
Short description about:

Elasticsearch is a distributed, free and open search and analytics engine for all types of data, including textual, numerical, geospatial, structured, and unstructured. Elasticsearch is built on Apache Lucene and was first released in 2010 by Elasticsearch N.V. (now known as Elastic). Known for its simple REST APIs, distributed nature, speed, and scalability, Elasticsearch is the central component of the Elastic Stack, a set of free and open tools for data ingestion, enrichment, storage, analysis, and visualization. Commonly referred to as the ELK Stack (after Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana), the Elastic Stack now includes a rich collection of lightweight shipping agents known as Beats for sending data to Elasticsearch.
Moving to questions and their Answers:
1. What is Elasticsearch?
Answer: Elasticsearch is an open-source distributed search and analysis engine built on Apache Lucene. With time, it has become a popular search engine that is commonly used for security intelligence, business analytics, operational intelligence, log analytics, full-text search, and more.
2. What are the features of Elasticsearch?
Answer: Here are important features of Elasticsearch:
- Full-Text Search
- An open-source search server is written using Java
- Used to index all types of heterogeneous data
- Near Real-Time (NRT) search
- Has REST API web interface with JSON output
- Sharded, replicated searchable, JSON document store.
- Multi-language & Geolocation support
- Schema-free, REST & JSON based distributed document store
3. What is the ELK stack?
Answer: In Elasticsearch, ELK Stack is a collection of three open-source products — Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana.
4. What is a cluster?
Answer: A cluster is a group of nodes with the same cluster. name attribute which together holds data and provides joined indexing and search capabilities.
5. What are the advantages of Elasticsearch?
Answer: Some of the biggest advantages of Elasticsearch are as follows –
- Creates and stores schema-less data
- Manipulates data records by using Multi-document APIs
- Filtering and querying data for insights
- Based on Apache Lucene and provides RESTful API
- Helps you to scale vertically and horizontally
6. What are the primary operations performed in a Document?
Answer: Here, are important operations performed on documents:
- Indexing a document
- Fetching documents
- Updating documents
- Deleting documents
7. Explain ELK stack architecture?
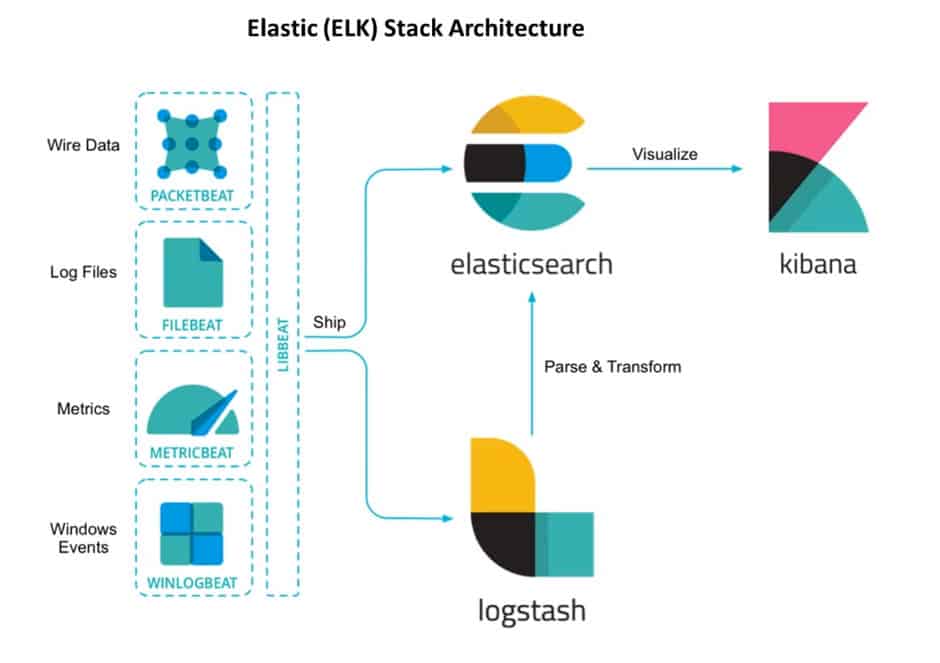
Answer: ELK stack allows users to fetch data from heterogeneous data sources and analyze, visualize it in real-time. ELK architecture consists of the following things –
Logs: First of all, the user identifies what server logs need to be analyzed
Logstash: Collect logs and events data. It also parses and transforms data.
ElasticSearch: The transformed data is then stored, searched, and indexed.
Kibana: Kibana uses Elasticsearch database to Explore, Visualize, and Share
8. What is a method to add a mapping in an Index?
Answer: Elasticsearch lets you create the mapping as per the data given by the user in the request body. Its bulk feature can be used to add more than one JSON object in the index.
