What is Oracle?

Oracle Corporation is a multinational computer technology corporation that provides a wide range of hardware and software products and services. It is best known for its flagship product, the Oracle Database, which is a widely used relational database management system (RDBMS). Oracle’s offerings extend beyond databases to include cloud services, enterprise software, middleware, and various other technologies.
What is top use cases of Oracle?
Top Use Cases of Oracle:
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS):
- Description: Oracle Database is one of the world’s leading relational database management systems. It is utilized for storing, managing, and retrieving structured data efficiently. Many organizations use Oracle Database for critical business applications and data-driven operations.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):
- Description: Oracle offers ERP solutions that integrate various business processes, such as finance, human resources, supply chain, and procurement. Organizations use Oracle ERP to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and have a unified view of their enterprise data.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Description: Oracle provides CRM solutions that help businesses manage customer interactions, sales, marketing, and customer support. Oracle CRM enables organizations to enhance customer satisfaction, increase sales, and build lasting customer relationships.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM):
- Description: Oracle SCM solutions assist organizations in optimizing their supply chain processes. This includes inventory management, order fulfillment, logistics, and demand planning. Oracle SCM helps improve supply chain visibility and responsiveness.
- Human Capital Management (HCM):
- Description: Oracle HCM solutions focus on managing human resources, talent acquisition, workforce development, and employee performance. Organizations leverage Oracle HCM to enhance HR processes and optimize workforce management.
- Cloud Infrastructure Services:
- Description: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provides a suite of cloud services, including computing, storage, networking, and various other infrastructure services. Businesses use OCI for building and deploying applications in the cloud.
- Data Warehousing:
- Description: Oracle offers data warehousing solutions that enable organizations to store, analyze, and manage large volumes of data. Oracle’s data warehousing solutions support business intelligence and analytics initiatives.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics:
- Description: Oracle provides BI and analytics tools that allow organizations to derive insights from their data. This includes tools for reporting, data visualization, and advanced analytics to support data-driven decision-making.
- Middleware and Integration:
- Description: Oracle Middleware products facilitate integration between different applications and systems. This includes technologies for application development, integration, and business process management.
- Java Development:
- Description: Oracle is the steward of the Java programming language and platform. Java is widely used for developing enterprise applications, web applications, and mobile applications.
- Financial Management:
- Description: Oracle Financial Management solutions help organizations manage financial processes, including accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. This is crucial for financial control and compliance.
- Healthcare Information Systems:
- Description: Oracle provides healthcare information systems to support healthcare providers in managing patient data, electronic health records (EHR), and healthcare workflows.
These use cases represent a subset of Oracle’s extensive portfolio. Oracle’s technologies are employed across various industries, including finance, healthcare, retail, telecommunications, government, and more. The company’s solutions cater to the diverse needs of businesses and organizations, helping them manage data, streamline processes, and drive innovation.
What are feature of Oracle?
Features of Oracle:
- Relational Database Management System (RDBMS):
- Description: Oracle is renowned for its powerful RDBMS, providing features such as ACID compliance, data integrity, and high-performance query optimization.
- Scalability:
- Description: Oracle databases are designed to scale vertically and horizontally to handle increasing data volumes and user loads. This scalability is critical for large enterprises and applications with growing data needs.
- Security:
- Description: Oracle emphasizes robust security features, including data encryption, access controls, and auditing. It provides a secure environment for sensitive and critical business data.
- High Availability:
- Description: Oracle offers features like Real Application Clusters (RAC) and Data Guard for high availability and disaster recovery. These technologies ensure that databases remain accessible and reliable even in the face of hardware failures or other disruptions.
- Performance Tuning:
- Description: Oracle Database includes tools and features for performance tuning, optimization, and monitoring. Database administrators can analyze and enhance the performance of SQL queries and database operations.
- In-Memory Database:
- Description: Oracle Database supports in-memory processing, allowing users to store and query data in memory for faster analytics and reporting.
