What is NSX-T Data Center?

NSX-T Data Center, now simply known as VMware NSX, is a comprehensive platform for virtualizing and securing your network infrastructure within data centers, clouds, and application frameworks. It empowers you to:
- Simplify network management: Abstract network complexity and manage it programmatically.
- Enhance agility and flexibility: Provision and configure networks on-demand.
- Improve security: Apply consistent security policies across diverse environments.
- Optimize resource utilization: Allocate and scale network resources efficiently.
Top 10 use cases of NSX-T Data Center?
Top 10 Use Cases of VMware NSX:
- Micro-segmentation: Securely isolate workloads at the application level for enhanced protection.
- Multi-cloud networking: Consistently manage and connect networks across private, public, and hybrid cloud environments.
- SD-WAN integration: Integrate with SD-WAN solutions for optimized and secure WAN connectivity.
- Network automation: Automate repetitive tasks for faster deployments and configuration changes.
- Disaster recovery: Simplify disaster recovery with automated failover and network replication.
- Compliance automation: Enforce security policies and compliance requirements automatically.
- Container networking: Manage and secure containerized applications seamlessly.
- Bare-metal integration: Extend network virtualization and security to bare-metal workloads.
- DevOps integration: Integrate with DevOps workflows for faster application delivery.
- Cost optimization: Optimize network resource utilization and reduce infrastructure costs.
Benefits of Using VMware NSX:
- Reduced complexity: Simplifies network management and eliminates manual configuration.
- Increased agility: Enables faster deployments and adapts to changing business needs.
- Enhanced security: Provides comprehensive security features and micro-segmentation for better protection.
- Improved efficiency: Optimizes resource utilization and reduces operational costs.
- Greater flexibility: Supports diverse deployment models and workloads.
What are the feature of NSX-T Data Center?
VMware NSX offers a wide range of features spanning across networking, security, automation, and operational simplicity. Here’s a breakdown of some key functionalities in each area:
Networking:
- Logical Switching and Routing: Create and manage virtual networks independently of the physical infrastructure.
- Layer 2/Layer 3 Services: Implement advanced networking features like VLANs, VXLANs, BGP routing, and more.
- Multi-Tenancy: Securely isolate network resources for different departments or tenants.
- Overlay Network: Deploy virtual networks on top of existing physical infrastructure.
- SD-WAN Integration: Integrate with SD-WAN solutions for optimized and secure WAN connectivity.
Security:
- Micro-segmentation: Securely isolate workloads at the application level, limiting lateral movement and reducing attack surface.
- Distributed Firewall: Enforce granular security policies at the east-west and north-south traffic, including next-generation firewall (NGFW) capabilities.
- Guest Introspection: Gain visibility and control over workloads running inside virtual machines.
- Security Groups: Apply consistent security policies to groups of workloads for simplified management.
- Identity Firewall: Enforce security based on user and application identities, offering finer-grained control.
Automation:
- API-driven: Programmatically manage and configure network and security elements.
- Terraform Integration: Leverage Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Terraform for automated deployments.
- Workflow Automation: Automate repetitive tasks and integrate with CI/CD pipelines.
- Policy-Based Management: Define and enforce consistent policies across your network infrastructure.
Operational Simplicity:
- Centralized Management: Manage your entire network from a single platform.
- Monitoring and Visibility: Gain comprehensive insights into network health, performance, and security posture.
- Troubleshooting: Leverage AI-powered analytics for faster troubleshooting and issue resolution.
- Scalability: Easily scale your network to meet growing demands.
Additional Features:
- Container Networking: Securely connect and manage containerized applications.
- Bare-metal Integration: Extend network virtualization and security to bare-metal workloads.
- Cloud Provider Integration: Manage networks seamlessly across multi-cloud environments.
- Guest Introspection: Gain visibility and control over workloads running inside virtual machines.
How NSX-T Data Center works and Architecture?
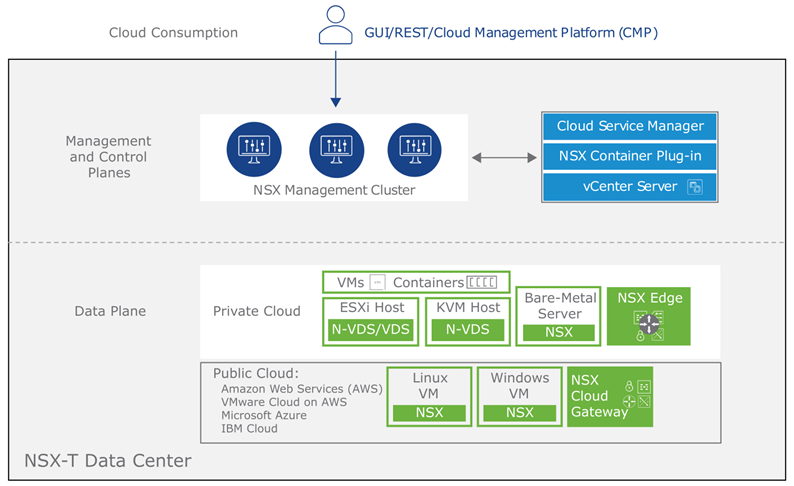
VMware NSX operates through a multi-layered architecture designed for scalability, performance, and centralized management of virtual networks and security. Here’s a breakdown of its key components and how they interact:
Components:
- NSX Manager: Centralized management platform for configuration, policy definition, and analytics.
- Transport Nodes: Distributed nodes deployed on hypervisors (ESXi, KVM) for data plane processing and enforcement.
- Logical Switches: Represent virtual network segments within the overlay network.
- Logical Routers: Connect different logical networks and provide routing services.
