What is SecOps Response?

SecOps Response, short for Security Operations Response, is a term that refers to the process and practices within an organization that are focused on responding to and mitigating security incidents. The goal of SecOps Response is to promptly identify, investigate, and address security threats and incidents to minimize potential damage and protect sensitive data and resources.
SecOps Response is a critical component of an organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy, ensuring that security incidents are addressed promptly and effectively to minimize business disruptions and protect sensitive data. It involves collaboration between security teams, IT teams, and other stakeholders to achieve a coordinated and proactive response to security threats.
Top 10 use cases of SecOps Response:
Here are the top 10 use cases of SecOps Response:
- Incident Triage: Quickly assess incoming security alerts and incidents to determine their severity and potential impact on the organization.
- Security Incident Investigation: Conduct thorough investigations into security incidents to gather evidence, understand the attack vector, and identify the scope of the incident.
- Malware and Ransomware Response: Detect and respond to malware infections and ransomware attacks, isolating affected systems and mitigating data loss.
- Data Breach Response: Take swift action to contain and mitigate data breaches, preserving evidence and complying with data breach notification requirements.
- Phishing and Social Engineering Response: Investigate and respond to phishing attacks and social engineering attempts, including identifying compromised accounts and educating users.
- Insider Threat Detection and Response: Monitor for and respond to insider threats, which may involve compromised employees or contractors with malicious intent.
- Vulnerability Management: Respond to vulnerabilities by identifying affected systems, prioritizing patching or remediation, and verifying fixes.
- Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Mitigation: Mitigate the impact of DoS and DDoS attacks by implementing traffic filtering and rerouting.
- Security Policy Violations: Respond to security policy violations, such as unauthorized access or configuration changes, by taking corrective actions and documenting incidents.
- Incident Recovery and Remediation: Develop and execute incident recovery plans to restore affected systems and services to normal operation and prevent future incidents.
- Incident Reporting and Documentation: Maintain detailed records of security incidents, actions taken, and lessons learned for compliance and post-incident analysis.
- Continuous Improvement: Review incident response processes and procedures regularly, making updates to enhance the organization’s security posture and readiness.
What are the feature of SecOps Response?
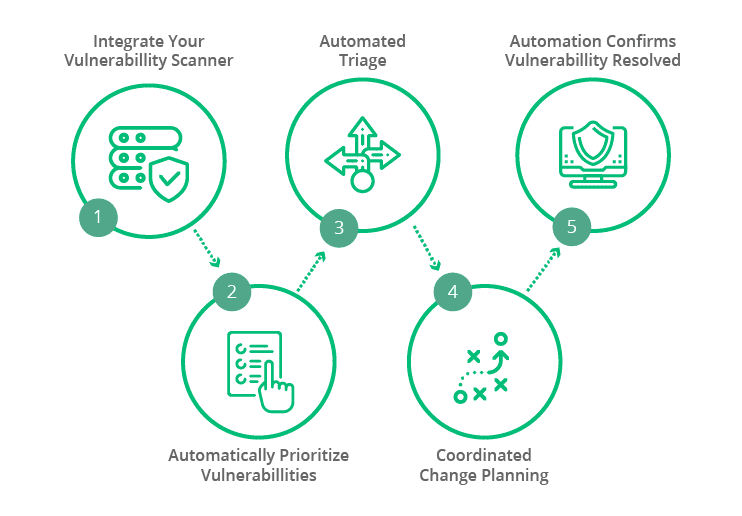
SecOps Response refers to the process and practices within an organization for responding to and mitigating security incidents. While it is a concept and approach rather than a specific technology or platform, it involves a set of key features and principles:
Key Features of SecOps Response:
- Incident Detection: The ability to identify and detect security incidents through various means, including security tools, monitoring, and alerting systems.
- Alerting and Notification: The capability to generate alerts and notifications when security incidents or anomalies are detected, ensuring that the response process is initiated promptly.
- Incident Triage: A process for quickly assessing the nature and severity of detected incidents to prioritize response efforts effectively.
- Incident Investigation: Tools and procedures for conducting thorough investigations into security incidents, including gathering evidence, identifying the scope, and understanding the attack vectors.
- Response Orchestration: The ability to orchestrate and automate incident response workflows, ensuring that predefined actions and processes are executed efficiently.
- Security Tools Integration: Integration with various security tools and technologies, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management), EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response), firewalls, and antivirus solutions, to facilitate a coordinated response.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: Integration with threat intelligence feeds and sources to provide context and information about known threats and attack indicators.
- Data and Asset Inventory: A comprehensive inventory of data assets and IT resources to help identify potential attack targets and assess the impact of incidents.
- Incident Reporting and Documentation: The ability to generate incident reports and maintain detailed records of incident response activities, actions taken, and lessons learned.
- Access Control and Privilege Management: Controls and procedures for managing access privileges and ensuring that only authorized personnel can respond to incidents.
- Communication and Collaboration: Tools and processes for facilitating communication and collaboration among security teams, IT teams, and other stakeholders during incident response.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular review and refinement of incident response processes, procedures, and policies to enhance the organization’s ability to respond effectively to evolving threats.