- Multitenant Architecture:
- Description: Oracle’s multitenant architecture enables the efficient management of multiple databases as containers within a single instance. This reduces overhead and simplifies administration.
- Cloud Integration:
- Description: Oracle provides cloud-based services, including Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), for deploying, managing, and scaling applications in the cloud.
- Data Warehousing:
- Description: Oracle Database supports features specifically tailored for data warehousing, including parallel processing and advanced analytics. This makes it suitable for business intelligence and decision support systems.
- Middleware and Integration:
- Description: Oracle Middleware products facilitate integration between different applications and systems. This includes technologies for application development, integration, and business process management.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):
- Description: Oracle’s ERP solutions offer comprehensive tools for managing various business processes, from finance and procurement to human resources and supply chain.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Description: Oracle CRM solutions help organizations manage customer interactions, sales, marketing, and customer support. These tools supply to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Java Development:
- Description: Oracle is the steward of the Java programming language and platform. Java is widely used for developing enterprise applications, web applications, and mobile applications.
- Cloud Infrastructure Services:
- Description: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provides a suite of cloud services, including computing, storage, networking, and various other infrastructure services. Businesses use OCI for building and deploying applications in the cloud.
What is the workflow of Oracle?
Workflow of Oracle:
The workflow of Oracle can vary based on the specific use case and product, but in a general sense, the workflow for an Oracle Database might include the following steps:
- Requirement Analysis:
- Action: Understand the data management and processing requirements of the organization or application.
- Activity: Engage with stakeholders to determine data structures, relationships, and performance expectations.
- Database Design:
- Action: Design the database schema and define tables, relationships, and constraints.
- Activity: Use Oracle SQL and tools to create a logical and physical design for the database.
- Implementation:
- Action: Implement the designed database structure and populate it with initial data.
- Activity: Use SQL statements or graphical tools to create tables, indexes, and other database objects.
- Application Integration:
- Action: Integrate the Oracle Database with applications and systems.
- Activity: Develop application code that interacts with the Oracle Database using SQL or programming interfaces.
- Security Configuration:
- Action: Configure security settings to protect the database from unauthorized access.
- Activity: Set up user accounts, roles, and permissions to control access to data and database operations.
- Performance Tuning:
- Action: Monitor and optimize the performance of the Oracle Database.
- Activity: Use Oracle’s performance tuning tools to analyze and enhance the execution of SQL queries and database operations.
- Backup and Recovery Planning:
- Action: Establish a backup and recovery strategy to protect against data loss and system failures.
- Activity: Implement regular backups and test recovery procedures to ensure data integrity and availability.
- High Availability and Scaling:
- Action: Implement high-availability solutions to ensure continuous access to the database.
- Activity: Configure features like Real Application Clusters (RAC) or Data Guard for fault tolerance and scalability.
- Monitoring and Maintenance:
- Action: Continuously monitor the database for performance issues and potential problems.
- Activity: Perform routine maintenance tasks, such as optimizing storage, updating statistics, and applying patches.
- Cloud Deployment (Optional):
- Action: Deploy the Oracle Database in the cloud if utilizing Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
- Activity: Use Oracle Cloud services to provision and manage database instances in a cloud environment.
- Upgrade and Migration (As Needed):
- Action: Plan and execute database upgrades or migrations to newer versions.
- Activity: Follow Oracle’s guidelines and tools to upgrade the database software and migrate data as necessary.
The workflow involves collaboration between database administrators, developers, and other stakeholders to ensure the effective design, implementation, and maintenance of the Oracle Database to meet the organization’s requirements.
How Oracle Works & Architecture?
