History & Origin of Splunk SIEM
The Splunk platform removes the barriers between data and action, empowering observability, IT and security teams to ensure their organizations are secure, resilient and innovative.
Founded in 2003, Splunk is a global company — with over 7,500 employees, 850 patents and availability in 21 regions around the world — and offers an open, extensible data platform that supports shared data across any environment so that all teams in an organization can get end-to-end visibility, with context, for every interaction and business process. Build a strong data foundation with Splunk.
Use this command to view your search history in the current application. This search history is presented as a set of events or as a table.
Syntax
| history [events=<bool>]
Required arguments
None.
Optional arguments
- events
- Syntax: events=<bool>
- Description: When you specify
events=true, the search history is returned as events. This invokes the event-oriented UI which allows for convenient highlighting, or field-inspection. When you specifyevents=false, the search history is returned in a table format for more convenient aggregate viewing. - Default: false
Fields returned when events=false.
-
-
Output field Description _timeThe time that the search was started. api_etThe earliest time of the API call, which is the earliest time for which events were requested. api_ltThe latest time of the API call, which is the latest time for which events were requested. event_countIf the search retrieved or generated events, the count of events returned with the search. exec_timeThe execution time of the search in integer quantity of seconds into the Unix epoch. is_realtimeIndicates whether the search was real-time (1) or historical (0). result_countIf the search is a transforming search, the count of results for the search. scan_countThe number of events retrieved from a Splunk index at a low level. searchThe search string. search_etThe earliest time set for the search to run. search_ltThe latest time set for the search to run. sidThe search job ID. splunk_serverThe host name of the machine where the search was run. statusThe status of the search. total_run_timeThe total time it took to run the search in seconds.
-
What is Splunk SIEM

How Splunk SIEM works aka Splunk SIEM architecture?

Basically, SIEM architecture collects event data from organized systems such as installed devices, network protocol, storage protocols (Syslog) and streaming protocols.
SIEM software works by collecting log and event data produced from applications, devices, networks, infrastructure, and systems to draw analysis and provide a holistic view of an organization’s information technology (IT).
SIEM solutions can reside either in on-premises or cloud environments. Analyzing all of the data in real-time, SIEM solutions use rules and statistical correlations to drive actional insight during forensic investigations. SIEM technology examines all data, sorting threat activity according to its risk level to help security teams identify malicious actors and mitigate cyberattacks quickly.
The Evolution of SIEM Software
SIEM solutions have been around for over 15 years, but today’s modern SIEMs have evolved from their original counterparts. Mark Nicolett and Amrit Williams established the term “SIEM” in a 2005 Gartner research report, Improve IT Security With Vulnerability Management. [1] These legacy SIEMs were a combination of integrated security methods into one management solution, including:
- Log management systems (LMS): Processes for simple collection and centralized storage of logs.
- Security information management (SIM): Tools for automated collection of log files for long-term storage, analysis, and reporting on log data.
- Security event management (SEM): Technology for real-time monitoring and correlating of systems and events with notification and console views.
As SIEM software transformed over time, the core components continue to provide value, but innovative technology within the competitive landscape paved the way for more comprehensive and advanced approaches to reducing risk in an organization. This led SIEM providers to eventually launch new features that have termed these enhanced products as “next-generation SIEM” solutions.

Use case of Splunk SIEM

What is a use case? A use case can be a mix of multiple technical rules within the SIEM tool, or can be a mix of actions from multiple rules, depending on the need. It converts business threats into SIEM technical rules, which then detect possible threats and send alerts to the SOC
- Basic Brute Force Detection.
- Basic Malware Outbreak.
- Basic Scanning.
- Endpoint Uncleaned Malware Detection.
- Multiple Infections on Host.
- Recurring Infections on Host.
- User Login with Local Credentials.
Feature and Advantage of using Splunk SIEM
- Data Ingestion. Splunk can ingest a variety of data formats like JSON, XML and unstructured machine data like web and application logs. …
- Data Indexing. The ingested data is indexed by Splunk for faster searching and querying on different conditions.
