What is QRadar?

IBM QRadar is a security information and event management (SIEM) solution designed to help organizations detect, investigate, and respond to security threats and incidents. It provides comprehensive security monitoring, analysis, and incident management capabilities.
QRadar’s capabilities make it a comprehensive SIEM solution suitable for organizations looking to enhance their cybersecurity posture, detect threats, and respond effectively to security incidents. It is particularly valuable in complex and dynamic security environments where real-time threat detection and response are critical.
Top 10 use cases of QRadar:
Here are the top 10 use cases of QRadar:
- Threat Detection and Alerting: QRadar continuously monitors network and system activity, analyzing logs and events in real-time to detect suspicious or malicious behavior. It generates alerts and notifications when potential threats are identified.
- Incident Investigation: Security teams can use QRadar to investigate security incidents by analyzing historical log and event data, identifying the root cause of incidents, and determining the extent of the compromise.
- Forensic Analysis: QRadar provides tools for performing forensic analysis on security incidents, helping organizations understand how an attack occurred and what data may have been compromised.
- Security Event Correlation: QRadar correlates data from various sources to identify complex attack patterns and advanced threats. It helps in connecting the dots between seemingly unrelated events.
- Vulnerability Management: QRadar integrates with vulnerability assessment tools to prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities based on their potential impact on the organization’s security posture.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): QRadar can analyze user and entity behavior to detect anomalies and potentially malicious activities. This is crucial for identifying insider threats and compromised accounts.
- Compliance and Reporting: QRadar helps organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements by providing predefined compliance reports and automated reporting capabilities.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: QRadar integrates with threat intelligence feeds and sources to provide up-to-date information about emerging threats and indicators of compromise (IOCs).
- Insider Threat Detection: QRadar assists in identifying insider threats by monitoring user activity and behavior to detect unusual or suspicious actions.
- Cloud Security Monitoring: Organizations can use QRadar to extend their security monitoring to cloud environments by integrating with cloud platforms and services to analyze log and event data.
- Network Traffic Analysis: QRadar provides network traffic analysis capabilities to monitor and analyze network activity, identify unauthorized access, and detect anomalies.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) Integration: QRadar can integrate with EDR solutions to enhance endpoint security by correlating endpoint data with network and system events.
- Security Orchestration and Automation: QRadar supports security orchestration and automation by integrating with workflow and automation tools to streamline incident response processes.
- Advanced Analytics: QRadar offers advanced analytics capabilities, such as machine learning and behavioral analytics, to detect threats that may evade traditional signature-based detection methods.
- IoT Security: As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows, QRadar can be used to monitor and secure IoT devices and networks by analyzing their activity and behavior.
What are the feature of QRadar?
IBM QRadar is a robust security information and event management (SIEM) solution with a wide range of features designed to help organizations monitor, detect, investigate, and respond to security threats and incidents. Below are some key features of QRadar, along with an overview of how it works and its typical architecture:
Key Features of QRadar:
- Log and Event Data Collection: QRadar can collect and normalize log and event data from a wide variety of sources, including network devices, servers, endpoints, applications, and cloud services.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: It provides real-time analysis of incoming logs and events, using predefined and custom rules to detect suspicious or malicious activities.
- Event Correlation: QRadar correlates data from multiple sources to identify complex attack patterns and prioritize security incidents based on their potential impact.
- Alerting and Notifications: The system generates alerts and notifications when security threats or policy violations are detected, allowing security teams to respond promptly.
- Incident Investigation: QRadar offers tools for incident investigation, enabling security analysts to explore and analyze historical log and event data to understand the scope and impact of security incidents.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): It can profile user and entity behavior to identify deviations from normal patterns and detect insider threats or compromised accounts.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: QRadar integrates with external threat intelligence feeds and sources to enrich data with contextual information about emerging threats and indicators of compromise (IOCs).
- Vulnerability Management Integration: It integrates with vulnerability scanning tools to prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities based on their risk level and potential impact.
- Compliance Management: QRadar helps organizations meet compliance requirements by providing predefined compliance reports and automating compliance monitoring.