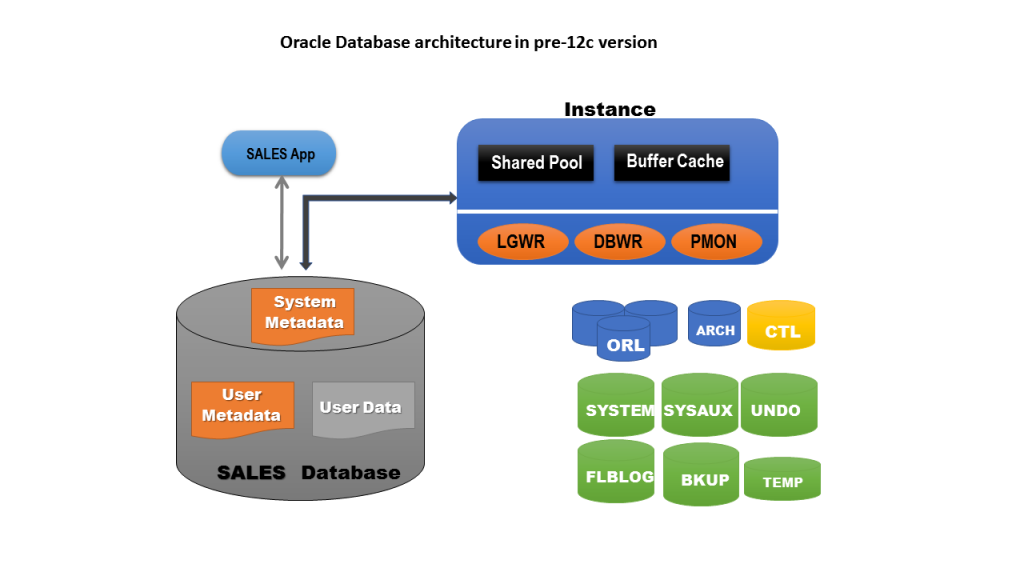
Oracle is a comprehensive suite of software products that include database management systems (DBMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and other applications. Following is a breakdown of how Oracle works and its architecture:
1. Core Functionality:
- Database Management: The heart of Oracle is its DBMS, which stores and manages data efficiently and reliably. It offers features like:
- ACID compliance for data integrity
- Scalability to handle large datasets
- High availability and disaster recovery
- Security features to protect sensitive data
- Enterprise Applications: Oracle provides a range of enterprise applications built upon its database platform. These include:
- ERP systems for managing financials, supply chain, and other business processes
- CRM systems for managing customer relationships and sales pipelines
- Business intelligence (BI) tools for analyzing data and making informed decisions
2. Architecture:
- Client-Server: Oracle typically operates in a client-server architecture, where:
- The database server stores and manages the data.
- Client applications on user machines interact with the database through a network connection.
- Multi-Tier Architecture: Oracle applications often follow a multi-tier architecture, which separates the application into distinct layers:
- Presentation layer: User interface for interacting with the application.
- Business logic layer: Carries the core functionality of the application.
- Data access layer: Handles communication with the database.
- Objects and Schemas: Oracle data is organized into objects like tables, views, and procedures. These objects are grouped into logical units called schemas.
3. Key Technologies:
- SQL: Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to interact with the Oracle database and retrieve or modify data.
- PL/SQL: Procedural Language/SQL is an extension of SQL that allows writing stored procedures and functions within the database.
- Java: Oracle applications often rely heavily on Java for the application logic and user interface.
4. Benefits of Oracle:
- Scalability and Performance: Oracle can handle large datasets and complex workloads efficiently.
- Reliability and Security: Oracle provides robust features for data integrity, disaster recovery, and security.
- Comprehensive Suite of Applications: Oracle offers a wide range of applications to address various business needs.
- Integration and Interoperability: Oracle products can integrate with other systems and applications.
Understanding how Oracle works and its architecture is crucial for using its products effectively. By exploring the core functionality, architecture, and key technologies, you can gain a solid foundation to utilize Oracle for various business needs.
How to Install and Configure Oracle?
Installing and Configuring Oracle Database
Installing and configuring Oracle Database can vary depending on the specific version you are using and your chosen platform (Windows, Linux, etc.). Following is a general overview of the process:
1. System Requirements:
- Ensure your system meets the minimum hardware and software requirements for the desired Oracle version.