- Data Searching. …
- Using Alerts. …
- Dashboards. …
- Data Model.
- Reduce Time to Detect. Ingest machine data from multicloud and on-premises deployments for full visibility to quickly detect malicious threats in your environment.
- Streamline Investigations. …
- Faster Time to Value.

Making data accessible, usable, and valuable
IT business operations – Splunk provides real-time monitoring, event management and alerting, and visibility into the health of physical and virtual IT infrastructure. Splunk also provides monitoring of applications and business and IT services.
Best Alternative of Splunk SIEM
- IBM Security QRadar.
- LogRhythm NextGen SIEM Platform.
- AlienVault USM (from AT&T Cybersecurity)
- OSSIM (Open Source)
- Microsoft Sentinel.
- FortiSIEM.
- Sumo Logic.
- InsightIDR.
Best Resources, Tutorials and Guide for Splunk SIEM
Free Video Tutorials of Splunk SIEM
Interview Questions and Answer for Splunk SIEM
Interview Questions and Answers:-
1) Define Splunk
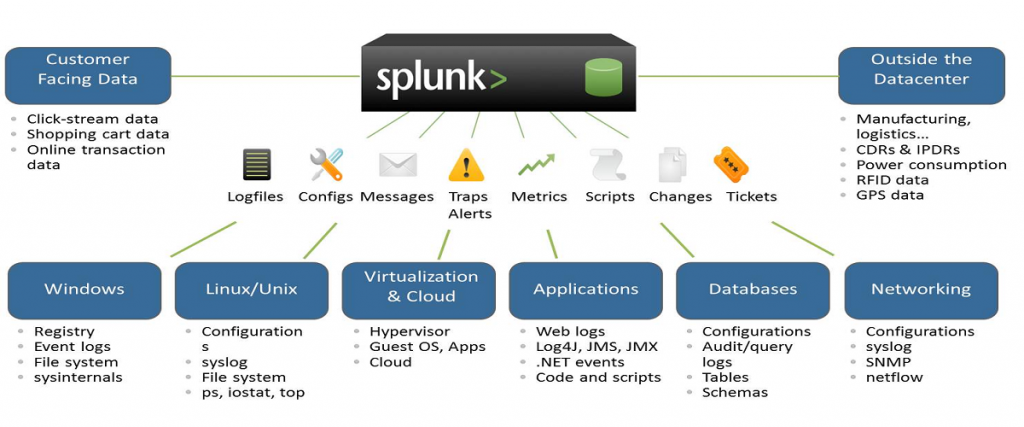
It is a software technology that is used for searching, visualizing, and monitoring machine-generated big data. It monitors and different types of log files and stores data in Indexers.
2) List out common ports used by Splunk.
Common ports used by Splunk are as follows:
- Web Port: 8000
- Management Port: 8089
- Network port: 514
- Index Replication Port: 8080
- Indexing Port: 9997
- KV store: 8191
3) Explain Splunk components
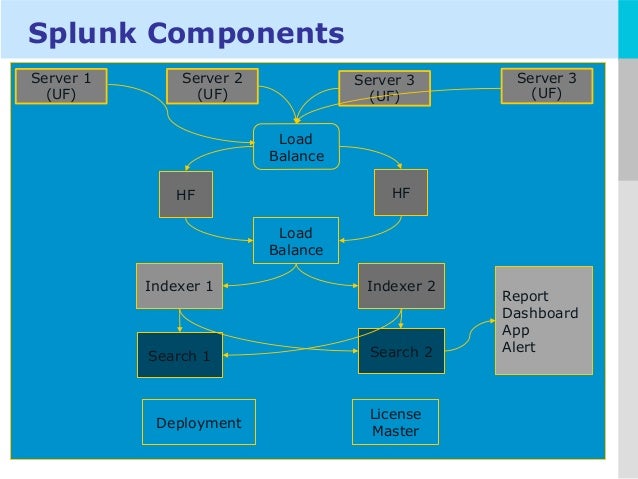
The fundamental components of Splunk are:
- Universal forward: It is a lightweight component which inserts data to Splunk forwarder.