How SecOps Response works and Architecture?
SecOps Response involves a series of steps and workflows, including:
- Detection: Security incidents are detected through various means, including automated security monitoring, alerting systems, or user reports.
- Triage: Incidents are triaged to assess their severity and impact, helping prioritize response efforts. This step often involves quick investigations and initial assessments.
- Notification: The incident response team is notified, and predefined response plans are initiated.
- Investigation: A deeper investigation into the incident is conducted, involving forensic analysis, data collection, and the identification of attack vectors and indicators.
- Containment and Eradication: Actions are taken to contain the incident and prevent further damage or unauthorized access. The goal is to eradicate the threat.
- Recovery: Systems and services affected by the incident are restored to normal operation. Recovery procedures may include patching vulnerabilities or restoring data from backups.
- Documentation: Detailed records of the incident and response activities are maintained for compliance, reporting, and post-incident analysis.
- Communication: Stakeholders are kept informed throughout the incident response process, including internal teams, executive leadership, and external parties if necessary.
SecOps Response architecture can vary widely depending on the organization’s size, complexity, and technology stack. However, some common elements include:
- Incident Detection Systems: Security tools, SIEM solutions, and monitoring systems that detect and alert on security incidents.
- Incident Response Platform: A central platform or system for managing and orchestrating incident response activities, including incident tracking, playbooks, and collaboration tools.
- Security Tools Integration: Integration with various security tools and technologies to automate response actions.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Integration with threat intelligence feeds and services to provide context and data on known threats.
- Data and Asset Inventory: A repository or database that maintains an inventory of data assets and IT resources.
- Communication and Collaboration Tools: Communication channels and collaboration platforms to facilitate communication among response teams and stakeholders.
- Documentation and Reporting: Tools and systems for incident reporting, documentation, and record-keeping.
- Access Control and Privilege Management: Mechanisms to control access to incident response systems and ensure that authorized personnel are involved.
The architecture should be designed to facilitate a coordinated and efficient response to security incidents, emphasizing automation, integration, and collaboration among response teams and stakeholders. It should also support continuous improvement through post-incident analysis and lessons learned.
How to Install SecOps Response?
To install SecOps Response, you must first have a ServiceNow instance. Once you have a ServiceNow instance, you can follow these steps to install SecOps Response:
- Navigate to the ServiceNow Store.
- Search for “SecOps Response” and click on the application.
- Press on the “Get It Now” button.
- Review the application details and click on the “Install” button.
- Implement the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Once SecOps Response is installed, you can access it by navigating to Security Operations > SecOps Response.
Some additional tips for installing SecOps Response:
- Make sure that you have the required permissions to install applications in ServiceNow.
- If you are installing SecOps Response in a production environment, it is recommended to create a test environment first to test the installation process.
- You can also contact ServiceNow support for assistance with installing SecOps Response.
Basic Tutorials of SecOps Response: Getting Started

The following steps are the Basic Tutorials of SecOps Response:
1. Create a new incident
- Navigate to Security Operations > SecOps Response > Incident.
- Click on the New button.
- Enter the incident details, such as the name, description, and type.
- Click on the Submit button.
2. Assign the incident to a team
- Open the incident record.
- Click on the Team tab.
- Select the team that you want to assign the incident to.
- Click on the Submit button.
3. Investigate the incident
The incident team will investigate the incident to determine the root cause and impact. This may involve collecting logs, interviewing witnesses, and analyzing the affected systems.
4. Remediate the incident
Once the incident team has identified the root cause of the incident, they will take steps to remediate it. This may involve patching vulnerabilities, removing malware, or restoring systems from backups.
5. Recover from the incident
Once the incident has been remediated, the incident team will help the organization to recover from the incident and restore normal operations. This may involve communicating with affected stakeholders, implementing additional security measures, and restoring business processes.
Additional tips for using SecOps Response:
- Use incident playbooks to provide step-by-step instructions on how to respond to common security incidents.
- Use collaboration tools to help teams work together to respond to incidents.
- Use reporting and analytics tools to track your incident response performance and identify areas for improvement.
Example use case:
An organization is alerted to a potential data breach on one of its servers. The organization’s security team uses SecOps Response to create a new incident and assign it to the incident response team. The incident response team investigates the incident and determines that the server has been compromised and that customer data has been stolen. The incident response team takes steps to remediate the incident, such as isolating the compromised server and patching the vulnerability that was exploited. The incident response team also works with the organization to notify affected customers and implement additional security measures to prevent future data breaches.
SecOps Response is a powerful tool that can help organizations to improve their incident response process. By following the steps in this tutorial, you can learn how to use SecOps Response to create, manage, and respond to security incidents.
- Why Can’t I Make Create A New Folder on External Drive on Mac – Solved - April 28, 2024
- Tips on How to Become a DevOps Engineer - April 28, 2024
- Computer Programming Education Requirements – What You Need to Know - April 28, 2024

