
- Explain what is Perl language?

Perl stands for “Practical Extraction and Reporting Language”. It’s a powerful scripting language and is rich in features. Using Perl, we can write powerful and efficient code that can be used in mission-critical projects.
2. What are the various uses of Perl?
Perl is used in a mission-critical project – like the defense industry. It is also used in “Rapid Prototyping”.
3. What are the various advantages and disadvantages of Perl?
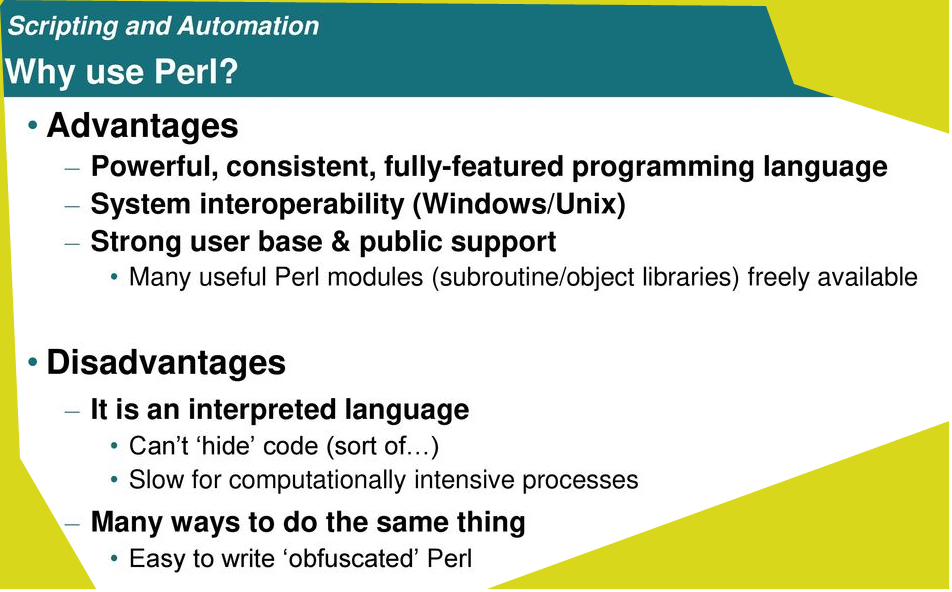
Advantages of Perl include:
- Perl is efficient and is easy-to-use.
- It is an Interpreted language i.e. Perl program is interpreted on a statement-by-statement basis.
- Perl is portable and cross-platform. Currently, it can run on more than 100 platforms.
- Perl is extendable. We can include various open-source packages and modules in a Perl program for any additional functionality. For example, we can import CPAN modules for database support in the Perl program.
The main disadvantage of Perl is that as it is an interpreted language, the execution speed is quite slow. Although it allows us to write high-level code, we cannot write complex code using Perl. Perl has too many features that can be exhaustive for a programmer to comprehend.
4. Explain the various characteristics of Perl?
Enlisted below are the various Characteristics of Perl:
- Case-sensitive
- Easy to code
- Open-source
- Portable and cross-platform.
- Extendable
- No distinction between the types of variables.
- Can return non-linear types likes arrays etc.
- Non-scalars can be used as loop indices.
- Supports high-level intrinsic operations – Example: stack Push/pop.
- Powerful text manipulation API including Regular expressions
5. What are the various flags/arguments that can be used while executing a Perl program?
The following arguments can be used while executing a Perl program.
- w – argument shows a warning.
- d – used for debugging.
- c – compiles only do not run.
- e – execute.
We can also use a combination of arguments like:
pl –wd filename.pl
Variables In Perl
6. Comment on data types and variables in Perl?
Perl variables do not have a data type. The data type of a variable in Perl is inferred from its value.
A variable in Perl can be defined as follows:
________________________
$x = 10;
$base_str = ‘Hello’;
__________________
Value needs to be assigned to a variable before using it. Without this, the program may result in an unexpected output.
7. What are Numeric Operators in Perl?
Numeric operators in Perl are as follows:
- Arithmetic operators (+,-,*/).
- Comparison operators to compare two numbers (>, <, ==, !=,<=,>=,<=>).
- Bitwise Operators(&(and), |(or),^(ex-or),~(not),<<(shift left),>>(shift right)).
- Arithmetic operators perform from left to right while Bitwise operators perform an operation from right to left.
8. Explain string comparison operators in Perl?
Perl supports various string operators as shown below:
| Equality | Operators |
Operators | eq |
| Not Equal | ne |
| Comparison | cmp |
| Less than | lt |
| Greater than | gt |
| Less than or equal | le |
| Greater than or equal | ge |
These operators can be used to compare two strings.