- Edge Gateways: Provide services like firewalling, NAT, VPN, and load balancing at the network edge.
- NSX Service Insertion Manager (optional): Manages and integrates third-party security and service insertion points.
Workflow and Interactions:
- Administrator defines network topology, policies, and security rules in NSX Manager.
- NSX Manager pushes configuration and policies to Transport Nodes.
- Transport Nodes create and manage logical switches and routers in the data plane.
- Workloads connect to logical switches for network access.
- Edge Gateways enforce security policies and provide network services at the perimeter.
- NSX Manager collects data from Transport Nodes and Edge Gateways for monitoring and analytics.
Architectural Benefits:
- Distributed architecture: Offers scalability and performance for large deployments.
- Modular design: Enables customization and integration with specific needs.
- API-driven communication: Facilitates automation and integration with external tools.
- Policy-based management: Simplifies configuration and ensures consistent enforcement.
Understanding VMware NSX’s architecture empowers you to:
- Effectively utilize features and manage your network security efficiently.
- Troubleshoot issues and identify root causes faster.
- Integrate with existing tools and workflows for a unified management experience.
Notes:
- The specific components and interactions may vary depending on your NSX version and deployment model (vSphere, multi-cloud).
- Consider using tools like NSX Cloud for managing networks across multiple clouds.
- Security practices like role-based access control are crucial for secure network management.
How to Install NSX-T Data Center it?
Installing VMware NSX-T Data Center (now simply known as VMware NSX) involves several steps and considerations depending on your chosen deployment method and environment. Here’s a breakdown of the common approaches:
1. vSphere Deployment:
- Pros: Most common and well-established option, suitable for on-premises vSphere environments.
- Cons: Requires vSphere infrastructure and licensing, more complex setup compared to cloud offerings.
- Options:
- Appliance-based: Deploy on pre-configured NSX appliances.
- Virtual Appliance: Deploy on your own vSphere cluster for more flexibility.
2. Multi-Cloud Deployment:
- Pros: Manages networks across various cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) and on-premises vSphere.
- Cons: Increased complexity in managing multi-cloud environments.
- Requires careful planning and configuration for seamless data flow and security.
- NSX Cloud: Cloud-based management platform for multi-cloud networking.
- NSX Advanced Networking Service (NSX-T Advanced): Offers deeper integration with specific cloud providers.
3. Bare-Metal Deployment:
- Pros: Extends NSX features to bare-metal workloads for consistent network management.
- Cons: Additional complexity in managing non-virtualized environments.
- Requires specific hardware and configuration considerations.
Additional Considerations:
- Choosing the right method: Consider your infrastructure type, technical expertise, budget, and security requirements.
- Pre-installation tasks: Prepare your infrastructure, licenses, and installation media.
- Post-installation configuration: Customize settings, integrate with other tools, and configure network elements.
These are just starting points. The specific installation process and chosen method will depend on your specific needs and environment.
Basic Tutorials of NSX-T Data Center: Getting Started

NSX-T Data Center is a software-defined networking platform for virtualized and cloud environments. These step-by-step tutorials will guide you through basic functionalities:
Prerequisites:
- Basic understanding of networking concepts and virtualization technologies.
- Access to an NSX-T Manager and vSphere environment.
- Administrative privileges for NSX-T and vSphere.
1. Installation:
- Deploy NSX-T Manager: Choose a deployment method (VMware vCenter Server, KVM, cloud marketplace) and follow the official installation guide: [<invalid URL removed>]
- Configure vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS): Create a VDS in vCenter Server for NSX-T communication.
2. Configure Uplink Profiles and Transport Nodes:
- Create Uplink Profile: Define physical uplink connections to external networks.
- Configure Transport Nodes: Associate physical network adapters with uplink profiles on ESXi hosts.
3. Deploy NSX-T Edge Nodes and Edge Clusters:
- Deploy Edge Nodes: Deploy virtual machines as NSX-T Edge nodes for routing and security services.
- Create Edge Cluster: Group Edge nodes for scalability and high availability.
4. Configure Gateways and Segments:
- Create Tier-0 Gateway: Connect your on-premises network to the NSX-T fabric.
- Create Tier-1 Gateways: Provide routing between tenant virtual networks.
- Create Segments: Define logical networks for tenant workloads.
5. Connect Workloads to Segments:
- Attach Segments to vNICs: Assign segments to virtual network interfaces (vNICs) of your workloads in vCenter Server.
- Verify Connectivity: Test communication between workloads within and across segments.
6. Basic Security Policies:
- Create Firewall Rules: Define rules to allow or deny traffic between segments based on IP addresses, protocols, and ports.
- Enable Security Groups: Assign security groups to workloads for granular security control.
Advanced Tutorials:
- Load Balancing: Implement load balancers for distributing traffic across multiple workloads.
- VPN Tunneling: Configure VPN tunnels for secure communication between remote networks.
- Service Insertion: Integrate security and other services into your network fabric.
- Multi-Tenancy: Create isolated network environments for multiple tenants.
Tips:
- Use the NSX-T Quick Start Guide for a streamlined initial setup: [<invalid URL removed>]
- Leverage the NSX-T Hands-on Labs for interactive learning: [<invalid URL removed>]
Note:
- These tutorials provide a basic introduction to NSX-T Data Center.
- Choose features and configurations that align with your specific network requirements and security needs.
- Thoroughly test and validate your configurations before deploying them in production.
By following these tutorials and exploring the resources provided, you can gain a solid foundation for using NSX-T Data Center to manage and secure your virtualized network infrastructure.
- Mutual of Omaha: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- AES: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- Amphenol: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024

