What is McAfee?

McAfee is a global computer security software corporation headquartered in San Jose, California. Founded in 1987, McAfee offers a wide range of security products and services for consumers, businesses, and governments.
Top 10 use cases of McAfee?
Here are the top 10 use cases of McAfee:
- Endpoint Protection: McAfee Endpoint Protection protects your devices from malware, ransomware, and other threats with real-time scanning, behavior analysis, and automatic updates.
- Network Security: McAfee Network Security protects your network from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats with firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and web filtering.
- Data Loss Prevention: McAfee Data Loss Prevention helps you prevent sensitive data from being leaked or stolen with data encryption, content inspection, and activity monitoring.
- Email Security: McAfee Email Security protects your email from phishing attacks, spam, and malware with email filtering, sandboxing, and encryption.
- Cloud Security: McAfee Cloud Security protects your cloud workloads from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats with security posture management, workload protection, and threat detection.
- Managed Security Services: McAfee Managed Security Services provide 24/7 monitoring and management of your security infrastructure by security experts.
- Identity and Access Management: McAfee Identity and Access Management helps you control access to your resources and data with multi-factor authentication, single sign-on, and privileged access management.
- Security Awareness Training: McAfee Security Awareness Training helps you educate your employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- DDoS Protection: McAfee DDoS Protection protects your website and applications from distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): McAfee EDR helps you detect, investigate, and respond to cyberattacks on your endpoints.
These are just a few of the many use cases for McAfee products and services. McAfee offers a wide range of solutions to meet the security needs of organizations of all sizes.
What are the feature of McAfee?
McAfee offers a diverse range of features across its product portfolio, addressing various security needs for individuals and organizations. Here’s a breakdown of some key areas and features:
Endpoint Protection:
- Real-time malware protection: Identifies and blocks viruses, ransomware, and other threats.
- Behavioral analysis: Detects suspicious activity even for unknown threats.
- Automatic updates: Ensures you have the latest protection against emerging threats.
- Web protection: Blocks malicious websites and phishing attempts.
- Firewall: Controls incoming and outgoing network traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
- Device control: Restricts unauthorized use of USB drives and other devices.
- Parental controls: Filters inappropriate content and limits screen time for children.
Network Security:
- Firewall: Protects your network from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Intrusion detection and prevention (IDS/IPS): Detects and blocks malicious network activity.
- Web filtering: Blocks access to malicious and inappropriate websites.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): Prevents sensitive data from being leaked or stolen.
- Email security: Protects your email from phishing attacks, spam, and malware.
- Security information and event management (SIEM): Collects and analyzes security data from across your network for threat detection and incident response.
Cloud Security:
- Workload protection: Secures your cloud workloads from unauthorized access, malware, and other threats.
- Security posture management: Assesses and manages the security posture of your cloud environment.
- Threat detection and response: Detects and responds to threats in your cloud environment.
- Data encryption: Encrypts your data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
Identity and Access Management:
- Multi-factor authentication: Adds an extra layer of security to logins by requiring multiple forms of identification.
- Single sign-on: Allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials.
- Privileged access management: Controls access to sensitive systems and data.
Additional Features:
- Managed security services: Provides 24/7 monitoring and management of your security infrastructure by security experts.
- Security awareness training: Helps you educate your employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices.
- DDoS protection: Protects your website and applications from distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR): Helps you detect, investigate, and respond to cyberattacks on your endpoints.
How McAfee works and Architecture?
