What is Symantec Endpoint Protection?

Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) is a comprehensive security software suite developed by Broadcom Inc. It protects laptops, desktops, and servers from various threats like malware, viruses, ransomware, spyware, and zero-day attacks.
Key Features:
- Anti-malware and Anti-virus: Detects and blocks known and unknown threats using multiple engines and behavior analysis.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): Monitors network traffic and blocks malicious activity before it reaches your device.
- Firewall: Controls inbound and outbound network traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
- Application Control: Whitelists and blacklists applications to prevent unauthorized software execution.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Monitors and restricts sensitive data from being stolen or leaked.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Provides real-time visibility into endpoint activity and enables rapid response to threats.
- Sandboxing: Isolates suspicious files and applications to prevent harm to your system.
- Patch Management: Automates software patching to keep your systems up-to-date and secure.
Top 10 use cases of Symantec Endpoint Protection?
Top 10 Use Cases for Symantec Endpoint Protection:
- Prevent Malware and Ransomware Attacks: Protects against a wide range of malware threats, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware, to safeguard your critical data and operations.
- Block Intrusions and Unauthorized Access: Monitors network traffic and blocks malicious activity before it can compromise your system, preventing data breaches and unauthorized access attempts.
- Strengthen Endpoint Security: Enhances endpoint security by controlling application execution, preventing unauthorized data loss, and ensuring endpoint visibility and threat detection.
- Simplify Patch Management: Automates software patching across your endpoint infrastructure, ensuring timely updates and closing security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Proactive Threat Hunting: Identifies hidden threats lurking within your network through advanced analytics and EDR capabilities, enabling preemptive action against potential attacks.
- Rapid Incident Response: Provides tools and insights to quickly respond to security incidents, minimizing damage and restoring normal operations.
- Protect Remote Workforces: Secures endpoints used by remote employees, regardless of their location or device, ensuring consistent protection without hindering productivity.
- Comply with Data Security Regulations: Helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by securing sensitive data and preventing unauthorized access and loss.
- Reduce Security Costs: Consolidates multiple security tools into a single platform, simplifying security management and potentially reducing overall security costs.
- Improve Security Posture: Provides a centralized view of your security posture, allowing you to identify vulnerabilities, track improvements, and make informed security decisions.
Overall, Symantec Endpoint Protection offers a comprehensive and feature-rich solution for organizations of all sizes seeking to protect their endpoints from diverse cyber threats. It can be a valuable tool for enhancing your overall security posture and mitigating the risks associated with modern cyberattacks.
What are the feature of Symantec Endpoint Protection?
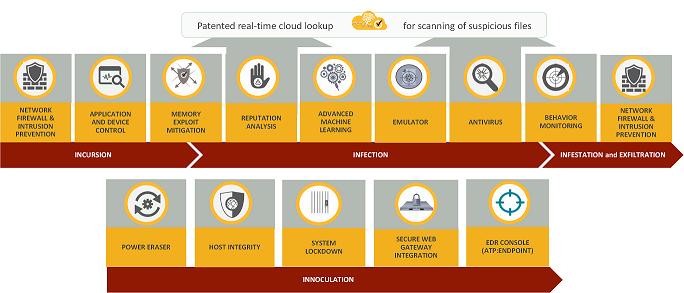
Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) boasts a rich suite of features designed to address diverse cybersecurity threats. Here’s a breakdown of some key highlights:
1. Multi-layered Malware Protection:
- Anti-virus & Anti-malware: Employs multiple antivirus engines and behavior analysis to detect and block known and unknown threats, including viruses, worms, Trojans, and ransomware.
- Machine Learning & AI: Leverages sophisticated machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious patterns and proactively address emerging threats.
- Application & Device Control: Granular control over application execution and device access to prevent unauthorized software and hardware from compromising your system.
- Memory Exploit Mitigation: Protects against zero-day attacks and memory-based vulnerabilities by hardening system memory against exploitation techniques.
2. Advanced Threat Detection and Response:
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Provides real-time visibility into endpoint activity and offers tools for investigating suspicious events, identifying threat indicators, and initiating rapid response actions.
- Network Threat Protection: Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) monitors network traffic and blocks malicious activity before it reaches your device, preventing data breaches and unauthorized access attempts.
- Deception Technology: Deploys honeypots and traps to lure attackers and gather valuable intelligence about their tactics and techniques, empowering proactive defense strategies.
3. Data Security and Compliance:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Monitors and restricts sensitive data from being stolen or leaked through various channels, such as email, USB drives, and cloud storage.
- Encryption: Provides data encryption capabilities to protect sensitive information at rest and in transit, ensuring confidentiality even if your systems are compromised.
- Compliance Management: Helps organizations comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by simplifying data security measures and demonstrating compliance efforts.