For example, POST website /_bulk.
9. What are some of the configuration management tools supported by Elasticsearch
Answer: Some important configuration management tool supported by Elasticsearch is as follows:
- Puppet – puppet-elastic search
- Chef – cookbook-elastic search
- Ansible – ansible-elastic search
10. Where is Elastic search stored?
Answer: Elastic search results are stored in a distributed document in different directories. Also, a user can retrieve complex data structures that are serialized as JSON documents.
11. What are the various ways of searching in Elasticsearch?
Answer: We have different ways of searching in Elasticsearch:
Multi-index, Multitype search: A user can search APIs that can be applied across several indices through a multi-index support system.
URI (uniform resource identifier) search: A user can execute a search request using a URI by providing the requested parameters.
Request body search: A search request needs to be executed by a search DSL.
12. What is Apache Lucene?
Answer: Apache Lucene is an open-source information retrieval software library written in Java language.
13. What is NRT in Elasticsearch?
Answer: NRT stands for Near Real-Time Search. It is a near real-time search platform ie. there will be a slight latency (approx. one second) from indexing a document until it becomes searchable.
14. List out different commands available in Elasticsearch cat API?
Answer: Command using with cat API are:
- Cat aliases, cat field data, cat allocation, cat count
- Cat health, pending tasks, cat plugins, cat indices, cat master, cat recovery
- cat repositories, cat templates, cat snapshots
15. What do you mean by ingest node?
Answer: Ingest node is used to pre-process the documents before the actual document indexing is done. It intercepts bulk and index requests and applies transformations to pass the documents back to the bulk API and index.
16. What do you mean by fuzzy query Elasticsearch?
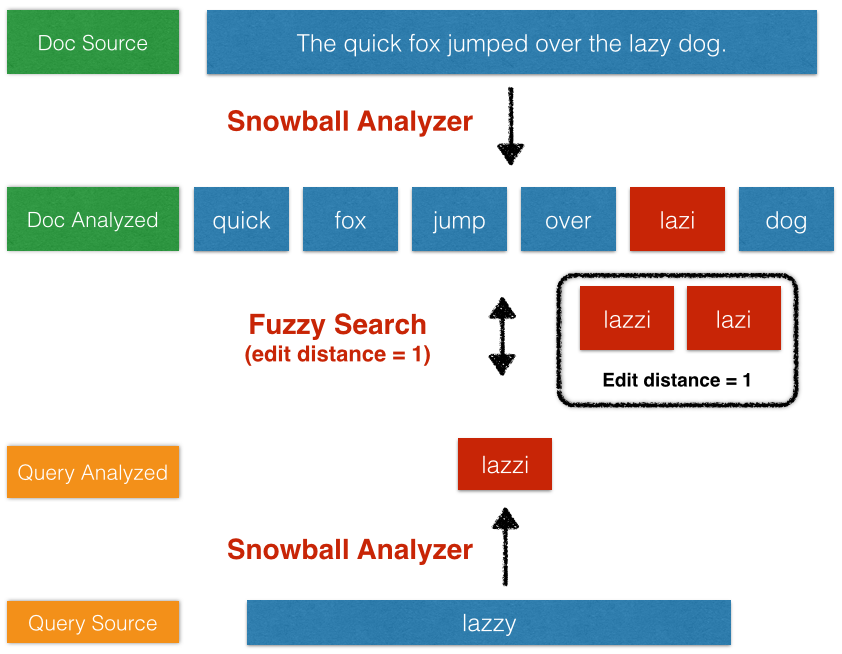
Answer: The fuzzy query returns the document that contains terms similar to the search terms. To find similar terms, a fuzzy query creates a set of possible variations of search terms within a specified edit distance. When a user searches for some terms using a fuzzy query, the system returns the most resembling terms for each expansion.
17. What is the explore API in Elasticsearch?
Answer: The explore API helps in extracting and summarizing information about the documents and terms in the elastic search index. You can understand the behavior of this API by using the Graph UI to explore connections.
18. Can you name five companies that have an elastic search as their search engine and database for their application?
Answer:
- Uber
- Stack Overflow
- DigitalOcean
- Udemy
- Wikipedia
- Netflix
19. Can you explain SHARDS in Elasticsearch?
Answer: When the number of documents increases, processing power goes down, and as a result responding to client requests gets delayed. In situations, indexed data is divided into small chunks called Shards, in order to improve the fetching of results during data search.
20. What is the syntax or code to add a Mapping in an Index?
Answer:
You can add a mapping in an index using the below syntax:
Syntax:
POST /_<index_name>/_type/_id21. What are the various types of queries that Elasticsearch supports?
Answer: Queries are categorized into two types: Full Text/Match Queries and Term-based Queries.