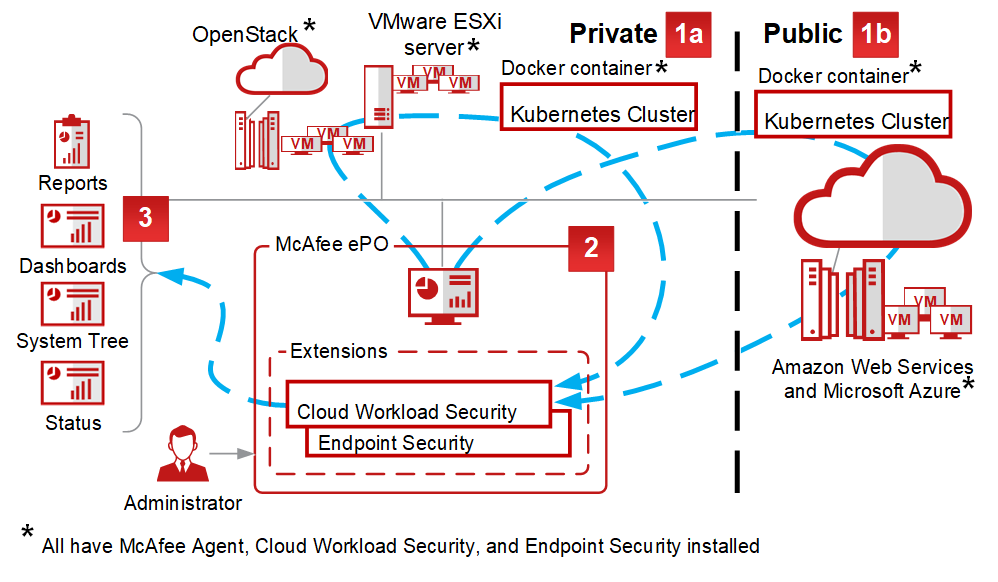
McAfee’s security solutions encompass various products and services, each with its own specific architecture and functionalities. Here’s a general overview of the underlying principles guiding their approach:
Core Architecture Principles:
- Client-Server Model: Many McAfee solutions employ a client-server architecture, where lightweight “agents” installed on devices (endpoints) communicate with central management servers that collect data, analyze threats, and deliver updates.
- Cloud-Based Security: An increasing focus on cloud-based delivery and management for scalability, flexibility, and centralized control.
- Machine Learning and AI: Integration of machine learning and artificial intelligence for advanced threat detection, behavioral analysis, and proactive security measures.
- Open Integration: Ability to integrate with diverse security tools and platforms for broader visibility and seamless security posture management.
Endpoint Protection Example:
Consider McAfee Endpoint Security as an example. It follows a client-server model:
- Endpoint Agents: Installed on devices, these agents monitor system activity, detect threats, and report data to the management server.
- Management Server: Analyzes data from agents, identifies threats, delivers updates, and sends remediation instructions to agents.
- Cloud Intelligence: Connects to McAfee’s cloud-based Threat Prevention System (TPS) for real-time threat intelligence and updates.
Additional Architectural Components:
Depending on the specific solution, additional components might be involved:
- Firewalls: Protect networks from unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): Detect and block malicious network activity.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Prevents sensitive data from being leaked or stolen.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collects and analyzes security data from across the network for threat detection and incident response.
Benefits of McAfee’s Architecture:
- Scalability: Adapts to organizations of all sizes and security needs.
- Centralized Management: Provides a single platform for managing security across diverse environments.
- Real-time Threat Intelligence: Ensures continuous protection against emerging threats.
- Automation: Automates tasks like threat detection, updates, and response for efficiency.
- Openness and Integration: Integrates with existing security tools and platforms for enhanced protection.
How to Install McAfee it?
Installing McAfee products involves different steps depending on the specific product you choose and your desired deployment method. Here’s a general overview to guide you:
1. Choose your McAfee product and deployment method:
- Identify the specific McAfee product that suits your needs. Consider options like Endpoint Protection, Network Security, Cloud Security, and more.
- Decide on your deployment method: Cloud-based or on-premises.
- Cloud-based: Managed entirely by McAfee in their cloud environment. No installation on your end required.
- On-premises: Requires installing software agents on your devices and potentially additional components like servers depending on the product.
2. Gather necessary information:
- Subscription details: Your McAfee subscription plan and activation key.
- System requirements: Ensure your devices meet the system requirements for the chosen product. Find these on the McAfee website.