9. Differentiate between Arrays and List in Perl?
Both list and array can be defined as a set of elements. The main difference between a list and an array in Perl is that a list is immutable i.e. it cannot be altered directly.
In Perl, a list is an array without a name. Hence, most of the times array and list are used interchangeably. An array is mutable and its contents can grow, shrink in size, etc.
Thus in order to change the contents of a list, we can store the list as an array. An array is a variable that provides dynamic storage for a list.
10. Difference between the variables in which chomp function work ?
- Scalar: It is denoted by $ symbol. Variable can be a number or a string.
- Array: Denoted by @ symbol prefix. Arrays are indexed by numbers.
The namespace for these types of variables is different. For Example: @add, $add. The scalar variables are in one table of names or namespace and it can hold single specific information at a time and array variables are in another table of names or namespace. Scalar variables can be either a number or a string
11. In Perl we can show the warnings using some options in order to reduce or avoid the errors. What are that options?
-The -w Command-line option: It will display the list if warning messages regarding the code.
– strict pragma: It forces the user to declare all variables before they can be used using the my() function.
– Using the built-in debugger: It allows the user to scroll through the entire program line by line.
12. In Perl, there are some arguments that are used frequently. What are that arguments and what do they mean?
- -w (argument shows warning)
- -d (use for debug)
- -c (which compile only not run)
- -e (which executes)
We can also use combination of these like:
-wd
13. How many types of primary data structures in Perl and what do they mean?
The scalar: It can hold one specific piece of information at a time (string, integer, or reference). It starts with dollar $ sign followed by the Perl identifier and Perl identifier can contain alphanumeric and underscores. It is not allowed to start with a digit. Arrays are simply a list of scalar variables.
Arrays:
Arrays begin with @ sign. Example of array:
________________________________________________________
my @arrayvar = ("string a", "string b "string c");
____________________________________________
Associative arrays: It also frequently called hashes, are the third major data type in Perl after scalars and arrays. Hashes are named as such because they work very similarly to a common data structure that programmers use in other languages–hash tables. However, hashes in Perl are actually a direct language supported data type.
14. Which functions in Perl allows you to include a module file or a module and what is the difference between them?
“use”
The method is used only for the modules (only to include .pm type file)
The included objects are verified at the time of compilation.
We don’t need to specify the file extension.
loads the module at compile time.
“require”
The method is used for both libraries and modules.
The included objects are verified at the run time.
We need to specify the file Extension.
Loads at run-time.
suppose we have a module file as “Module.pm”
use Module;
or
require “Module.pm”;
(will do the same)
15. Which guidelines by Perl modules must be followed?
Below are guidelines and are not mandatory
The name of the package should always begin with a capital letter.
The entire file name should have the extension “.pm”.
In case no object oriented technique is used the package should be derived from the Exporter class.
Also if no object oriented techniques are used the module should export its functions and variables to the main namespace using the @EXPORT and @EXPOR_OK arrays (the use directive is used to load the modules).
16. How the interpreter is used in Perl?
Every Perl program must be passed through the Perl interpreter in order to execute. The first line in many Perl programs is something like:
________________________________
!/usr/bin/perl
_____________________The interpreter compiles the program internally into a parse tree. Any words, spaces, or marks after a pound symbol will be ignored by the program interpreter. After converting into parse tree, interpreter executes it immediately. Perl is commonly known as an interpreted language, is not strictly true. Since the interpreter actually does convert the program into byte code before executing it, it is sometimes called an interpreter/compiler. Although the compiled form is not stored as a file.
17. For a situation in programming, how can you determine that Perl is a suitable?
If you need faster execution the Perl will provide you that requirement. There a lot of flexibility in programming if you want to develop a web based application. We do not need to buy the license for Perl because it is free. We can use CPAN (Comprehensive Perl Archive Network), which is one of the largest repositories of free code in the world.
18. Where the command line arguments are stored and if you want to read command-line arguments with Perl, how would you do that?
The command line arguments in Perl are stored in an array @ARGV.
- $ARGV[0] (the first argument)
- $ARGV[1] (the second argument) and so on.
$#ARGV is the subscript of the last element of the @ARGV array, so the number of arguments on the command line is $#ARGV + 1
19. What is the use of -w, -t and strict in Perl?
When we use –w, it gives warnings about the possible interpretation errors in the script.
Strict tells Perl to force checks on the definition and usage of variables. This can be invoked using the use strict command. If there are any unsafe or ambiguous commands in the script, this pragma stops the execution of the script instead of just giving warnings.
When used –t, it switches on taint checking. It forces Perl to check the origin of variables where outside variables cannot be used in sub shell executions and system calls.
20. List the data types that Perl can handle?
- Scalars ($): It stores a single value.