- Heavy forward: It is a heavy component that allows you to filter the required data.
- Search head: This component is used to gain intelligence and perform reporting.
- License manager: The license is based on volume & usage. It allows you to use 50 GB per day. Splunk regular checks the licensing details.
- Load Balancer: In addition to the functionality of default Splunk loader, it also enables you to use your personalized load balancer.
4) What do you mean by Splunk indexer?
It is a component of Splunk Enterprise which creates and manages indexes. The primary functions of an indexer are 1) Indexing raw data into an index and 2) Search and manage Indexed data.
5) What are the disadvantages of using Splunk?
Some disadvantages of using Splunk tool are:
- Splunk can prove expensive for large data volumes.
- Dashboards are functional but not as effective as some other monitoring tools.
- Its learning curve is stiff, and you need Splunk training as it’s a multi-tier architecture. So, you need to spend lots of time to learn this tool.
- Searches are difficult to understand, especially regular expressions and search syntax.
6) What are the pros of getting data into a Splunk instance using forwarders?
The advantages of getting data into Splunk via forwarders are TCP connection, bandwidth throttling, and secure SSL connection for transferring crucial data from a forwarder to an indexer.
7) What is the importance of license master in Splunk?
License master in Splunk ensures that the right amount of data gets indexed. It ensures that the environment remains within the limits of the purchased volume as Splunk license depends on the data volume, which comes to the platform within a 24-hour window.
8) Name some important configuration files of Splunk
Commonly used Splunk configuration files are:
- Inputs file
- Transforms file
- Server file
- Indexes file
- Props file
9) Explain license violation in Splunk.
It is a warning error that occurs when you exceed the data limit. This warning error will persist for 14 days. In a commercial license, you may have 5 warnings within a 1-month rolling window before which your Indexer search results and reports stop triggering.
However, in a free version, license violation warning shows only 3 counts of warning.
10) What is the use of Splunk alert?
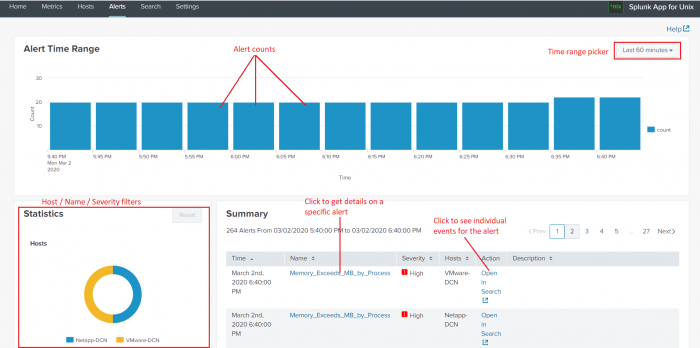
Alerts can be used when you have to monitor for and respond to specific events. For example, sending an email notification to the user when there are more than three failed login attempts in a 24-hour period.
11) Explain map-reduce algorithm
Map-reduce algorithm is a technique used by Splunk to increase data searching speed. It is inspired by two functional programming functions 1) reduce () 2) map().
Here map() function is associated with Mapper class and reduce() function is associated with a Reducer class.
12) Explain different types of data inputs in Splunk?
Following are different types of data inputs in Splunk:
- Using files and directories as input
- Configuring Network ports to receive inputs automatically
- Add windows inputs. These windows inputs are of four types: 1) active directory monitor, 2) printer monitor, 3) network monitor, and 4) registry inputs monitor.
13) How Splunk avoids duplicate log indexing?
Splunk allows you to keep track of indexed events in a fish buckets directory. It contains CRCs and seeks pointers for the files you are indexing, so Splunk can’t if it has read them already.
14) Explain pivot and data models.
Pivots are used to create the front views of your output and then choose the proper filter for a better view of this output. Both options are beneficial for the people from a semi-technical or non-technical background.
Data models are most commonly used for creating a hierarchical model of data. However, it can also be used when you have a large amount of unstructured data. It helps you make use of that information without using complicated search queries.
