions, popularly known as “the billion-dollar error,” are one of the most prevalent problems that cause Java projects to break.
By default, Kotlin is null-safe. It is not possible to assign a null value to a variable. However, with Java, we may give null values to variables, which might result in a null pointer exception, which can cause the application to crash.
Using Getters and Setters:-
For getting data from variables in modal classes, we must utilise getter and setter methods in Java. Model classes are only used to store information. The getters and setters may be used to access data from model classes.
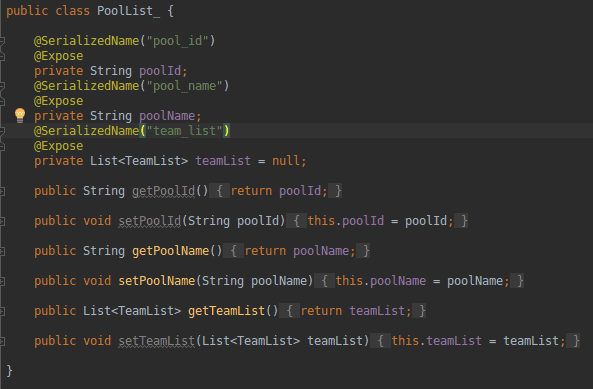
We don’t need all those getter and setter functions in Kotlin. The variable name may be used to get all of the data. Take a look at the sample below.
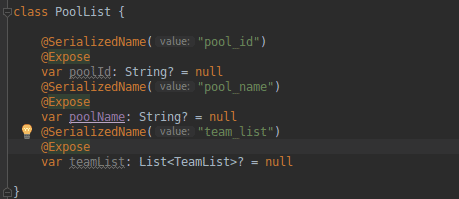
Instead of writing the getter and setter methods, this modal class in Kotlin simply needs to specify the variables. When we compare the two pictures above, we can plainly see that Kotlin requires less code than Java.
Interoperability:-
The Kotlin programming language is interoperable. This implies that Java and Kotlin are close enough that we can utilise Java commands and libraries in a Kotlin project.
Because most programmers still use Java, Kotlin has been designed to be compatible with it. It will not create any issues when used with existing Java classes. The compiler will ensure that the code including Java and Kotlin classes runs well.
Developers may easily switch from Java to Android thanks to this functionality.
Immutability:-
An immutable object is one whose state is unchangeable after it has been formed.
To make it easier for developers to understand which values can be reassigned in Kotlin, variables are specified with val or var.
Using val in our code makes it incredibly tidy, and we can confidently trust that the properties will never change and will never be null. The advantage is that you can focus only on the project at hand.
Video recommendation for Kotlin:-
- Degree Pursuit: Navigating the Path to Educational Excellence - July 4, 2024
- Why Is Studying English Important in a Business Environment? - July 4, 2024
- Top 10 Data Science Skills You Need in 2024 - July 3, 2024