4. Additional Features:
- Patch Management: Automates software patching across your endpoints, ensuring timely updates and closing security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Cloud-based Management: Offers centralized management and visibility into your security posture from a cloud-based console, simplifying administration and providing scalability.
- Vulnerability Management: Identifies and prioritizes software vulnerabilities across your environment, allowing you to address critical vulnerabilities first and mitigate security risks.
- Sandboxing: Isolates suspicious files and applications to prevent harm to your system in a controlled environment, aiding in threat analysis and secure execution.
Overall, Symantec Endpoint Protection stands out for its comprehensive security features, AI-powered threat detection, and data security capabilities. It caters to organizations seeking robust protection against evolving cyber threats and simplifies compliance with data privacy regulations.
How Symantec Endpoint Protection works and Architecture?
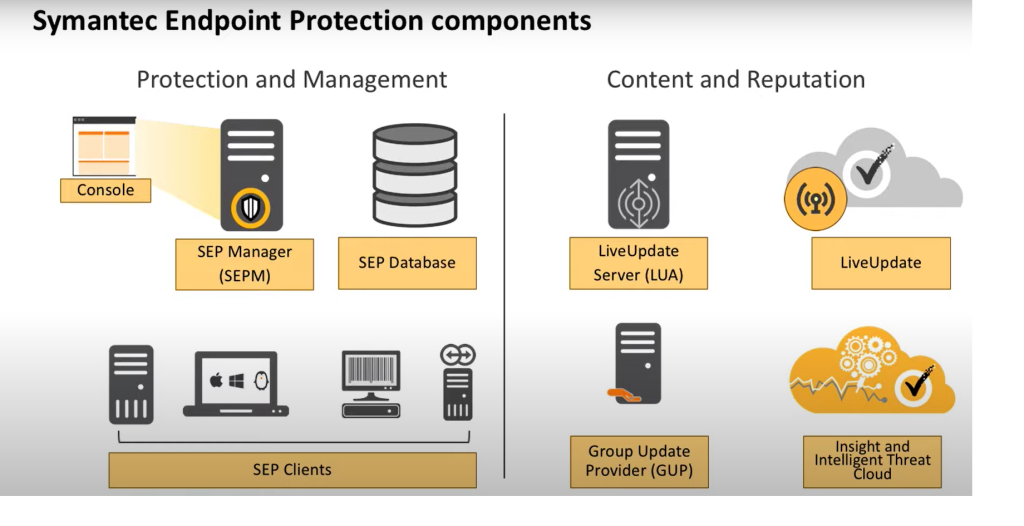
Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) operates through a sophisticated architecture designed to deliver multi-layered defense against cyber threats. Here’s a breakdown of its workings:
1. Data Collection and Ingestion:
- Client Agent: Installed on endpoints, it continuously monitors system activity, file changes, network traffic, and other relevant data.
- Symantec Management Center: Acts as a central hub for receiving and processing data from client agents across the network.
2. Threat Detection and Analysis:
- Multi-layered Engine: Employing antivirus signatures, behavior analysis, machine learning algorithms, and threat intelligence, SEP performs real-time analysis of the collected data to identify suspicious activity and potential threats.
- Advanced Techniques: Features like memory exploit mitigation, application whitelisting/blacklisting, and network intrusion prevention provide additional layers of protection beyond traditional antivirus scanning.
3. Threat Response and Remediation:
- Automatic Actions: SEP can automatically quarantine infected files, block malicious connections, roll back system changes, and even initiate targeted scans based on its analysis.
- Manual Response: Security teams can access detailed investigation tools to further analyze threats, determine the scope of the attack, and take informed response actions, such as isolating compromised devices or conducting forensic analysis.
4. Reporting and Visibility:
- Centralized Console: Provides a unified view of security events across the entire network, including threat detections, blocked attacks, system vulnerabilities, and compliance status reports.
- Customizable Dashboards: Security teams can tailor dashboards to prioritize specific metrics and insights relevant to their security posture and incident response needs.
5. Continuous Improvement:
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: SEP leverages a global network of Symantec Security Labs and researchers to gather threat intelligence on the latest malware, vulnerabilities, and attack tactics.
- Automatic Updates: SEP regularly receives updates for signatures, machine learning models, and threat intelligence, ensuring continuous improvement in its detection and response capabilities.
Key Architectural Components:
- Client Agent: The frontline soldier on each endpoint, collecting and transmitting data for analysis.
- Symantec Management Center: The central brains of the operation, receiving, processing, and analyzing data from all agents.
- Detection Engines: Multi-layered engines employing various techniques to identify threats.
- Response Mechanisms: Automated and manual tools for taking action against threats.
