What is Splunk?

Splunk is a powerful data analytics and visualization platform designed for log management, monitoring, and real-time data analysis. It is widely used across industries to collect, index, and correlate machine-generated data from various sources.
Splunk’s versatility and extensibility make it a valuable tool for a wide range of use cases, from IT operations and security to business analytics and compliance. Its ability to ingest, analyze, and visualize data from diverse sources makes it a popular choice for organizations looking to gain insights from their machine-generated data.
Top 10 use cases of Splunk:
Here are the top 10 use cases of Splunk:
- Log Management: Splunk is often used for centralized log management, allowing organizations to collect, store, and analyze logs from various systems, applications, and devices. This helps in troubleshooting, compliance, and security analysis.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Splunk can function as a SIEM solution by ingesting and correlating security-related data from multiple sources. It helps in detecting and responding to security incidents and threats.
- Incident Response: Splunk assists organizations in incident response by providing real-time visibility into security incidents, enabling security teams to investigate and mitigate threats quickly.
- IT Operations Monitoring: Splunk is used for monitoring the performance and health of IT systems and infrastructure. It can provide insights into network traffic, server performance, application availability, and more.
- Application Monitoring: Organizations can use Splunk to monitor the performance and availability of their applications. It helps in identifying and resolving issues that may impact user experience.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Splunk can be used for UEBA, which involves monitoring user and entity behavior to detect anomalous or suspicious activity that may indicate insider threats or compromised accounts.
- Business Analytics: Splunk can be used for business intelligence and analytics by analyzing data to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency.
- Compliance and Audit: Splunk helps organizations meet compliance requirements by providing the ability to collect and retain logs and generate reports required for audits. It’s commonly used for compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- DevOps and Application Development: Splunk can be integrated into the DevOps process to provide real-time visibility into application and infrastructure performance. It helps in identifying issues early in the development and testing stages.
- IoT Data Analysis: Organizations can use Splunk to analyze data generated by Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, and connected systems. This helps in extracting valuable insights and improving operational efficiency.
- Fraud Detection: Splunk can be used to detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction data, user behavior, and other relevant information to identify anomalies and patterns associated with fraud.
- Customer Support and Service Insights: Splunk can be employed to analyze customer support and service data, helping organizations improve customer satisfaction by identifying issues, trends, and areas for improvement.
- Network and Infrastructure Security: Splunk plays a critical role in monitoring network traffic and infrastructure security. It helps in detecting and responding to security breaches, unusual network behavior, and potential threats.
What are the feature of Splunk?
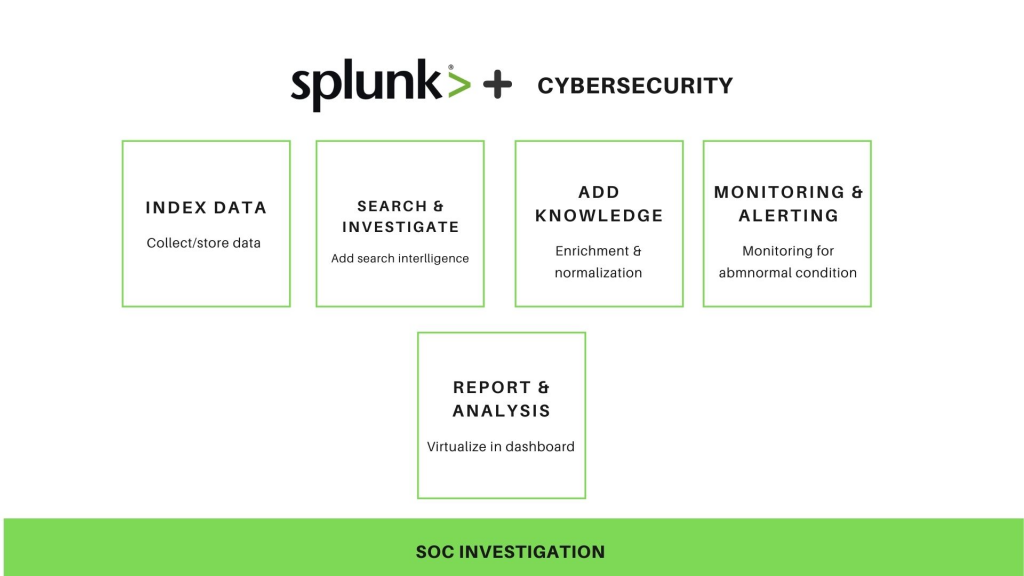
Splunk is a versatile data analytics and visualization platform designed for collecting, indexing, and analyzing machine-generated data from various sources. It offers a wide range of features to help organizations make sense of their data. Here are some key features of Splunk:
Key Features of Splunk:
- Data Collection: Splunk can collect data from a multitude of sources, including log files, metrics, network traffic, databases, cloud services, and IoT devices.