Text Queries include basic match, match phrase, common terms, query-string, multi-match, match phrase prefix, simple query string.
Term Queries include term exists, type, wildcard, regexp term set, range, prefix, ids, and fuzzy.
22. What is the difference between Term-based queries and Full-text queries?
Answer:
Full-text queries analyze the query string before executing it whereas term-level queries operate on the exact terms stored in the inverted index without analyzing.
The full-text queries are commonly used to run queries on full-text fields like the body of an email whereas term level queries are used for structured data like numbers, dates, and enums, rather than full-text fields.
23. What is aggregation in Elasticsearch?
Answer: Aggregations help in collecting data through queries used in the search. Different types of aggregations are Sum and stats, Metrics, Average, Minimum, Maximum based on different purposes.
24. What are Single document APIs in Elasticsearch?
Answer:
- Get API
- Index API
- Delete API
- Update API
25. List out X-Pack commands?
Answer: X-Pack commands are listed below:
- Certgen
- Migrate
- setup-passwords
- syskeygen
- users
26. What is the difference between Master node and Master eligible no4de?
Answer: Master node functionality includes the creation of index/indices, monitor an account of nodes forming a cluster, deletion of index/indices. Whereas, Master eligible nodes are those nodes that get elected to become Master Node.
27. Where and how Kibana will be useful in Elasticsearch?
Answer: Kibana is part of the ELK Stack – log analysis solution. It is an open-source visualization tool used to analyze data available in graph formats such as pie bar, coordinate map, line, etc.
28. What is dynamic mapping in Elasticsearch?
Answer: The process of automatic detection and addition of new fields is called dynamic mapping. Also, a user can customize the dynamic mapping rules to suit the requirement.
29. List out the use cases related to ELK log analytics?
Answer: ELK log analytics use cases are listed below:
- Compliance
- raud detection
- Market Intelligence
- Risk management
- Security analysis
- E-commerce Search solution
30. How Elastic Stack Reporting is used?
Answer: Reporting API is used to retrieve data in image PNG format, PDF format as well as spreadsheet CSV format that can be shared or saved as per requirement.
31. What software is required to install Elasticsearch?
Answer: The latest JDK or Java version 1.8.0 is a prerequisite to installing Elasticsearch.
32. What is the importance of installing X-Pack for Elasticsearch?
Answer: X-Pack is an extension that gets installed with Elasticsearch. Some of the functionalities of X-Pack are security (Roles and User security, Role-based access, Privileges/Permissions), monitoring, alerting, reporting, and more.
33. What is the functionality of cat API in Elasticsearch?
Answer: Cat API commands provide an overview of the Elasticsearch cluster including data related to aliases, allocation, indices, node attributes, etc. These cat commands use query string as a parameter that returns queried data from the JSON document.
34. How Beats can be used with Elasticsearch?
Answer: Beats is an open-source tool used to transfer data to Elasticsearch where data is processed before being viewed using Kibana. Data such as audit data, log files, window event logs, cloud data, and network traffic are transported.
35. What is the step-by-step procedure to start an Elasticsearch server?
Answer:
Follow the given steps to start an elasticsearch server
First of all open, the command prompt from the windows start menu
Change the directory to the bin folder of the elasticsearch folder which was created after its installation
Type/Elasticsearch.bat and press enter to start the Elasticsearch server
By following these steps, Elasticsearch will start in CMD in the background. Further, open the browser and type http://localhost:9200, and press enter. This will show you the elasticsearch cluster name and meta value related to the database.
36. What is a document in ElasticSearch?
Answer: A document is similar to a row in relational databases. The difference is that each document in an index can have a different structure (fields), but should have the same data type for common fields. Each field can occur multiple times in a document with different data types. Fields can contain other documents too.
37. What is an index in ElasticSearch?
Answer: An index is similar to a table in relational databases. The difference is that relational databases would store actual values, which is optional in ElasticSearch. An index can store actual and/or analyzed values in an index.
38. What is a shard in ElasticSearch?
Answer: Due to resource limitations like RAM, CPU, etc, for scale-out, applications need to employ multiple instances of ElasticSearch on separate machines. Data in an index can be divided into multiple partitions, each handled by a separate node (instance) of ElasticSearch. Each such partition is called a shard. By default, an ElasticSearch index has 5 shards.
39. Does ElasticSearch have a schema?
Answer: Yes, ElasticSeach can have mappings that can be used to enforce a schema on documents.
40. What are the various possible ways in which we can perform a search in Elasticsearch?
Answer: Mentioned below are the various possible ways in which we can perform a search in Elasticsearch:
Applying search API across multiple types and multiple indexes: Search API, we can search an entity across multiple types and indices.
Search request using a Uniform Resource Identifier: We can search requests using parameters along with URI i.e. Uniform Resource Identifier.