- Reporting and Visualization Tools: Providing insights into security posture and facilitating incident response.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: Continuously updating the platform’s knowledge of emerging threats.
Overall, Symantec Endpoint Protection’s architecture offers a multifaceted approach to cybersecurity, combining real-time data analysis, advanced threat detection techniques, automated response capabilities, and centralized visibility tools. This empowers organizations to proactively counter cyber threats and maintain a robust security posture.
How to Install Symantec Endpoint Protection it?
Installing Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) requires some preparation and specific steps depending on your chosen deployment method. Following is a general guide to get you started:
1. Prerequisites:
- Valid SEP license: Ensure you have a valid license and access to the Symantec Endpoint Protection Manager (SEPM) installation package.
- Administrator privileges: You’ll need administrative privileges on the target devices to install the client agent.
- System Requirements: Check the system requirements for the SEP version you’re installing to ensure compatibility with your devices.
2. Deployment Methods:
- Remote Push: The SEPM can push the client agent installation package to managed devices within the network. This is the recommended method for centralized deployment.
- Manual Installation: Download the appropriate client agent installer from the SEPM and manually run it on each device. This is suitable for smaller deployments or when remote push isn’t feasible.
3. Remote Push Installation:
- Open SEPM: Log in to the Symantec Endpoint Protection Manager console.
- Create/Configure Package:
- Go to Clients > Client Packages.
- Click New Package Deployment.
- If using an existing package, select it from the list. Otherwise, click Next to create a new package.
- Choose the client platform (Windows, macOS, Linux) and installation settings.
- Click Finish to create the package.
- Deploy Package:
- Select the desired client group(s) for deployment.
- Right-click and choose Push Client Packages.
- Select the previously created package and click Next.
- Configure advanced settings (optional) and click Finish.
4. Manual Installation:
- Download Agent Installer:
- Go to Clients > Client Management.
- Select the desired client platform (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Click Download Client Installer.
- Run Installer on Target Device:
- Transfer the downloaded installer file to the target device.
- Run the installer with administrator privileges.
- Use the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
5. Verify Installation:
- Open SEPM and navigate to Clients > Client Status.
- Ensure the installed client agent appears in the list with “Online” status.
- You can also check individual device security status on the SEPM console.
Basic Tutorials of Symantec Endpoint Protection: Getting Started

Symantec Endpoint Protection (SEP) provides a robust defense against cyber threats. Let’s explore some basic tutorials to get you started:
1. Installing SEP Client Agent:
Preparation:
- Valid SEP license and access to SEPM console
- Administrator privileges on target devices
- System meets SEP version requirements
Deployment Methods:
A. Remote Push (recommended):
- Open SEPM: Log in to the Symantec Endpoint Protection Manager console.
- Create/Configure Package:
- Go to Clients > Client Packages.
- Click New Package Deployment.
- Choose client platform (Windows, macOS, Linux), installation settings, and click Finish.
- Deploy Package:
- Select desired client group(s). Right-click, choose Push Client Packages.
- Select created package, click Next, and configure advanced settings if needed. Click Finish.
B. Manual Installation:
- Download Agent Installer:
- Go to Clients > Client Management.
- Select desired platform, click Download Client Installer.
- Run Installer on Target Device:
- Transfer downloaded file to target device.
- Run installer with administrator privileges and follow on-screen instructions.
Verification:
- Open SEPM, go to Clients > Client Status.
- Ensure installed client agent appears with “Online” status.
- Check individual device security status on the SEPM console.
2. Exploring the SEPM Console:
- Navigation bar: Provides access to key functionalities like Clients, Policies, Reports, Settings.
- Dashboard: Displays security metrics, active detections, device health, and vulnerability trends.
- Widgets: Drag and drop to personalize your layout, offering deeper insights into threats, devices, investigations, and reports.
3. Basic Threat Hunting:
- Go to Investigate: Click the Investigate tab in the navigation bar.
- Build a Search: Enter keywords, indicators of compromise (IOCs), or filter by specific parameters like device name, process name, or source IP address.
- Explore Results: Analyze event details, timelines, and associated files for further investigation.
- Take Action: If suspicious activity is found, isolate the endpoint, block a file, or initiate an investigation workflow.
4. Managing Endpoint Policies:
- Go to Policies: Click the Policies tab in the navigation bar.
- Browse existing policies or create a new one: Click New Policy.
- Configure settings: Define antivirus scanning, application control, device control, and response actions.
- Assign policies to groups: Select target endpoint groups for each policy application.
These are basic tutorials. As you progress, explore SEP’s advanced features and security tools to maximize your endpoint protection.
- PPG Industries: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 3, 2024
- Fiserv: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 3, 2024
- Estee Lauder: Selection and Interview process, Questions/Answers - April 3, 2024