- Security Orchestration and Automation: It supports security orchestration and automation by enabling the creation of custom workflows and automated response actions.
- Custom Dashboards and Reports: QRadar allows users to create custom dashboards and reports to visualize and present security data in a way that meets their specific needs.
- Multi-Tenancy: It offers multi-tenancy capabilities, allowing organizations to manage and monitor security data for different business units or customers from a single platform.
How QRadar works and Architecture?
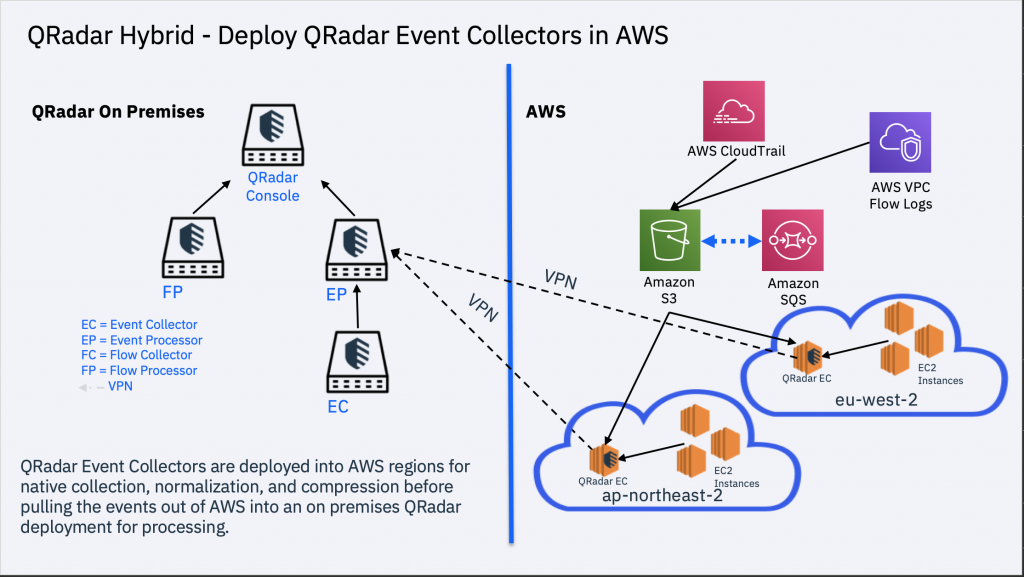
- Data Collection: QRadar collects log and event data from various sources, including network devices, servers, endpoints, applications, and cloud services.
- Normalization and Parsing: The collected data is normalized and parsed to ensure it is in a consistent format and can be analyzed effectively.
- Real-Time Analysis: QRadar analyzes incoming data in real-time using predefined and custom rules to detect security threats and anomalies.
- Correlation Engine: The system’s correlation engine correlates data from multiple sources to identify patterns and prioritize incidents based on risk.
- Alerting and Notifications: When a potential security incident is detected, QRadar generates alerts and notifications for security analysts to investigate.
- Incident Investigation: Security analysts can use QRadar’s tools to investigate incidents, analyze historical data, and determine the root cause of security events.
QRadar Architecture:
QRadar’s architecture is typically composed of the following components:
- Event Collectors: These agents collect log and event data from various sources and forward it to the QRadar Console or Event Processor.
- Event Processors: Event processors parse, normalize, and analyze incoming data. They perform event correlation and generate alerts.
- QRadar Console: The console provides the user interface for managing and monitoring security events. It allows security analysts to investigate incidents and configure rules and reports.
- Flow Processors: Flow processors analyze network flow data, providing insights into network traffic and behavior.
- Data Storage: QRadar stores normalized data and indexed data for historical analysis and reporting.
- Custom Rules and Offenses: Custom rules can be defined to meet specific security requirements, and offenses are generated when rule conditions are met.
- Reference Data: QRadar uses reference data, such as threat intelligence feeds and vulnerability data, to enrich and contextualize security events.
- External Integrations: QRadar can integrate with external systems, such as ticketing systems, SIEM solutions, and threat intelligence feeds, to enhance its capabilities.
QRadar’s distributed architecture is designed for scalability and high availability, allowing organizations to handle large volumes of data and ensure continuous monitoring and detection of security threats. It provides a comprehensive platform for security operations and incident response.
