What is Kubeadm?
Kubeadm helps you bootstrap a minimum viable Kubernetes cluster that conforms to best practices. Kubeadm is a tool built to provide kubeadm init and kubeadm join as best-practice “fast paths” for creating Kubernetes clusters.
Goal
- To Install a single master Kubernetes cluster
- To Install a high availability master Kubernetes cluster
- To Install a Pod network on the cluster so that your Pods can talk to each other.
kubeadm’s simplicity means it can serve a wide range of use cases:
- New users can start with kubeadm to try Kubernetes out for the first time.
- Users familiar with Kubernetes can spin up clusters with kubeadm and test their applications.
- Larger projects can include kubeadm as a building block in a more complex system that can also include other installer tools.
Pre-requisite
- One or more machines running a deb/rpm-compatible OS, for example Ubuntu or CentOS
- 2 GB or more of RAM per machine. Any less leaves little room for your apps.
- 2 CPUs or more on the master
- Full network connectivity among all machines in the cluster. A public or private network is fine
Pre-requisite – Installing Docker [ This need to be there in Master and Worker Node. Both]
As part of the installation, every node (master and minions) needs:
- kubeadm: the command to bootstrap the cluster.
- kubelet: the component that runs on all of the machines in your cluster and does things like starting pods and containers.
- kubectl: the command line util to talk to your cluster.
- Docker: Container Enginer
- CNI: Container Network interfacer
Master: Setting Up a Kubernetes Control Plane
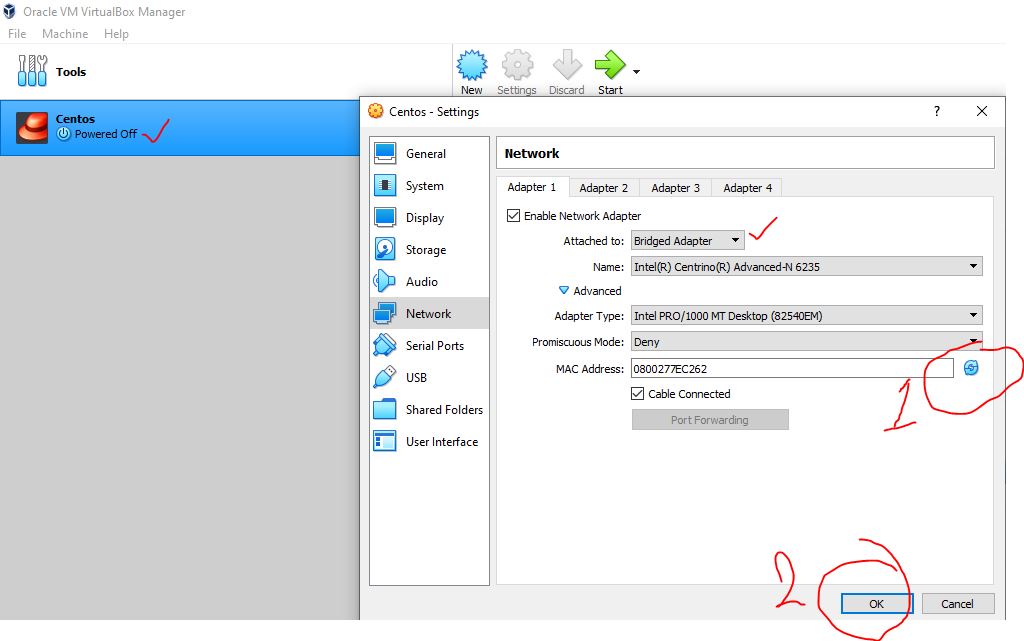
Step 1 – Change VMs Mac Address in Virtual box -> Setting -> Network ->Advance
Note – Please POWER off the VM before changing Mac Address.