Search using Query DSL i.e. (Domain Specific Language) within the body: DSL i.e. Domain Specific Language is utilized for JSON request body.
41. Please explain the working of aggregation in Elasticsearch?
Answer: Aggregations help in the collection of data from the query used in the search. Different types of aggregations are Metrics, Average, Minimum, Maximum, Sum, and stats, based on different purposes.
42. Can you compare Term-based queries and Full-text queries?
Answer: Domain-Specific Language (DSL) Elasticsearch query which is known as Full-text queries utilizes the HTTP request body, offers the advantage of being clear and detailed in their intent, over time it is simpler to tune these queries.
Term-based queries utilize the inverted index, a hash map-like data structure that helps to locate text or string from the body of email, keyword or numbers or dates, etc. used in analysis purposes.
43. What is an Elasticsearch Analyzer?
Answer: Analyzers are used for Text analysis, it can be either built-in analyzers or custom analyzers. The analyzer consists of zero or more Character filters, at least one Tokenizer, and zero or more Token filters.
- Character filters break down the stream of string or numerical into characters by stripping out HTML tags, searching the string for key, and replacing them with the related value defined in mapping char filter as well as replacing the characters based on a specific pattern.
- Tokenizer breaks the stream of string into characters, For example, whitespace tokenizer breaks the stream of string while encountering whitespace between characters.
- Token filters convert these tokens into lower case, remove from string stop words like ‘a’, ‘an’, ‘the’. or replace characters into equivalent synonyms defined by the filter.
44. How do Filters work in an Elasticsearch?
Answer: Token filters receive text tokens from tokenizers and can manipulate them to compare the tokens for search conditions. These filters compare tokens with the searched stream, resulting in Boolean values, like true or false.
The comparison can be whether the value for searched condition matches with filtered token texts, OR does not match, OR matches with one of the filtered token text returned OR does not match any of the specified tokens, OR value of the token text is within given range OR is not within a given range, OR the token texts exist in search condition or does not exist in the search condition.
45. How does a character filter in Elasticsearch Analyzer utilized?
Answer: Character filter in Elasticsearch analyzer is not mandatory. These filters manipulate the input stream of the string by replacing the token of text with the corresponding value mapped to the key.
We can use mapping character filters that use parameters as mappings and mappings_path. The mappings are the files that contain an array of key and corresponding values listed, whereas mappings_path is the path that is registered in the config directory that shows the mappings file present.
46. While installing Elasticsearch, please explain different packages and their importance?
Answer: Elasticsearch installation includes the following packages:
- Linux and macOS platform needs tar.gz archives to be installed.
- Windows operating system requires .zip archives to be installed.
- Debian, Ubuntu-based systems deb pack needs to be installed.
- Red Hat, Centos, OpenSuSE, SLES needs the rpm package to be installed.
- Windows 64 bits system requires the MSI package to be installed.
- Docker images for running Elasticsearch as Docker containers can be downloaded from Elastic Docker Registry.
- X-Pack API packages are installed along with Elasticsearch that helps to get information on the license, security, migration, and machine learning activities that are involved in Elasticsearch.
47. What are configuration management tools are supported by Elasticsearch?
Answer: Ansible, Chef, Puppet, and Salt Stack are configuration tools supported by Elasticsearch used by the DevOps team.
48. Can you please explain the functionality and importance of the installation of X-Pack for Elasticsearch?
Answer: X-Pack is an extension that gets installed along with Elasticsearch. Various functionalities of X-Pack are security (Role-based access, Privileges/Permissions, Roles, and User security), monitoring, reporting, alerting, and many more.
49. Can you list X-Pack commands?
Answer: X-Pack commands are listed below:
- Certgen
- Migrate
- setup-passwords
- syskeygen
- users
50. Can you please list the field data type majorly available concerning Elasticsearch?
Answer:
Enlisted below are the data types for the document fields:
- String data type which includes text and keywords such as email addresses, zip codes, hostnames.
- Numeric data types like byte, short, integer, long, float, double, half_float, scaled_float.Date, Date nanoseconds, Boolean, Binary (Base64 encoded string, e.g 000000 for char ‘A’ or 011010 for char ‘a’)
- Range (integer_range, long_range, double_range, float_range, date_range)
- Complex data types that include object (Example: single JSON object) and Nested (array of JSON objects)
- Geo datatypes include latitude/longitude which is geo-points and geo-shape which includes shapes like a polygon.
- Specialized datatypes, Arrays (values in the array should have the same data type)
- Mastering Qualitative Research: The Role of Focus Groups in Data Collection - July 11, 2024
- What is robots ops? - July 10, 2024
- 5 Effective Online Learning Strategies for DevOps Professionals - July 4, 2024