- Real-time Data Processing: It provides real-time data ingestion and processing capabilities, allowing organizations to monitor and analyze data as it streams in.
- Search and Query Language: Splunk uses a powerful search and query language (SPL) that enables users to search and analyze data using simple, intuitive commands.
- Data Indexing: Splunk indexes ingested data, making it searchable and enabling fast, efficient querying and analysis.
- Dashboards and Visualizations: It offers a range of tools for creating customizable dashboards and visualizations to help users gain insights from their data.
- Alerting and Monitoring: Splunk allows users to set up alerts based on specific criteria, helping organizations proactively detect and respond to issues and anomalies.
- Machine Learning and AI: Splunk integrates with machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities to provide predictive analytics and anomaly detection.
- Data Security: Splunk provides security features to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, including access controls and encryption.
- Data Integration: It supports data integration with various data sources and systems through connectors, APIs, and add-ons.
- Data Retention and Archiving: Organizations can define data retention policies and archiving strategies to manage and store data efficiently.
How Splunk works and Architecture?
Splunk works by ingesting, indexing, and analyzing machine-generated data. Here’s an overview of how Splunk typically operates:
- Data Ingestion: Data is ingested into Splunk from various sources, such as log files, APIs, event streams, and databases. Splunk provides multiple mechanisms for data collection, including forwarders, connectors, and cloud integrations.
- Data Parsing: Splunk parses ingested data, extracting fields and creating a structured representation of the data. Users can define custom data parsing configurations.
- Data Indexing: The parsed data is indexed, making it searchable and enabling fast and efficient querying. Splunk uses a distributed indexing mechanism to handle large data volumes.
- Search and Query: Users can perform searches and queries on the indexed data using the Splunk Search Processing Language (SPL). Searches can be simple keyword searches or complex queries involving filters, aggregations, and statistical operations.
- Visualization: Splunk provides visualization tools to create charts, graphs, and dashboards that help users understand and present their data effectively.
- Alerting: Users can configure alerts based on specific conditions and thresholds. When an alert condition is met, Splunk can trigger notifications and automated actions.
- Machine Learning and AI: Splunk supports machine learning and AI models for tasks like predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and clustering to uncover insights and patterns in the data.
- Reporting and Export: Users can generate reports and export data for further analysis or sharing with stakeholders.
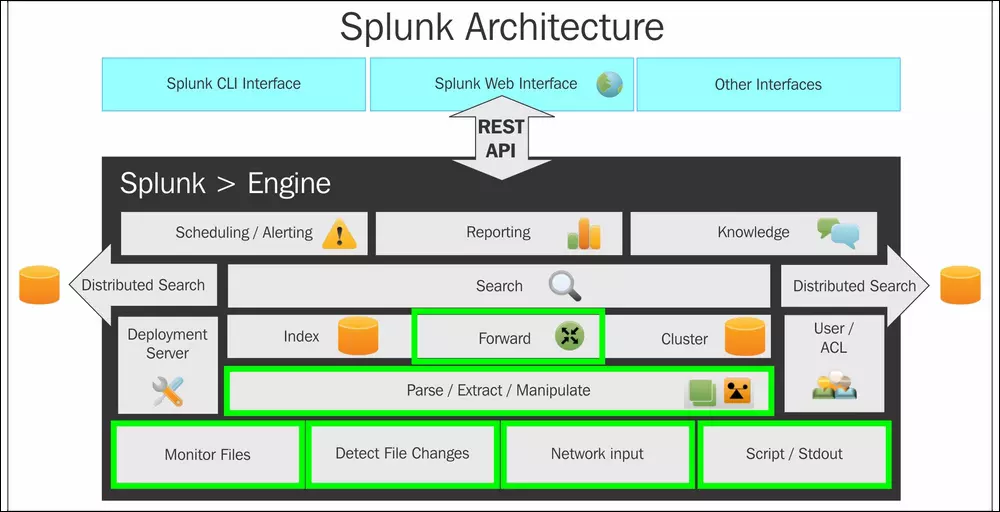
Splunk Architecture:
Splunk has a distributed architecture that consists of several key components:
- Data Sources: These are the systems, devices, and applications that generate machine data. Data sources send data to Splunk for processing.
