Contents
What is Teradata Database?
Teradata – A Brief History
Why Teradata?
What is a Data Warehouse?
What is a Relational Database?
Teradata Database Advantages
The Features That Makes Teradata Database Unique from Others Databases
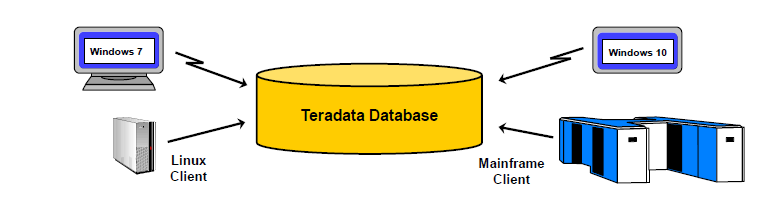
What is Teradata Database?
- Teradata is a Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) for the world’s largest commercial databases.
- It is possible to have databases with petabytes of data in size.
- This characteristic makes Teradata an obvious choice for large data warehousing applications.
- With its parallelism and scalability, Teradata allows you to start small with a single node and grow large with many nodes through linear expandability.
- Teradata is comparable to a large database server, with multiple client application making inquiries against it concurrently.
- Teradata is a massively open processing system that supports Unix/Linux/Windows server platforms.
- The latest Teradata release is 17.10 and executes as a SUSE Linux (SLES 11) application.
Teradata – A Brief History
Teradata was a division of NCR Corporation. It incorporated in 1979 but parted away from NCR in October 2007. Michael Koehler became the first CEO of Teradata.
Milestones of Teradata Corporation:
- 1979 – Teradata was incorporated
- 1984 – Release of first database computer DBC/1012
- 1986 – Fortune magazine declared Teradata as ‘Product of the Year’
- 1999 – Largest database built using Teradata with 130 Terabytes
- 2002 – Teradata V2R5 version release with compression and Partition Primary
- 2006 – Launch of Teradata Master Data Management solution
- 2008 – Teradata 13.0 released with Active Data Warehousing
- 2011 – Acquires Teradata Aster and plunges into the Advanced Analytics Space
- 2012 – Teradata 14.0 introduced
- 2014 – Teradata 15.0 introduced
- 2015- Teradata Buys Apps Marketing Platform Appoxee
- 2016- Terada join hands with Big data
- 2017- Teradata Acquires San Diego’s StackIQ
- 2018- Introduced of Teradata Vantage
- 2019- Teradata introduces Vantage Customer Experience and Vantage Analyst
- 2020- High Customer Satisfaction Led to Teradata’s Leadership Distinction in Q4 Big Data Warehouse Landscape Report by The Information Difference.
Why Teradata?
- Teradata offers a full suite of service which focuses on Data warehousing
- The system is built on open architecture. So whenever any faster devices are made available, it can be incorporated into the already build architecture.
- Teradata supports 50+ petabytes of data.
- Single operation view for a large Teradata multi-node system using Service Workstation
- Compatible with wide range of BI tool to fetch data.
- It can act as a single point of control for the DBA to manage the Database
- High performance, diverse queries, in-database analytics and sophisticated workload management
- Teradata allows you to get the same data on multiple deployment options
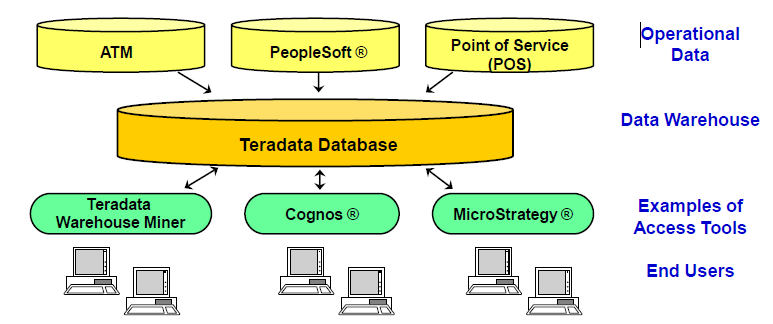
What is a Data Warehouse?
A Data Warehouse is a central, enterprise-wide database that contains information extracted from Operational Data Stores (ODS).
- Based on enterprise-wide model
- Can begin small but may grow large rapidly
- Populated by extraction/loading data from operational systems
- Responds to end-user “what if” queries
- Can store detailed as well as summary data
What is a Relational Database?