Step 2 – Change Host Name of Master Server
$ hostnamectl set-hostname rajesh.master.comStep 3 – Stop and Disable Firewall
$ systemctl stop firewalld
$ systemctl disable firewalldStep 4 – Disable swap
$ sudo swapoff -a
$ sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^/#/' /etc/fstab
# Reboot a machine after that.
$ shutdown -r nowStep 5 – Install and Start Docker Community Editon in Master Server
Special Step – For Docker Only with Kubernetes 1.22
Step 6 – Setup yum repo for kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Step 7 – Set SELinux in permissive mode (effectively disabling it)
$ setenforce 0
$ sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/configStep 8 – Install kubelet kubeadm kubectl and enable kubelet
$ yum install -y kubelet-1.22.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.22.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.22.0-0.x86_64 --disableexcludes=kubernetes
$ systemctl enable --now kubelet
# Latest
$ yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl --disableexcludes=kubernetes
# Kubernetes 1.23
$ yum install -y kubelet-1.23.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.23.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.23.0-0.x86_64 --disableexcludes=kubernetes
# Kubernetes 1.22
$ yum install -y kubelet-1.22.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.22.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.22.0-0.x86_64 --disableexcludes=kubernetes
# Kubernetes 1.21
$ yum install -y kubelet-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.21.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.21.0-0.x86_64 --disableexcludes=kubernetes
# Kubernetes 1.20
$ yum install -y kubelet-1.20.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.20.0-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.20.0-0.x86_64 --disableexcludes=kubernetesStep 9 – Finally, initialize a kubernetes clusters
$ kubeadm init --ignore-preflight-errors all
# How to install older version of Kubernetes
# kubeadm init --kubernetes-version=v1.9.2 Step 10 – Output
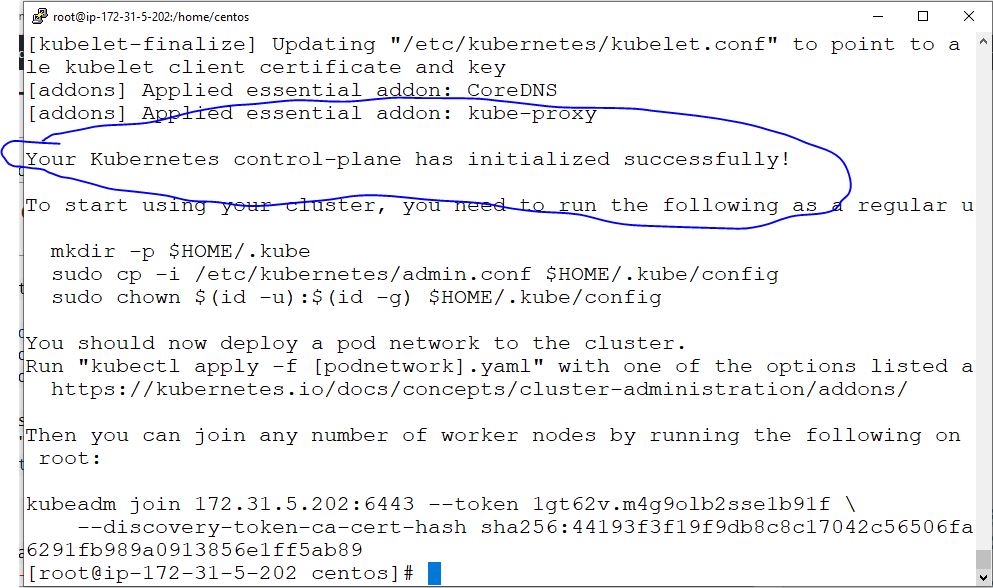
Workstation: Setting Up a Kubernetes Workstation
Step 11 – Setup Workstation in the Master node only. You can be regular user for it.