2. Download Installation Files:
- Download the Oracle Database software from the official website:
- Select your desired platform and version.
- Accept the license agreement and download the files.
3. Install Oracle Database:
- Run the downloaded installer and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Choose the installation type (typical, custom, etc.).
- Specify the installation location, database name, and other configuration details.
- Complete the installation process and create an initial administrative user (SYS).
4. Configure Oracle Net Listener:
- The Oracle Net Listener manages network connections to the database.
- Configure the listener to accept connections on appropriate ports.
- Ensure firewall rules allow access to the listener ports.
5. Create a Database:
- Use the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) to create a database.
- Specify database storage locations, memory allocation, and other settings.
- Start the database instance once created.
6. Configure Database Users and Roles:
- Create additional database users and assign them roles with appropriate permissions.
- Use SQL*Plus or other tools to manage user accounts and access privileges.
7. Additional Configuration:
- Depending on your specific needs, you may need to perform additional configuration tasks:
- Configure network settings for remote access.
- Set up backup and recovery procedures.
- Install and configure additional software (e.g., Oracle Enterprise Manager).
Some additional tips for installing and configuring Oracle Database:
- Download and install the latest patches and updates for your Oracle version.
- Refer to the official Oracle documentation for detailed instructions and troubleshooting steps.
- Consider seeking assistance from a qualified Oracle database administrator for complex installations or configurations.
- Back up your database regularly to ensure data integrity.
Remember, the specific steps and configuration options may differ based on your chosen version and environment. It’s recommended to consult the official documentation and seek help from experienced users or professionals if needed.
Fundamental Tutorials of Oracle: Getting started Step by Step

Following is a breakdown of basic tutorials to get you started with Oracle:
1. Getting Started:
- Download and install Oracle Database: Follow the official documentation for your specific version and platform.
- Configure the Oracle Net Listener: Enable network connections to the database.
- Create a test database: Use the Oracle Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA).
- Connect to the database: Use SQL*Plus or other tools like Oracle SQL Developer.
2. SQL Basics:
- Learn basic SQL commands:
SELECT: Retrieve data from tables.INSERT: Add new data to tables.UPDATE: Modify existing data in tables.DELETE: Remove data from tables.WHERE: Filter data based on conditions.ORDER BY: Sort data based on specific columns.
- Practice using SQL commands:
- Execute queries on your test database.
- Experiment with different clauses and functions.
- Refer to the SQL*Plus documentation for detailed information on each command.
3. Creating and Managing Database Objects:
- Tables: Create tables to store your data, defining columns and data types.
- Views: Generate virtual tables based on existing data for specific purposes.
- Indexes: Refine query performance by generating indexes on frequently used columns.
- Constraints: Define rules for data integrity and consistency.
- Procedures and Functions: Implement custom logic using PL/SQL within the database.
4. User Management:
- Create database users: Assign appropriate roles and permissions.
- Manage user privileges: Grant or revoke access to specific database objects and operations.
- Implement security measures: Utilize passwords, encryption, and access controls.
5. Backup and Recovery:
- Create regular backups of your database: Ensure data protection in case of failures or accidents.
- Learn about different recovery options:
- Point-in-time recovery.
- Standby databases.
- Data Guard.
- Implement a disaster recovery plan: Ensure business continuity in case of major disruptions.
Important Tips:
- Start with the basics and gradually progress to more advanced topics.
- Practice regularly with the available resources and tutorials.
- Join online communities and forums to link with other users and experts.
- Consider attending Oracle training courses for a deeper understanding.
- Refer to the official documentation for complete information and troubleshooting steps.
Remember, mastering Oracle takes time and dedication. By consistently working through these basic tutorials, practicing with SQL, and utilizing available resources, you can gain a solid foundation for working with Oracle Database.
- Mutual of Omaha: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- AES: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024
- Amphenol: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 15, 2024

