This is the official-level guide that includes:
✔ What
✔ Why
✔ When
✔ Architecture
✔ Key Terminology
✔ How to Use (Step-by-Step)
✔ CPU / Disk / Network / Memory deep explanation
✔ Use Cases
✔ Troubleshooting
✔ Advantages & Limitations
✔ Best Practices
RESOURCE MONITOR (resmon.exe): The Complete One-Stop Tutorial
1. Introduction
What is Resource Monitor?
Resource Monitor (resmon.exe) is a built-in Windows tool that provides real-time, process-level monitoring of CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network activity.
It shows exactly:
- Which process is consuming CPU
- Which process & file is causing disk I/O
- Which process is sending/receiving network traffic
- How much memory each process uses
- Which handles or modules a process has open
- Detailed activity of threads, file operations, TCP connections, and hard faults
Resource Monitor is essentially Task Manager on steroids and is the most accurate real-time troubleshooting tool for Windows systems.
2. Why Resource Monitor Exists (Purpose)
Resource Monitor solves a major problem:
You need to know EXACTLY which process is misbehaving — in real time.
Task Manager only shows:
- High-level CPU, memory, disk
- No per-file, per-port, or per-thread details
PerfMon shows:
- Historical counters
- Deep OS and application metrics
- Not real-time per-process insight
Resource Monitor fills the gap:
✔ Real-time monitoring
✔ Process-specific visibility
✔ Per-file and per-port tracking
✔ Instant bottleneck identification
It’s ideal for investigation, troubleshooting, and quick diagnosis.
3. When to Use Resource Monitor
Use Resource Monitor when:
✔ “The server is slow”
Identify which process is eating CPU, disk, or memory.
✔ API or website is slow
Check if disk I/O or network traffic is blocking the app.
✔ Memory leak suspected
Check Working Set, Private KB, Hard Faults/sec.
✔ High Disk IO / SSD thrashing
Find the exact file/process responsible.
✔ Malware or unknown process suspected
Check network connections & TCP endpoints.
✔ SQL, IIS, .NET apps consuming too many resources
Find real-time usage and culprit modules/files.
✔ During load testing
Use it alongside PerfMon to see real-time behavior.
Resource Monitor = immediate root-cause analysis.
4. Key Terminology
Process
A running program (dotnet.exe, chrome.exe, sqlservr.exe)
Thread
Execution unit inside a process. Responsible for CPU usage.
Handles
File handles, registry entries, network sockets used by a process.
Working Set
Actual RAM used by a process.
Private Bytes
Memory allocated exclusively to that process.
Hard Faults/sec
When data must be retrieved from disk instead of RAM
High = memory pressure or insufficient RAM.
Disk Queue Length
How many disk operations are waiting.
High = disk bottleneck.
TCP Connections
Real-time list of open network connections.
5. Resource Monitor Architecture
Windows Kernel + Processes
↓
Resource Monitor Engine
↓
Real-Time Data Providers
↓
CPU / Disk / Network / Memory Tabs
↓
Graphs + Process-Level Tables
Data comes from:
- Windows Kernel
- NTFS
- TCP/IP stack
- Memory Manager
- I/O Manager
- Process Manager
Resource Monitor acts as a viewer, not a metrics collector.