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
$ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configStep 12 – Verify Clustors
$ kubectl get nodes
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces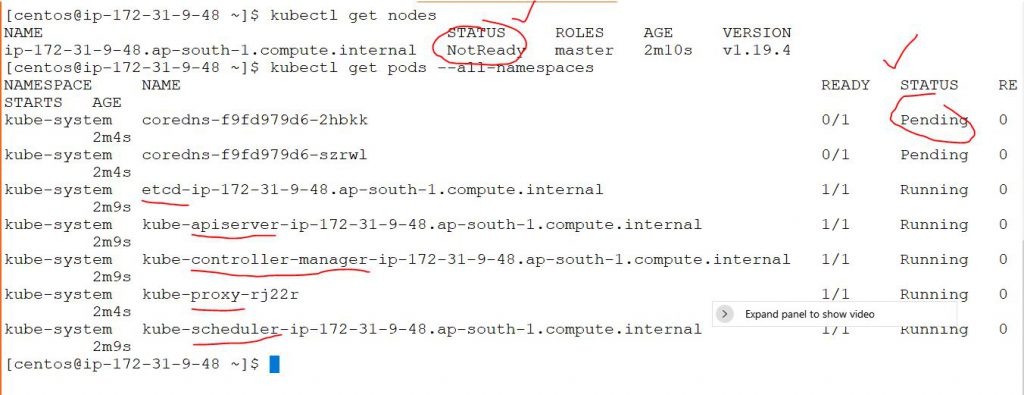
Step 13 – Install Kubernetes pod networking
Weave Net provides networking and network policy, will carry on working on both sides of a network partition, and does not require an external database. Kubernetes versions 1.6 and above:
$ kubectl apply -f "https://cloud.weave.works/k8s/net?k8s-version=$(kubectl version | base64 | tr -d '\n')"
$ kubectl get nodes
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
$ kubectl get nodes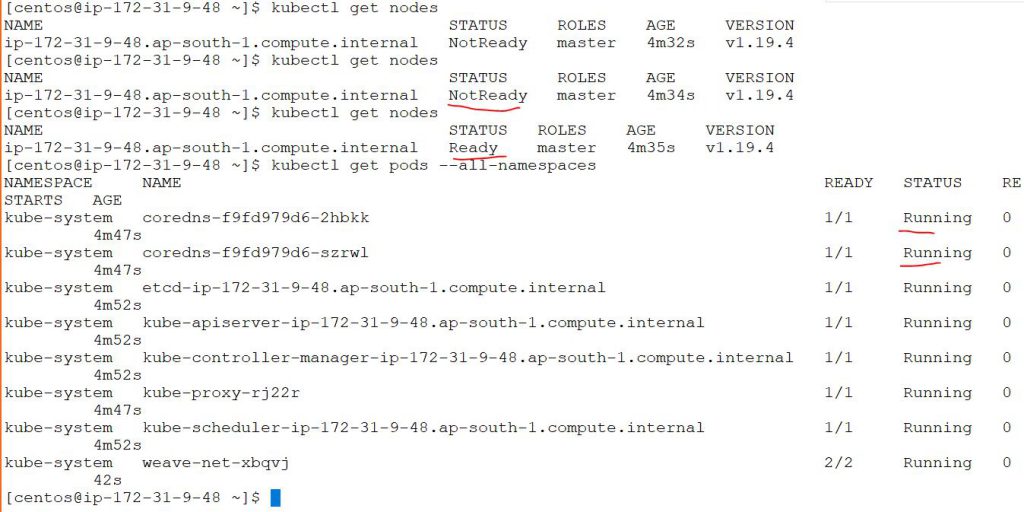
Worker: Setting Up a Kubernetes Worker
Step 14 – Setup nodes [ In the node aka worker
# Follow Step 1
# Follow Step 2
# Follow Step 3
# Follow Step 4
# Follow Step 5
# Follow Step 6
# Follow Step 7
# Follow Step 8
# Run following commands which we got from kubeadm init
$ kubeadm join 172.31.31.106:6443 --token pdn6in.r0dzhpx1ucrs69au --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:a9385951e659a3c67f55ccfbdc1169b1f660ba09aaf8cc6d5cc96d71b71900d2Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 1
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 2
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 3
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 4
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 5
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 6
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 7
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 8
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 9
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 10
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 11
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 12
Beginner to Advanced Complete Kubernetes Tutorial in 15 hours 5-2021 Part – 13
Latest posts by Rajesh Kumar (see all)
- Apache Lucene Query Example - April 8, 2024
- Google Cloud: Step by Step Tutorials for setting up Multi-cluster Ingress (MCI) - April 7, 2024
- What is Multi-cluster Ingress (MCI) - April 7, 2024