- Network configuration details: Understand your network topology and IP addressing scheme, especially relevant for on-premises deployments.
3. Follow the installation guide:
- McAfee provides detailed installation guides on their website specific to each product and deployment method. Navigate to the support section and search for your chosen product and deployment type.
- These guides typically cover:
- Cloud deployment: Activating your subscription and adding devices through the McAfee web console.
- On-premises deployment: Downloading and installing agents on your devices, configuring servers (if applicable), and integrating with your network.
4. Additional considerations:
- Licensing: Ensure you have the necessary licenses for your chosen product and devices.
- Configuration customization: Tailor settings based on your specific security needs and policies.
- Post-installation tasks: Update agents, integrate with other security tools, and monitor system health.
Important notes:
- Due to the variations in products and deployment methods, I cannot provide specific installation instructions without knowing your chosen details.
- Consider seeking professional assistance for complex on-premises deployments or if you lack technical expertise.
Basic Tutorials of McAfee: Getting Started

McAfee provides a range of cybersecurity solutions, including antivirus, endpoint protection, and other security products. Below are step-by-step basic tutorials to help you get started with McAfee Endpoint Security, one of their key offerings:
Prerequisites:
- McAfee Endpoint Security Software:
- Ensure that McAfee Endpoint Security software is installed on the target endpoints.
2. Access to McAfee ePO (ePolicy Orchestrator):
- Access to the McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator console, which is used for central management.
Tutorial 1: Installing McAfee Endpoint Security
- Download McAfee Endpoint Security:
- Obtain the McAfee Endpoint Security installer from the official McAfee website or your organization’s McAfee portal.
2. Install McAfee Endpoint Security:
- Run the installer on each endpoint and follow the on-screen instructions to install McAfee Endpoint Security.
Tutorial 2: McAfee ePO Console Setup
- Access McAfee ePO Console:
- Open a web browser and navigate to the McAfee ePO console URL.
- Log in using your ePO credentials.
2. Navigate to Systems:
- In the ePO console, navigate to the “Systems” section to view and manage endpoint systems.
Tutorial 3: Creating and Assigning Policies
- Create Endpoint Security Policies:
- Navigate to the “Policy Catalog” in the ePO console.
- Create or customize endpoint security policies based on your organization’s security requirements.
2. Assign Policies to Systems:
- Assign the created policies to specific systems or groups of systems.
- This ensures that each endpoint follows the designated security policy.
Tutorial 4: Deploying Updates and Patches
- Check for Updates:
- In the ePO console, check for the latest security updates and patches available for McAfee Endpoint Security.
2. Deploy Updates:
- Deploy the updates to endpoints to ensure they have the latest security definitions and protection.
Tutorial 5: Monitoring and Reporting
- Review Security Dashboards:
- Explore the security dashboards in the ePO console to monitor the security status of endpoints.
2. Generate Reports:
- Generate and review reports on security incidents, threat detections, and overall system health.
Tutorial 6: Endpoint Scans and Threat Detection
- Perform Endpoint Scans:
- Schedule or initiate manual endpoint scans using McAfee Endpoint Security to detect and remove threats.
2. Investigate Threat Detections:
- Investigate and respond to any threat detections reported by McAfee Endpoint Security.
Tutorial 7: Endpoint Quarantine and Remediation
- Quarantine Infected Systems:
- Use McAfee Endpoint Security to quarantine or isolate infected systems to prevent the spread of threats.
2. Remediate Systems:
- Initiate remediation actions to clean and restore systems that have been affected by security incidents.
Tutorial 8: Policy Updates and Optimization
- Periodic Policy Review:
- Periodically review and update security policies based on emerging threats and organizational changes.
2. Optimize McAfee Endpoint Security Settings:
- Explore and adjust settings in McAfee Endpoint Security to optimize its performance and effectiveness.
These tutorials provide a basic introduction to configuring and managing McAfee Endpoint Security using the McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator console.
- Mutual of Omaha: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- AES: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- Amphenol: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024