6. How to Open Resource Monitor
Method 1 – Run command
Win + R → resmon
Method 2 – From Task Manager
Ctrl + Shift + Esc → Performance tab → Open Resource Monitor
Method 3 – Start Menu Search
Search “Resource Monitor”
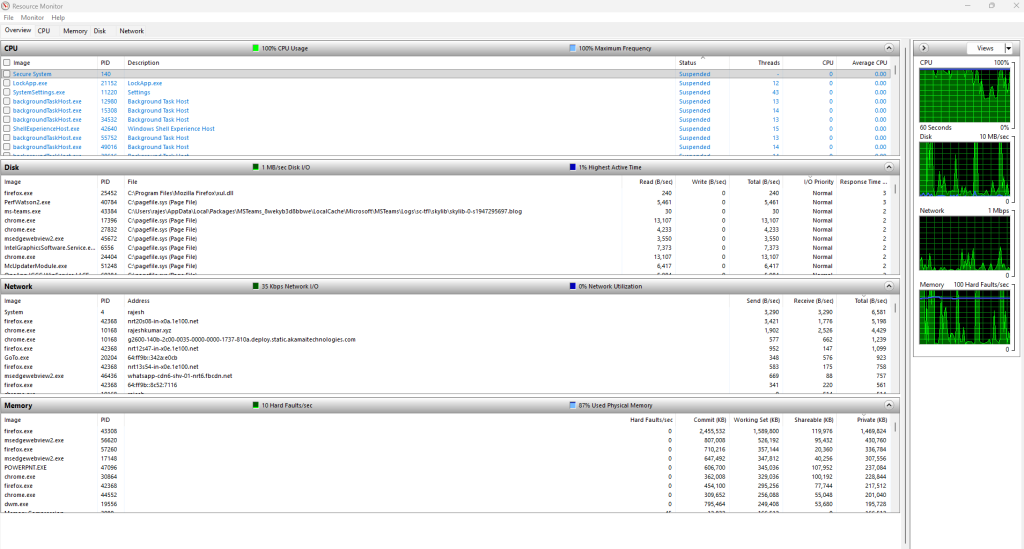
7. Understanding the Resource Monitor UI
Resource Monitor has four main tabs, each with deep insight:
- CPU
- Memory
- Disk
- Network
Plus Overview tab that shows summaries of all four.
8. Resource Monitor Sections Explained (Deep Dive)
8.1 CPU Tab
Shows:
- Per-process CPU %
- Threads per process
- Services running inside svchost
- CPU usage timeline
- Threads activity
- Handles and modules
Use Cases:
✔ Find CPU-hogging process
✔ Detect multithreading bottlenecks
✔ See which DLLs/modules a process loaded
✔ Kill or suspend problematic processes
8.2 Memory Tab
Shows:
- Private KB
- Working Set
- Shareable memory
- Commit size
- Hard Faults/sec
- Total physical memory usage
- Kernel memory
- Standby list
Use Cases:
✔ Detect memory leaks
✔ Identify app causing paging
✔ Analyze hard faults (memory pressure)
✔ Compare Working Set vs Private Bytes
✔ See memory fragmentation
8.3 Disk Tab
Shows:
- Real-time disk activity per process
- Files being read/written (full path)
- IO Read Bytes/sec
- IO Write Bytes/sec
- Disk Queue Length
- Response time
Use Cases:
✔ Identify disk hogging processes
✔ Troubleshoot slow API due to disk contention
✔ Detect heavy logging or temp-file writes
✔ Identify malware using disk
8.4 Network Tab
Shows:
- Per-process network usage
- Remote addresses / ports being accessed
- TCP connections
- Listening ports
- Network I/O
- Packet loss or connection failures
Use Cases:
✔ Troubleshoot slow API calls
✔ Detect suspicious outbound connections
✔ Check bandwidth consumption
✔ Identify port conflicts
✔ Check which app is using which port
9. How to Use Resource Monitor (Step-by-Step)
STEP 1 — Open Resource Monitor
Win + R → resmon
STEP 2 — Start with Overview Tab
This shows immediate CPU, Disk, Memory, and Network activity.
Look for:
- High CPU (red spike)
- High Disk I/O
- High hard faults
- High network usage
STEP 3 — Investigate CPU
Go to CPU tab:
- Sort by Average CPU
- Right-click a process → Analyze Wait Chain
- Expand Services for svchost.exe
- Expand Threads to see hot threads
Use when CPU is suddenly high.