- Arrays (@): It stores a list of scalar values.
- Hashes (%): It stores associative arrays which use a key value as index instead of numerical indexes
21. What is the use of -n and -p options?
The -n and -p options are used to wrap scripts inside Loops. The -n option makes the Perl execute the script inside the loop. The -p option also used the same loop as -n loop but in addition to it, it uses continue. If both the -n and -p options are used together the -p option is given the preference.
22. How can you use Perl warnings and what is the importance to use them?
The Perl warnings are those in which Perl checks the quality of the code that you have produced. Mandatory warnings highlight problems in the lexical analysis stage. Optional warnings highlight cases of possible anomaly.
_____________________________________
use warnings; # it is same as importing "all"
no warnings; # it is same as unimporting "all"
use warnings::register;
if (warnings::enabled()) {
warnings::warn("any warning");
}
if (warnings::enabled("void")) {
warnings::warn("void", "any warning");
}
___________________________
23. Remove the duplicate data from @array=(“perl”,”php”,”perl”,”asp”) ?
__________________________
sub uniqueentr
{
return keys %{{ map { $_ => 1 } @_ }};
}
@array = ("perl","php","perl","asp");
print join(" ", @array), "\n";
print join(" ", uniqueentr(@array)), "\n";
________________________
24. Why Perl aliases are considered to be faster than references?
In Perl, aliases are considered to be faster than references because they do not require any dereferencing.
25. How can memory be managed in Perl?
Whenever a variable is used in Perl, it occupies some memory space. Since the computer has limited memory the user must be careful of the memory being used by the program. For Example:
_________________________
use strict;
open(IN,"in");
my @lines = <IN>
close(IN);
open(OUT,">out");
foreach (@lines)
{
print OUT m/([^\s]+)/,"\n";
}
close(OUT);
__________________
26. List the prefix dereferencer in Perl?
- $-Scalar variables
- %-Hash variables
- @-arrays
- &-subroutines
- Type globs-*myvar stands for @myvar, %myvar.
27. What are the advantages of c over Perl?
There are more development tools for C than for PERL. PERL execute slower than C programs. Perl appears to be an interpreted language but the code is complied on the fly. If you don’t want others to use your Perl code you need to hide your code somehow unlike in C. Without additional tools it is impossible to create an executable of a Perl program.
28. Perl regular expressions match the longest string possible”. What is the name of this match?
It is called as “greedy match” because Perl regular expressions normally match the longest string possible.
29. What interface used in PERL to connect to database? How do you connect to database in Perl?
We can connect to database using DBI module in Perl.
_____________________________
use DBI;
my $dbh = DBI->connect('dbi:Oracle:orcl', 'username', 'password',)
_______________________
30. Explain which feature of PERL provides code reusability?
To provide code re-usability in PERL inheritance feature is used. In Inheritance, the child class can use the methods and property of the parent class.
31. Mention the difference between die and exit in Perl?
Die will print a message to the std err before ending the program while Exit will simply end up the program.
32. In Perl, what is grep function used for?
To filter the list and return only those elements that match certain criteria Perl grep function is used.
33. What is the syntax used in Perl grep function?
The syntax used in Perl is
- grep BlOCK LIST
- grep ( EXPR, LIST )
- BLOCK: It contains one or more statements delimited by braces, the last statement determines in the block whether the block will be evaluated true or false.
- EXPR: It represents any expression that supports $, particularly a regular expression. Against each element of the list, expression is applied, and if the result of the evaluation is true, the current element will be attached to the returned list
- LIST: It is a list of elements or an array.
34. Mention how many ways you can express string in Perl?
You can express string in Perl in many ways
For instance “this is guru99.”
- qq/this is guru99 like double quoted string/
- qq^this is guru99 like double quoted string^
- q/this is guru99/
- q&this is guru99&
- q(this is guru99)
35. What does -> symbol indicates in Perl?
In Perl, the arrow – > symbol is used to create or access a particular object of a class.
36. Explain what is Polymorphism in Perl?
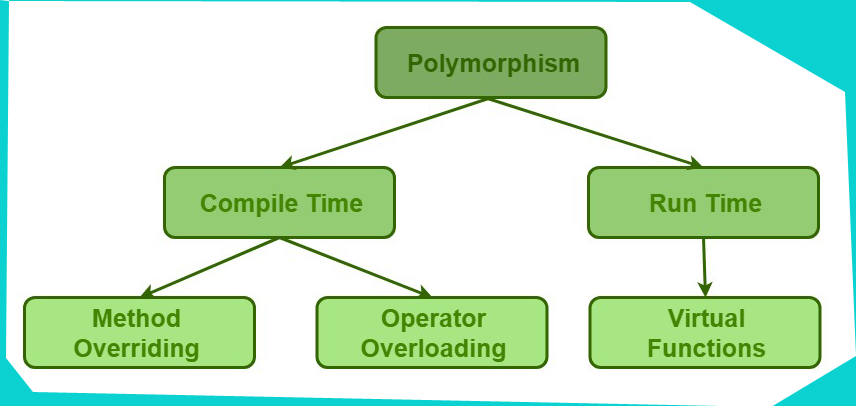
In Perl, Polymorphism means the methods defined in the base class will always over-ride the methods defined in the parent class.