15) Explain search factor and replication factor?
Search factor determines the number of data maintained by the indexer cluster. It determines the number of searchable copies available in the bucket.
Replication factor determines the number of copies maintained by the cluster as well as the number of copies that each site maintains.
16) What is the use of lookup command?
Lookup command is generally used when you want to get some fields from an external file. It helps you to narrow the search results as it helps to reference fields in an external file that match fields in your event data.
17) Explain default fields for an event in Splunk
There are 5 default fields which are barcoded with every event into Splunk. They are: 1) host, 2) source, 3) source type, 4) index, and 5) timestamp.
18) How can you extract fields?
In order to extract fields from either sidebar, event lists or the settings menu using UI.
Another way to extract fields in Splunk is to write your regular expressions in a props configuration file.
19) What do you mean by summary index?
A summary index is a special index that stores that result calculated by Splunk. It is a fast and cheap way to run a query over a longer period of time.
20) How to prevent events from being indexed by Splunk?
You can prevent the event from being indexed by Splunk by excluding debug messages by putting them in the null queue. You have to keep the null queue in transforms.conf file at the forwarder level itself.
21) Define Splunk DB connect
It is a SQL database plugin which enables to import tables, rows, and columns from a database add the database. Splunk DB connect helps in providing reliable and scalable integration between databases and Splunk Enterprises.
22) Define Splunk buckets
It is the directory used by Splunk enterprise to store data and indexed files into the data. These index files contain various buckets managed by the age of the data.
23) What is the function of Alert Manager?
The alert manager adds workflow to Splunk. The purpose of alert manager o provides a common app with dashboards to search for alerts or events.
24) How can you troubleshoot Splunk performance issues?
Three ways to troubleshoot Splunk performance issue.
- See server performance issues.
- See for errors in splunkd.log.
- Install Splunk app and check for warnings and errors in the dashboard.
25) What is the difference between Index time and Search time?
Index time is a period when the data is consumed and the point when it is written to disk. Search time take place while the search is run as events are composed by the search.
26) How to reset the Splunk administrator password?
In order to reset the administrator password, perform the following steps:
- Login into the server on which Splunk is installed
- Rename the password file and then again start the Splunk.
- After this, you can sign into the server by using username either administrator or admin with a password changeme.
27) Name the command which is used to the “filtering results” category
The command which is used to the “filtering results” category is: “where,” “Sort,” “rex,” and “search.”
28) List out different types of Splunk licenses
The types of Splunk licenses are as follows:
- Free license
- Beta license
- Search heads license
- Cluster members license
- Forwarder license
- Enterprise license
29) List out the number of categories of the SPL commands.
The SPL commands are classified into five categories:
1) Filtering Results, 2) Sorting Results, 3) Filtering Grouping Results, 4) Adding Fields, and 5) Reporting Results.
30) What is eval command?
This command is used to calculate an expression. Eval command evaluates boolean expressions, string, and mathematical articulations. You can use multiple eval expressions in a single search using a comma.
Jobs & Salary Prospectus of Splunk SIEM skills
A SIEM analyst is responsible for the migration of rules, queries and filters that will collect security information and events of interest to production or active database of the SIEM infrastructure while ensuring continuous routine maintenance of security tools and SIEM infrastructure.
Best Certifications in Splunk SIEM
People that are Splunk certified make extremely good money from what ive seen. Companies are willing to pay top dollar for people that can navigate splunk full time for whatever their company needs just so they dont have to stop and waste time and money trying to learn Splunk themselves.
- Splunk Core Certified User.
- Splunk Core Certified Power User.
- Splunk Core Certified Advanced Power User.
- Splunk Cloud Certified Admin.
- Splunk Enterprise Certified Admin.
- Splunk Enterprise Certified Architect.
- Splunk Core Certified Consultant.
- Mastering Qualitative Research: The Role of Focus Groups in Data Collection - July 11, 2024
- What is robots ops? - July 10, 2024
- 5 Effective Online Learning Strategies for DevOps Professionals - July 4, 2024