How to Install QRadar?
To install QRadar, you will need the following:
- A QRadar appliance or a QRadar virtual appliance
- A QRadar license
- A network connection
- A web browser
To install QRadar on a QRadar appliance:
- Connect the QRadar appliance to a network and power it on.
- Wait for the QRadar appliance to boot up.
- Open a web browser and navigate to the following URL:
https://<QRadar appliance IP address>:8443- Enter the QRadar appliance username and password. The default password and username are
passwordandadmin. - Apply the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
To install QRadar on a QRadar virtual appliance:
- Deploy the QRadar virtual appliance to a hypervisor.
- Power on the QRadar virtual appliance.
- Wait for the QRadar virtual appliance to boot up.
- Open a web browser and proceed to the below URL:
https://<QRadar virtual appliance IP address>:8443- Enter the QRadar virtual appliance username and password. The default password and username are
passwordandadmin. - Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
Once the installation process is complete, you will need to configure QRadar.
Here are some additional tips for installing QRadar:
- Make sure that your network has the required bandwidth and latency to support QRadar.
- If you are installing QRadar in a production environment, it is recommended to follow the QRadar hardening guide to secure your installation.
- You can also find a variety of tutorials and other resources on the IBM QRadar website.
QRadar is a powerful security information and event management (SIEM) platform that can help you to improve your security posture by helping you to collect, analyze, and respond to security threats. By following the steps above, you can learn how to install QRadar and start using it to improve your security posture.
Basic Tutorials of QRadar: Getting Started
Let’s have a look at a basic tutorial on how to use QRadar to improve your security posture:
1. Getting Started
- Install QRadar. You can install QRadar on a QRadar appliance or a QRadar virtual appliance.
- Configure QRadar. Once QRadar is installed, you need to configure it to collect, analyze, and respond to security threats.
- Learn the basics of QRadar. QRadar is a complex platform, but there are some basic concepts that you need to understand in order to use it effectively.
- Review the QRadar documentation. The QRadar documentation provides a comprehensive overview of the platform and its features.
- Take advantage of QRadar training resources. IBM offers a variety of QRadar training resources, including online courses, in-person training, and self-paced training.
2. Collecting Data
- Identify the data sources that you want to collect. QRadar can collect data from a variety of sources, including SIEMs, firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
- Configure QRadar to collect the data. QRadar provides a variety of tools and wizards to help you configure data collection.
- Verify that QRadar is collecting the data that you need. You can use the QRadar Console to verify that QRadar is collecting the data that you need.
3. Analyzing Data
- Create rules to analyze the data. QRadar provides a variety of rules that you can use to analyze the data that you collect. You can also create your own rules.
- Use the QRadar Console to analyze the data. The QRadar Console provides a variety of tools and widgets to help you analyze the data.
- Generate reports to summarize the data. QRadar provides a variety of reports that you can use to summarize the data. You can also create your own reports.
4. Responding to Threats
- Use the QRadar Console to identify and investigate threats. The QRadar Console provides a variety of tools and widgets to help you identify and investigate threats.
- Use the QRadar Console to respond to threats. The QRadar Console provides a variety of tools and wizards to help you respond to threats.
- Work with other security tools to respond to threats. QRadar can be integrated with other security tools to help you respond to threats more effectively.
Some additional tips for using QRadar to improve your security posture:
- Use the QRadar community to get help and support from other QRadar users.
- Take advantage of IBM QRadar support. IBM offers a variety of QRadar support options, including paid support and community support.
- Regularly review your QRadar configuration and rules. It is important to regularly review your QRadar configuration and rules to ensure that they are still meeting your needs.
QRadar is a powerful SIEM platform that can help you to improve your security posture by helping you to collect, analyze, and respond to security threats. By following the steps above, you can learn how to use QRadar to improve your security posture.
- Why Can’t I Make Create A New Folder on External Drive on Mac – Solved - April 28, 2024
- Tips on How to Become a DevOps Engineer - April 28, 2024
- Computer Programming Education Requirements – What You Need to Know - April 28, 2024

