What is Tenable?

Tenable is a cybersecurity company known for its vulnerability management and threat detection solutions. Tenable’s products and services help organizations identify and manage security vulnerabilities, assess compliance, and detect threats to improve their overall cybersecurity posture.
Top 10 use cases of Tenable:
Here are the top 10 use cases of Tenable:
- Vulnerability Management: Tenable’s flagship product, Tenable.sc (formerly SecurityCenter), and Tenable.io provide vulnerability assessment and management capabilities. They help organizations identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities across their IT infrastructure.
- Threat Detection and Response: Tenable offers threat detection and response solutions, including Tenable.io with Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) and Tenable.ot (formerly Indegy). These solutions help organizations monitor network traffic and detect suspicious or malicious activities.
- Asset Inventory: Tenable helps organizations maintain a comprehensive inventory of assets, including devices, servers, applications, and cloud resources. This visibility is essential for effective security management.
- Patch Management: Tenable solutions help organizations identify missing patches and prioritize their deployment to address critical vulnerabilities and enhance security.
- Compliance Assessment: Tenable enables organizations to assess their compliance with various security standards and regulations, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, by conducting compliance scans and generating compliance reports.
- Container Security: Tenable provides container security solutions to assess and secure containerized applications and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, helping organizations identify and address vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
- Web Application Scanning: Tenable’s solutions can scan web applications for vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and security misconfigurations.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Tenable helps organizations secure their cloud environments by identifying misconfigurations, compliance violations, and security risks in cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- IoT Security: Tenable helps organizations assess the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and identify vulnerabilities that may exist in IoT implementations.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Tenable’s solutions, such as Tenable.sc and Tenable.ot, can monitor user and entity behavior to detect insider threats, compromised accounts, and unusual activities.
These are some of the primary use cases for Tenable’s solutions. Tenable aims to provide organizations with a comprehensive cybersecurity platform that assists in managing vulnerabilities, responding to threats, and improving their overall security posture.
What are the feature of Tenable?
Here are some common features and an overview of how Tenable works:
Key Features of Tenable Solutions:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Tenable’s solutions, including Tenable.sc (formerly SecurityCenter) and Tenable.io, provide automated vulnerability scanning to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and security weaknesses in networks, systems, and applications.
- Threat Detection: Tenable helps organizations detect and respond to security threats through solutions like Tenable.io with Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) and Tenable.ot (formerly Indegy). These tools monitor network traffic and behavior for suspicious activities and potential breaches.
- Asset Inventory: Tenable solutions help organizations maintain a comprehensive asset inventory, offering visibility into devices, servers, applications, and cloud resources.
- Patch Management: Tenable assists in patch management by identifying missing patches and prioritizing their deployment to address critical vulnerabilities.
- Compliance Assessment: Tenable enables organizations to assess their compliance with various security standards and regulations by conducting compliance scans and generating reports.
- Container Security: Tenable’s container security solutions assess and secure containerized applications and orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, identifying vulnerabilities and misconfigurations.
- Web Application Scanning: Tenable can scan web applications for vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and security misconfigurations.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Tenable helps organizations secure their cloud environments by identifying misconfigurations, compliance violations, and security risks in cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- IoT Security: Tenable assesses the security of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and helps identify vulnerabilities in IoT implementations.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Tenable’s solutions monitor user and entity behavior to detect insider threats, compromised accounts, and unusual activities.
How Tenable works and Architecture?
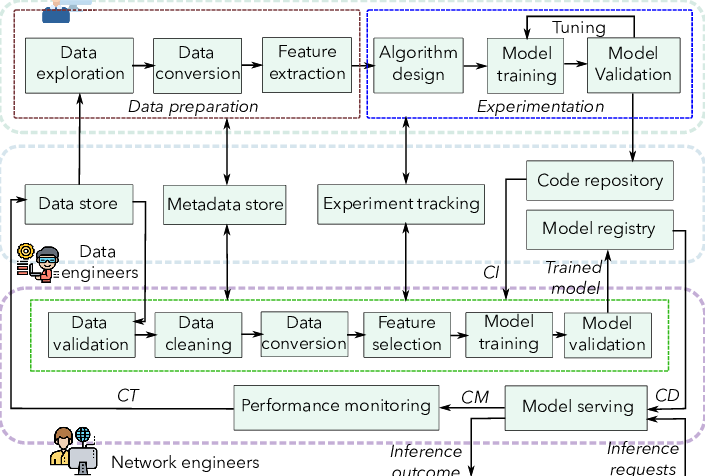
Tenable’s solutions operate as part of an organization’s cybersecurity infrastructure. Here’s a simplified overview of how Tenable works:
- Deployment: Organizations subscribe to Tenable’s cloud-based services (Tenable.io) or deploy on-premises solutions (Tenable.sc) based on their requirements.
- Asset Discovery: Tenable solutions begin by discovering and profiling assets in an organization’s environment, including devices, servers, applications, and cloud resources.
- Scanning and Monitoring: Automated scans are conducted to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and potential threats. Tenable’s continuous monitoring provides ongoing visibility into security posture.
- Data Analysis and Threat Detection: Tenable’s analytics engines analyze data collected from scans, logs, and network traffic to detect security threats and vulnerabilities. Behavioral analytics and machine learning are applied to identify anomalies.
- Incident Response: When security incidents are detected, Tenable’s solutions, along with incident response processes, help organizations investigate, respond to, and mitigate the incidents.