- Data Forwarders: Forwarders are lightweight agents installed on data source systems to collect and forward data to Splunk indexers.
- Indexers: Indexers receive and index incoming data. They store the indexed data and make it available for searching and analysis.
- Search Heads: Search heads are the user interfaces for interacting with Splunk. Users submit queries and create dashboards using search heads.
- Indexer Clusters: To handle large data volumes and provide high availability, Splunk indexers are often deployed in clusters.
- Search Head Clusters: Search heads can also be deployed in clusters for scalability and fault tolerance.
- Deployment Server: The deployment server manages configurations and updates for forwarders, making it easier to manage a large number of forwarders.
- Universal Forwarders: These are lightweight forwarders used for data collection on remote systems. They send data to indexers or other forwarders.
- Heavy Forwarders: Heavy forwarders are used when additional processing or transformation of data is needed before indexing.
Splunk’s architecture is designed to be highly scalable, allowing organizations to expand their Splunk deployments to handle growing data volumes. It also offers redundancy and fault tolerance to ensure data availability and reliability. The distributed nature of Splunk allows for flexibility in deployment configurations to meet specific requirements.
How to Install Splunk?
To install Splunk on Linux, apply these steps:
- Download the Splunk installer from the Splunk website.
- Make sure that you have the required system requirements.
- Extract the Splunk installer to a directory on your server.
- Open a terminal window and navigate to the directory where you extracted the Splunk installer.
- Run the following command to start the Splunk installation process:
./splunk start --accept-license- Follow the on-screen instructions to accomplish the installation process.
Once the installation is complete, you will need to create a Splunk admin user and password. To do this, run the below command:
./splunk add user admin --password passwordYou can now log in to the Splunk web UI at the following URL:
https://<your_server_IP_address>:8000The default username and password for the Splunk web UI are admin and password.
Some additional tips for installing Splunk:
- If you are installing Splunk in a production environment, it is recommended to follow the Splunk hardening guide to secure your installation.
- You can also find a variety of tutorials and other resources on the Splunk website.
Splunk is a powerful logging and analytics platform that can help you to improve your security posture by helping you to collect, analyze, and visualize your security data. By following the steps above, you can learn how to install Splunk on Linux and start using it to improve your security posture.
Basic Tutorials of Splunk: Getting Started

The following steps are the basic tutorial on how to use Splunk to improve your security posture:
- Getting Started
- Create a Splunk account.
- Login to the Splunk web UI.
- Review the Getting Started documentation.
- Adding Data
- Add your security data to Splunk.
- Splunk can import data from a variety of sources, including SIEMs, firewalls, and security tools.
- Creating Dashboards
- Create dashboards in Splunk to visualize your security data.
- Dashboards can help you to identify trends and patterns in your security data.
- Creating Reports
- Create reports in Splunk to track your security posture and to identify areas for improvement.
- Splunk provides a variety of reports, including incident reports, threat intelligence reports, and compliance reports.
- Searching Data
- Use the Splunk search language to search your security data for specific events or patterns.
- Splunk’s search language is a powerful tool that can help you to investigate security incidents and identify threats.
- Alerts
- Create alerts in Splunk to notify you when certain events or patterns are detected in your security data.
- Alerts can help you to respond to security incidents quickly and effectively.
Some additional tips for using Splunk:
- Use the Splunk community to get help and support from other Splunk users.
- Take advantage of Splunk’s training resources to learn more about the platform and how to use it effectively.
- Contact Splunk support if you have any questions or problems.
Splunk is a powerful logging and analytics platform that can help you to improve your security posture by helping you to collect, analyze, and visualize your security data. By following the steps above, you can learn how to use Splunk to create dashboards, reports, searches, and alerts to improve your security posture.
- Degree Pursuit: Navigating the Path to Educational Excellence - July 4, 2024
- Why Is Studying English Important in a Business Environment? - July 4, 2024
- Top 10 Data Science Skills You Need in 2024 - July 3, 2024