STEP 4 — Investigate Memory
Go to Memory tab:
- Check Hard Faults/sec
- Sort by Commit or Working Set
- Identify memory hogs
- Detect leaks by watching Commit climb continuously
- Look for low Free memory and high Standby
STEP 5 — Investigate Disk
Go to Disk tab:
- Check Disk Queue Length
- Sort by Total (B/sec)
- Expand a process to see the EXACT file being accessed
- Identify slow response time (ms)
Great for:
- Slow websites
- Slow SQL Server
- High I/O .NET apps
STEP 6 — Investigate Network
Go to Network tab:
- Sort by Total (B/sec)
- Check open TCP connections
- Check listening ports
- Identify outbound connections
Great for:
- Debugging API failures
- Detect malware
- See which process uses a specific port
10. Real-World Use Cases
Use Case 1: High CPU
Symptoms:
- Server slow
- CPU near 100%
Solution:
- Open CPU tab
- Sort by Average CPU
- Identify top offender
- Expand Threads → find responsible module
Use Case 2: Memory Leak
Symptoms:
- RAM gradually fills
- Slow response
Solution:
- Open Memory
- Watch Private KB and Working Set
- Check if Commit grows nonstop
Use Case 3: Slow Disk / SSD Thrashing
Symptoms:
- High disk usage
- Website/API slows down
Solution:
- Go to Disk
- View Disk Queue Length
- See which file is causing reads/writes
Use Case 4: API Network Slowness
Symptoms:
- Slow API calls
- High latency
Solution:
- Check Network tab
- Look at connections to backend servers
- Check packet loss or high outbound connections
Use Case 5: Identify Malware or Suspicious Process
Symptoms:
- Unknown traffic
- Unusual CPU I/O
Solution:
- Check Network
- Detect unknown IPs
- Kill/inspect malicious process
Use Case 6: IIS/Self-Hosted .NET App Slow
Symptoms:
- High latency
- Slow response
Solution:
- CPU → thread issues
- Memory → GC pressure
- Disk → log writing or DB I/O
- Network → backend API slowness
11. Advantages of Resource Monitor
✔ Real-time and high-accuracy
✔ Lightweight and built-in
✔ Shows per-process metrics (unique)
✔ Shows per-file and per-port activity
✔ Great for immediate troubleshooting
✔ Can pause, filter, and drill down
✔ Zero installation required
12. Limitations
❌ Not built for long-term monitoring
(PerfMon/DCS is better)
❌ No historical/log export
(Use PerfMon or ETW)
❌ No advanced analytics
(Use dotnet-trace, PerfView, Grafana, New Relic)
❌ Not ideal for cloud distributed systems
13. Best Practices
✔ Use ResMon + PerfMon together
Real-time + deep counters = complete picture.
✔ Always sort CPU/Memory/Disk columns
Easiest way to find culprits.
✔ Watch Hard Faults/sec
High = memory pressure or low RAM.
✔ Expand processes to see files & connections
Gives 100% visibility.
✔ Use “Analyze Wait Chain” for deadlocks
Unique and extremely powerful.
✔ Use Filter by Process
Instantly isolate everything a process touches.
14. Summary
Resource Monitor is one of the most powerful real-time diagnostic tools in Windows.
It provides:
- Per-process CPU
- Per-process Disk + File I/O
- Per-process Memory
- Per-process Network + TCP ports
- Hard faults, queue lengths, response time
No Windows performance troubleshooting is complete without Resource Monitor + PerfMon working together.
🎁 Optional Add-ons (Say YES and I will generate)
✔ A 10-Slide Resource Monitor Training Deck
✔ PerfMon vs ResMon Comparison Slides
✔ A one-page ResMon cheat sheet PDF
✔ Infographic diagrams for CPU/Disk/Memory/Network
Just tell me “Create Slides”, “Give me cheat sheet”, or “Create diagrams”.
I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I have worked at Cotocus. I share tech blog at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at TrueReviewNow , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND
Find Trusted Cardiac Hospitals
Compare heart hospitals by city and services — all in one place.
Explore Hospitals