Tenable Architecture:
Tenable’s architecture may vary depending on the specific product or service being used. However, here are some common components:
- Tenable.sc or Tenable.io: These are central components of Tenable’s architecture. Tenable.sc is an on-premises solution, while Tenable.io is cloud-based. They serve as the core platforms for vulnerability management, threat detection, and compliance assessment.
- Scanners: Scanners are responsible for conducting vulnerability scans. In the case of on-premises solutions, organizations deploy scanners within their network. Cloud-based solutions may use virtual scanners or agents for scanning.
- Agents: Tenable agents are lightweight software components that can be installed on individual hosts to collect data and facilitate real-time monitoring and scanning.
- Data Storage and Analysis: Tenable’s solutions store and analyze data collected from scans, logs, and network traffic. Advanced analytics engines are applied for threat detection and risk assessment.
- Integration Points: Tenable’s solutions are designed to integrate with other security tools, SIEM platforms, and third-party services to create a comprehensive security ecosystem.
Tenable’s architecture is designed to be flexible and adaptable to the evolving needs of organizations, making it suitable for businesses of various sizes and industries. It provides the foundation for managing vulnerabilities, responding to threats, and enhancing overall cybersecurity posture.
How to Install Tenable?
To install Tenable Nessus, you will need to download the installation package from the Tenable Downloads site. The package you download will be specific to your operating system and processor.
Once you have downloaded the installation package, follow the steps below to install Tenable Nessus:
On Linux:
- Open a terminal window.
- Proceed to the directory where you downloaded the installation package.
- Run the following command to install Tenable Nessus:
sudo sh nessus-<version>-<platform>.runReplace <version> with the version of Tenable Nessus you are installing, and replace <platform> with your operating system platform.
On Windows:
- Double-click on the Tenable Nessus installation package to open the InstallShield Wizard.
- Implement the live-screen instructions to complete the installation.
On macOS:
- Open a Terminal window.
- Proceed to the directory where you downloaded the installation package.
- Run the following command to install Tenable Nessus:
sudo sh nessus-<version>-<platform>.pkgReplace <version> with the version of Tenable Nessus you are installing, and replace <platform> with your operating system platform.
Once Tenable Nessus is installed, you will need to create an account and activate your license. You can do this by opening Tenable Nessus in a web browser and following the on-screen instructions.
Additional notes:
- If you are installing Tenable Nessus on a remote server, you will need to enable SSH port forwarding on the client machine.
- If you are installing Tenable Nessus on a Linux server, you will need to install the following packages:
sudo yum install -y epel-release
sudo yum install -y openssl-devel python-devel sqlite-devel- If you are installing Tenable Nessus on a macOS server, you will need to install the following packages:
brew install openssl
brew install python3
brew install sqlite3To install Tenable Security Center:
- Download the Tenable Security Center installation RPM file from the Tenable Security Center downloads page.
- If necessary, depending on the operating system of the host, move the installation RPM file onto the host.
- From the command line, run the following command to install Tenable Security Center:
sudo rpm -Uvh tenable-sc-<version>.rpmReplace <version> with the version of Tenable Security Center you are installing.
Once Tenable Security Center is installed, you will need to open a web browser and navigate to https://localhost:8443. You will then be prompted to create an account and activate your license.
Basic Tutorials of Tenable: Getting Started

The following are the Stepwise basic tutorials of Tenable:
1. Install Tenable Nessus and Tenable Security Center.
Tenable Nessus is a vulnerability scanner that identifies vulnerabilities in your network assets. Tenable Security Center is a central management console for Tenable Nessus and other Tenable products.
2. Create an account and activate your license.
Once you have installed Tenable Nessus and Tenable Security Center, you will need to create an account and activate your license. You can do this from the Tenable Security Center web interface.
3. Add your assets to Tenable Security Center.
Tenable Security Center needs to know about your network assets in order to scan them for vulnerabilities. You can add your assets manually or by importing a list of assets from a file.
4. Create a scan policy.
A scan policy specifies the types of scans to perform, the frequency of scans, and the assets to scan. You can create scan policies for different types of assets or for different networks.
5. Run a scan.
Once you have created a scan policy, you can run a scan to identify vulnerabilities on your assets. You can run scans manually or on a schedule.
6. Review the scan results.
Once a scan has completed, you can review the results in the Tenable Security Center web interface. The scan results will show you which assets have vulnerabilities and what the vulnerabilities are.
7. Remediate vulnerabilities.
Once you have identified vulnerabilities, you need to take steps to remediate them. This may involve patching software, updating firmware, or implementing security controls.
Simple example of how to use Tenable to identify and remediate vulnerabilities:
- Create a scan policy that scans all of your assets for vulnerabilities.
- Run the scan policy.
- Review the scan results.
- Recognize any vulnerabilities that require to be remediated.
- Prioritize the remediation of vulnerabilities based on their severity and risk.
- Take steps to remediate the vulnerabilities.
- Run the scan policy again to verify that the vulnerabilities have been remediated.
You can repeat this process on a regular basis to ensure that your assets are protected from known vulnerabilities.
Additional tips for using Tenable:
- Use Tenable Security Center to centrally manage your Tenable Nessus scanners and other Tenable products.
- Use Tenable Security Center to create and manage user accounts and permissions.
- Use Tenable Security Center to create and manage asset groups.
- Use Tenable Security Center to generate reports on your vulnerability management progress and trends.
- Use Tenable Security Center to integrate with other security tools, such as SIEM systems and ticketing systems.
- Why Can’t I Make Create A New Folder on External Drive on Mac – Solved - April 28, 2024
- Tips on How to Become a DevOps Engineer - April 28, 2024
- Computer Programming Education Requirements – What You Need to Know - April 28, 2024