37. what is the scalar data and scalar variables in Perl?
Scalar in Perl means a single entity like a number or string. So, the Java concept of int, float, double and string equals to perls scalar and the numbers and strings are exchangeable. While scalar variable is used to store scalar data. It uses $ sign and followed by one or more alphanumeric characters or underscore. It is a case sensitive.
38. What is the closure in PERL?
The closure is a block of code that is used to capture the environment where it is defined. It particularly captures any lexical variables that block consists of and uses in an outer space.
39. Explain what is Perl one liner?
One liner is one command line programs and can be executed from the command line immediately.
For example,
run program under the debugger
perl-d my_file
40. What is the difference between Perl and C?
| Perl | C |
| There are several development tools in Perl as compare to C | Development tools are less and are not very advanced |
| It executes more slowly than C in a few situations | C has speed almost equal to that of Perl |
| Code can be hidden in Perl | The same is not possible in the case of C |
The executable can be created without depending on the additional tools | Additional tools are the prime requirement |
41. Is it possible in Perl to use code again and again? If so, which feature enables the user to that?
Yes, it is possible in Perl. However, there is a limit on the usage of the same code in the same program. The users need not worry about the complexity either as Perl is equipped with a code trimming feature. It automatically guides users on how to keep the code as short as possible.
Code reusability is a prime example of this. The feature that enables users to simply keep up the pace towards this is “Inheritance”. The child class in this feature can use the methods of their parent class.
42. How can you represent the warning signs in the Perl in case of an error and what are the options through which this task can be performed?
There is an option in Perl which is known as the Command-Line. All the warning messages can be displayed using this and the pragma function simply makes sure that the user can declare the variables during the appearance of warning messages. The entire program can be scrolled easily and in fact, in a very short span of time using the in-built debugger.
43. While writing a program, why the code should be as short as possible?
Complex codes are not always easy to handle. They are not even easy to be reused. Moreover, finding a bug in them is not at all a difficult job. Any software or application if has complex or lengthy code couldn’t work smoothly with the hardware and often have compatibility issues. Generally, they take more time to operate and thus become useless or of no preference for most of the users. The shortcode always makes sure that the project can be made user-friendly and it enables programmers to save a lot of time.
44. What are “Require” and “Use” statement in Perl and when it is used?

It is considered when it comes to importing the functions in a way that they can be accessed directly during the program. The users are free to get the results in case the substatements are not accurate. On the other side, the use statement is generally executed during parsing.
45. In Perl, is it possible for the programmers to prefer a dynamic approach when it comes to loading the binary extension?
Yes, it is possible. The only need for this is the system a programmer is using must support it. The other option is to accomplish this task statically in case the system doesn’t allow the same. The dynamic approach can help users to save time as they are free to perform some basic tasks in their own way.
46. For executing a program in Perl, is there any basic condition which the users have to fulfill?
The users must make sure that the program they have accomplished should be passed through the interpreter before its actual execution. It actually compiles the program reliably and the best part is the users are free to ignore any spaces or marks in the same.
47. How can you say that Perl is a compiler?
It is because the interpreter in Perl is actually free to convert simply the program into small codes.
(OR)
Is Perl a compiler or Interpreter?
The programming language can also be used both as a compiler and as an interpreter. It takes in the source codes and converts the same into bytecode that is understandable by the programming language. You can then execute and run the program. Therefore, the programming language can both be regarded as an interpreter and a compiler.
48. Tell how can an array be made empty in Perl?
This can be done easily. For this, the value of the array is set to zero and the users can then perform this task by assigning the null list to it.
49. Tell one reason why Perl aliases are good enough to be considered and are faster than references?
They don’t need dereferencing and that is one of the best things about it. A lot of tasks that are not required or are not usually can be avoided easily.
50. Tell something about memory management in Perl?
When the programmers make use of a variable in Perl, some memory get occupies. The users have to make sure that memory is utilized in the best possible manner. After a program is executed, the files can be divided into sections easily and can then be managed.
- Mastering Qualitative Research: The Role of Focus Groups in Data Collection - July 11, 2024
- What is robots ops? - July 10, 2024
- 5 Effective Online Learning Strategies for DevOps Professionals - July 4, 2024