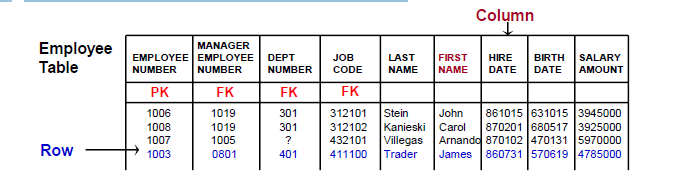
A Relational Databaseconsists of a set of logically related tables.
- A tableis a two dimensional representation of data consisting of rows and columns.
- Each row is in the table uniquely identified by a Primary Key (PK)–1 or more columns.
–A PK cannot have duplicate values and cannot be NULL; only one per table.
–A PK are considered “non-changing” values. - A table may optionally have 1 or more Foreign Keys (FK).
–A FK can be 1 or more columns, can have duplicate values, and allows NULLs
–Each FK value must exist somewhere as a PK value
Teradata Database Advantages
- Unlimited, Proven Scalability–amount of data and number of users; allows for an enterprise wide model of the data.
- Unlimited Parallelism–parallel access, sorts, and aggregations.
- Mature Optimizer–handles complex queries, up to 128 joins per query, ad-hoc processing.
- Models the Business–normalized data (usually in 3NF), robust view processing, & provides star schema capabilities.
- Provides a “single version of the business”.
- Low TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)–ease of setup, maintenance, & administration; no re-orgs, lowest disk to data ratio, and robust expansion utility (RECONFIG).
- High Availability–no single point of failure.
- Parallel Load and Unload utility–robust, parallel, and scalable import and export capabilities via Teradata Parallel Transporter (TPT).
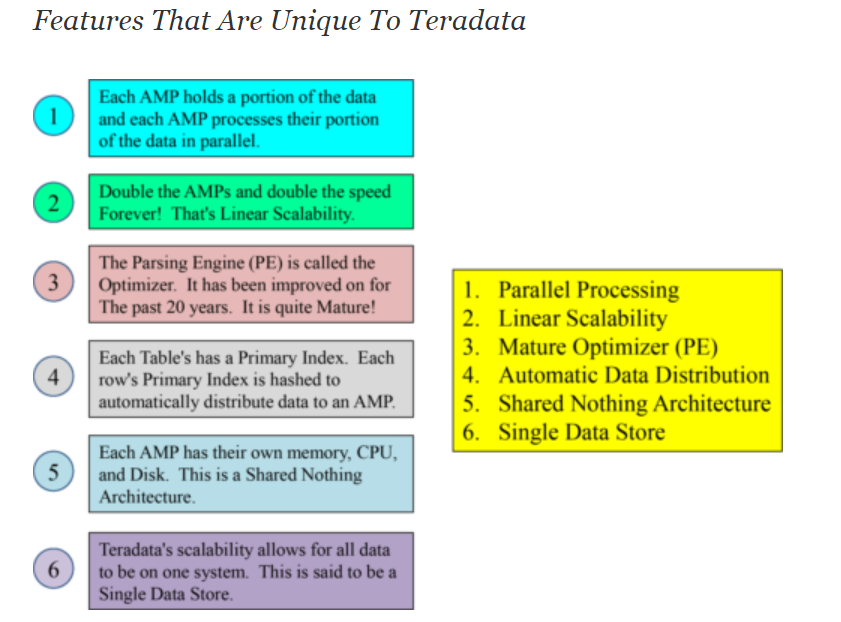
The Features That Makes Teradata Database Unique from Others Databases
‘1. Parallel Processing
Each AMP holds a portion of data and each AMP processes their portion of the data in parallel.
2. Linear Scalability
Double the AMPs and double the speed forever!
3. Mature Optimizer (PE)
The Parsing Engine (PE) is called the optimizer. It has been improved on for the past 20 years . It is quite Mature!
4. Automatic Data Distribution
Each table’s has Primary Index. Each row’s primary index hashed to automatically distribute data to an AMP.
5. Sharing Nothing Architecture
Each AMP has their own CPU, memory and disk. This is shared nothing Architecture.
6. Single Data Store
Teradata Scalability allows for all data to be on one system. This sis said to be Single Data Store.
Latest posts by Jami Raj (see all)
- How to become a devops freelancer - July 15, 2023
- DevOps Support Services Market in India - July 15, 2023
- 5 Key Considerations Before Embarking on An App Development Project - July 14, 2023

