What is Kubeadm?
Kubeadm helps you bootstrap a minimum viable Kubernetes cluster that conforms to best practices. Kubeadm is a tool built to provide kubeadm init and kubeadm join as best-practice “fast paths” for creating Kubernetes clusters.
Goal
- To Install a single master Kubernetes cluster
- To Install a high availability master Kubernetes cluster
- To Install a Pod network on the cluster so that your Pods can talk to each other.
kubeadm’s simplicity means it can serve a wide range of use cases:
- New users can start with kubeadm to try Kubernetes out for the first time.
- Users familiar with Kubernetes can spin up clusters with kubeadm and test their applications.
- Larger projects can include kubeadm as a building block in a more complex system that can also include other installer tools.
Pre-requisite
- One or more machines running a deb/rpm-compatible OS, for example Ubuntu or CentOS
- 2 GB or more of RAM per machine. Any less leaves little room for your apps.
- 2 CPUs or more on the master
- Full network connectivity among all machines in the cluster. A public or private network is fine
As part of the installation, every node (master and minions) needs:
- Docker
- Kubelet
- Kubeadm
- Kubectl
- CNI
Step 1 – Update Ubuntu and install apt-transport-https
$ apt-get update && apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
$ curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | apt-key add -Step 2 – Add Ubuntu apt repo for docker kubeadm kubectl kubelet kubernetes-cni
$ cat <<EOF >/etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
deb http://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOFStep 3 – Install docker kubeadm kubectl kubelet kubernetes-cni
$ apt-get update
$ apt-get install -y docker.io kubeadm kubectl kubelet kubernetes-cni
$ apt-get install -y docker.io kubeadm kubectl kubelet kubernetes-cniStep 4 – Finally, initialize a kubernetes clusters
$ kubeadm initStep 5 – Output
To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/
Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root:
kubeadm join 172.31.25.244:6443 --token 1j1lj9.bw6nb02omjv92owd \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:caca50bf253855d96133c6fdde763629a6fba07d8c57b6b52eacece83f88b4b9Step 6 – Setup Workstation in the Master node only. You can be regular user for it.
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configStep 7 – Verify Clustors
$ kubectl get nodes
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespacesStep 8 – Install Kubernetes pod networking
Weave Net provides networking and network policy, will carry on working on both sides of a network partition, and does not require an external database. Kubernetes versions 1.6 and above:
$ kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
$ kubectl get nodes
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
$ kubectl get nodesStep 9 – Setup nodes [ In the node aka worker ]
# Follow Step 1
# Follow Step 2
# Follow Step 3
# Run following commands which we got from kubeadm init
$ kubeadm join 172.31.31.106:6443 --token pdn6in.r0dzhpx1ucrs69au --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:a9385951e659a3c67f55ccfbdc1169b1f660ba09aaf8cc6d5cc96d71b71900d2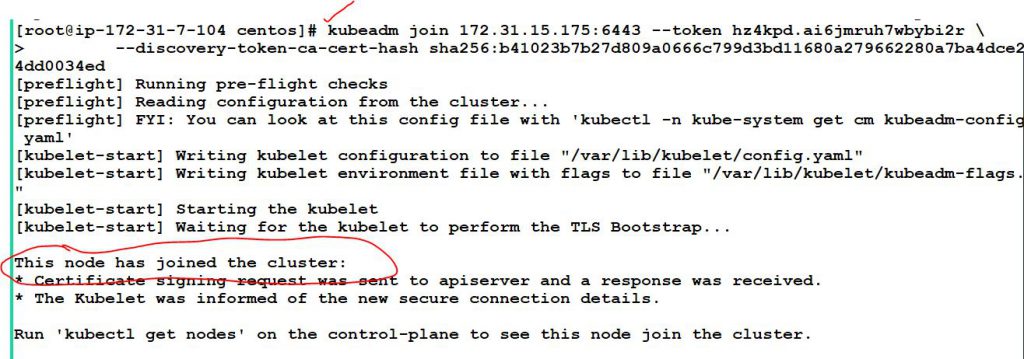
- How to remove sensitive warning from ms office powerpoint - July 14, 2024
- AIOps and DevOps: A Powerful Duo for Modern IT Operations - July 14, 2024
- Leveraging DevOps and AI Together: Benefits and Synergies - July 14, 2024

