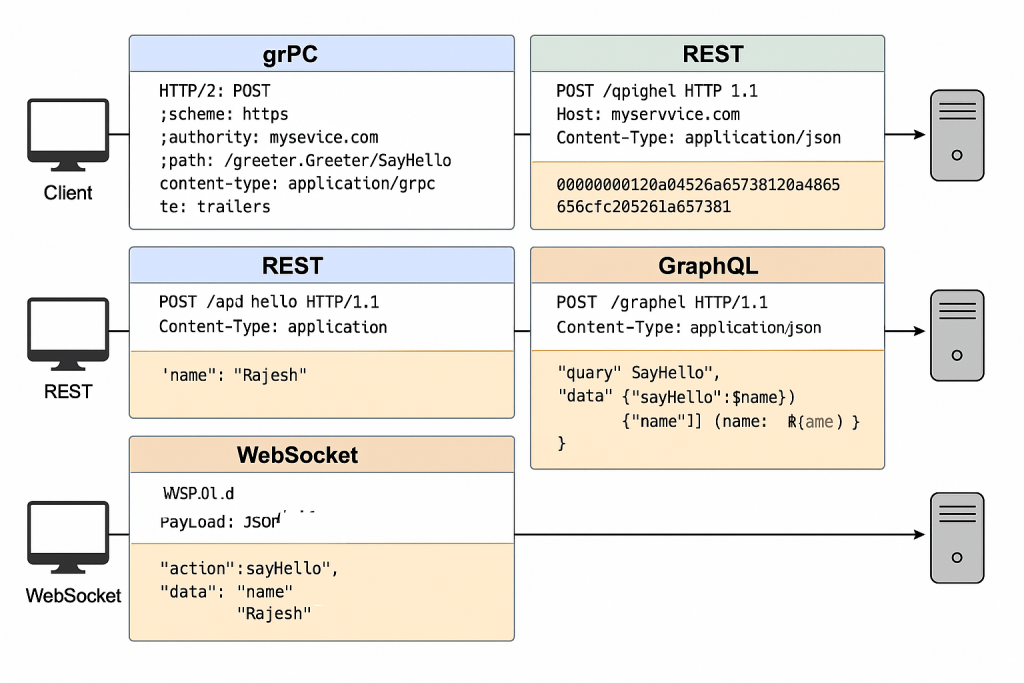
That’s a great question. The reason it’s hard to visually spot the difference in a gRPC request is because it’s a binary protocol over HTTP/2, unlike human-readable formats like REST (JSON) or GraphQL (JSON). But let’s break it down for you in a side-by-side comparison, using the same logical operation — a simple SayHello(name) API — to highlight the key differences:
🧪 1. gRPC Request (Over HTTP/2 + Protobuf)
🔹 Summary:
- Uses HTTP/2 as the transport
- Uses binary Protobuf messages
- Includes custom HTTP/2 headers
🔸 gRPC HTTP/2 Headers:
:method: POST
:scheme: https
:authority: myservice.com
:path: /greeter.Greeter/SayHello
content-type: application/grpc
te: trailers
grpc-timeout: 5S
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)🔸 Binary Protobuf Payload (Encoded):
00000000120a0452616a657368120a48656c6c6f2c2052616a65736821
⚠️ Note: This payload is not human-readable. It’s a binary encoding of:
message HelloRequest {
string name = "Rajesh"
}
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)🧪 2. REST Request (Over HTTP/1.1 + JSON)
🔹 Summary:
- Uses HTTP/1.1
- JSON payload
- Simple headers
🔸 HTTP/1.1 Headers:
POST /api/hello HTTP/1.1
Host: myservice.com
Content-Type: application/json
Code language: HTTP (http)🔸 JSON Body:
{
"name": "Rajesh"
}
Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)✅ Human-readable and easily debuggable.
🧪 3. GraphQL Request (Over HTTP/1.1 + JSON)
🔹 Summary:
- Sends a query/mutation in the body
- Still over HTTP/1.1
🔸 Headers:
POST /graphql HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
Code language: HTTP (http)🔸 JSON Body:
{
"query": "query SayHello($name: String!) { sayHello(name: $name) }",
"variables": { "name": "Rajesh" }
}
Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)🧪 4. WebSocket Message (Example Payload)
🔹 Summary:
- Bi-directional persistent connection
- Custom or JSON-encoded data
🔸 JSON Message:
{
"action": "sayHello",
"data": {
"name": "Rajesh"
}
}
Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)🧠 Key Differences
| Feature | gRPC | REST | GraphQL | WebSocket |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transport | HTTP/2 | HTTP/1.1 | HTTP/1.1 | WebSocket (TCP) |
| Encoding | Protobuf (binary) | JSON | JSON | JSON / Custom |
| Readability | ❌ Not human-readable | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes (usually JSON) |
| Schema Enforcement | ✅ Yes (Protobuf contracts) | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (GraphQL schema) | ❌ Custom per app |
| Streaming | ✅ Native support | ❌ No | 🚫 Only with extra libs | ✅ Native support |
🔍 How to Inspect gRPC Requests
Since gRPC requests are binary:
- Use
grpcurlto simulate or inspect requests - Use
BloomRPCor Postman (gRPC beta) to explore APIs - Add interceptors to log decoded messages in dev
Example with grpcurl:
grpcurl -plaintext localhost:50051 list
grpcurl -d '{"name": "Rajesh"}' -plaintext localhost:50051 greeter.Greeter/SayHello
Code language: PHP (php)I’m a DevOps/SRE/DevSecOps/Cloud Expert passionate about sharing knowledge and experiences. I have worked at Cotocus. I share tech blog at DevOps School, travel stories at Holiday Landmark, stock market tips at Stocks Mantra, health and fitness guidance at My Medic Plus, product reviews at TrueReviewNow , and SEO strategies at Wizbrand.
Do you want to learn Quantum Computing?
Please find my social handles as below;
Rajesh Kumar Personal Website
Rajesh Kumar at YOUTUBE
Rajesh Kumar at INSTAGRAM
Rajesh Kumar at X
Rajesh Kumar at FACEBOOK
Rajesh Kumar at LINKEDIN
Rajesh Kumar at WIZBRAND
Find Trusted Cardiac Hospitals
Compare heart hospitals by city and services — all in one place.
Explore Hospitals
